As described in our last blog, Red Hat is participating in a number of catalysts for TMForum Digital Transformation World 2023. All of these catalysts depend on similar capabilities from Red Hat OpenShift—the telco-grade, cloud-native application platform that extends core capabilities to the edge of the network. In this blog, we will look at the key capabilities that are utilized by these catalysts. Whilst these capabilities were used to help the catalysts deliver their solutions during the collapsed timeframe, enterprises can also take advantage of the platform too, deploying into production.
Catalyst platform capabilities
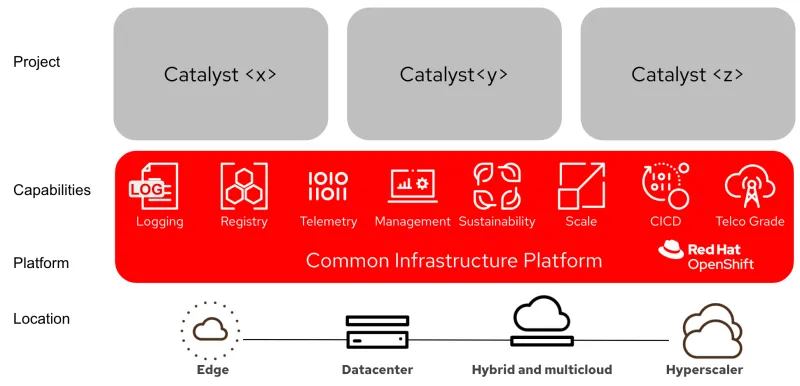
In each of the catalysts, our partners use core capabilities from OpenShift. These platform capabilities can be run across multiple locations including at the edge and core central data center. Additionally, the same platform can be extended to a hyperscaler cloud provider to scale any production deployment.
Location
The ability for applications to be deployed onto a number of different locations allows catalysts to choose the right location to meet their business and technical needs. These options include:
- Hyperscalers, which allow for quick provisioning of infrastructure for the catalyst, can also be deprovisioned once the catalyst has completed.
- Datacenter is where traditional workloads have lived. In a catalyst context, there can be a single physical server but the platform needs to be able to scale to cope with large workloads to take the concept from concept to production.
- Edge computing needs flexibility when it comes to running workloads at scale. Infrastructure can vary from low powered specific compute for sensors to larger scale infrastructure to run a private mobile network, sometimes without reliable power, cooling or network connectivity. OpenShift has a number of flexible deployment options from an isolated single node configuration to a compact cluster as well as composable features—bringing consistency of features, tools and processes across an entire hybrid cloud. For the smallest scale compute, Red Hat provides a Linux platform (Red Hat Enterprise Linux) with specific features to run edge applications. Further details about edge computing with Red Hat can be found here.
The same platform can be used across these locations. For prototypes like the catalyst, it allows you to use certified software to be up and running quickly. For production deployments, there are a wealth of benefits on top of this, including the ability to use the same processes and skills to manage the infrastructure, being able to scale bidirectionally, even using burst capacity in other locations as needed.
Carrier grade network platform
A number of the catalyst projects have used carrier grade characteristics on the platform. This covers the platform that the operational support system and business support system (OSS/BSS) have been comfortable running on but now also core network functions such as the User Plane Function (UPF) and moving to the radio access network (RAN). The UPF is important for those that are looking at edge computing scenarios as it allows for the data to be broken out closer to where it is generated and consumed (i.e. at the edge) providing lower latency access and resilience.
Sustainability
Within the TM Forum and the wider telecommunications industry, the environment continues to be an important factor for service providers and their customers alike. As such, being able to improve resource utilization is of growing importance. The Red Hat platform proposition helps across the industry, by allowing a single platform to be used for a number of purposes, extending what the Network Function Virtualization (NFV) amplifies, giving more granular control and allowing more resource optimization.
Red Hat has worked with its customers and partners to demonstrate the potential savings that can be achieved. This includes work with Ericsson and Intel to find savings in the RAN, more here and with NEC and Intel here. A detailed look at sustainability for service providers can be found in this report.
Another part of our sustainability perspective is linked with making sure that information on the infrastructure is made available to northbound platforms. Red Hat works with the Kepler project with the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF). Kepler provides information about the hardware that the Kubernetes platform is running on to Prometheus for use in machine learning (ML) models and decision making. Further details on Kepler are located here and here.
From a catalyst perspective, Red Hat can show what data is available to make decisions and can demonstrate savings that are available to be made upon deployment.
Management
Using the enterprise Kubernetes platform, Red Hat OpenShift, a number of key enhancements are made to aid with the management of applications that run on it. Some key capabilities that have been used in catalysts include:
- Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes - In our catalysts that use edge computing nodes, Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management provides a way of managing the applications across a large number of clusters. If the edge nodes are running single node OpenShift, Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management provides a way to distribute applications to them and manage the clusters from a single console.
- Quay container registry - Providing a secure, trusted location for containers to be stored that is accessible becomes important as a larger number of use cases start to be layered on the platform. Previous catalysts have used the registry when there were a number of containers needed to fulfill the demonstration.
- Operator framework - Red Hat OpenShift uses the operator framework to manage applications through their lifecycle, allowing for the application and its components to be built, deployed, updated and removed with greater ease than having to consider the different components in turn.
Telemetry/performance metrics
The concepts of zero touch provisioning and automation rely on a detailed understanding of the status and performance of the infrastructure. Red Hat OpenShift provides a number of capabilities for gathering detailed information on its performance and availability. Using OpenTelemetry and Prometheus, the platform makes this information available and using the aforementioned Kepler we can also provide energy consumption data.
This data can be consumed by analytics and machine learning to predict what is currently happening on the platform, and what may happen if no action is taken. Automation can then be used to remediate any issues or make savings.
Red Hat 2023 Catalyst participation
For DTW Ignite 2023, Red Hat is participating in three catalysts including:
Intelligent edge for sustainable agriculture
In its second phase, the Intelligent Edge for Sustainable Agriculture catalyst looks at how technology, powered by mobile networks, can make a positive difference to agriculture. The team used analytics to help understand animal health, crop health and irrigation needs. The solution includes computer vision data gathered from drones and data processed at the edge of the network. Finally, in order to promote the overall vision of sustainable agriculture, the infrastructure that runs the solution needed to be sustainable too. Platform capabilities include:
- Unified Platform - OpenShift running from the edge to core to cloud.
- Edge - OpenShift is able to run machine learning models at the edge of the network.
- Sustainability - Using Kepler, the platform is able to provide information about how much energy it is consuming.
More information here.
Unlocking revenue and efficiency with intent-driven autonomous operations
This third phase catalyst has shown how a network can be provisioned based on a customers intent, i.e. “I want to perform some live streaming and a sporting event.” Using the TMForum Intent Management API (TMF921A) the required infrastructure is provisioned and assured, before being decommissioned after the event. OpenShift provides a platform for many of the networking components provided by Nokia. Data from these platforms is fed back to the Nokia assurance solution which makes decisions on how to shape the deployment. Additionally the edge streaming application is constructed to run on OpenShift.
- Edge - There is a server side edge application that runs with the application on the streaming device. This application runs on OpenShift (single node), the application is distributed to the edge using Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management.
- Core network and OSS Platform - Many network applications can run on OpenShift. More of the Nokia network will move to run on Red Hat over the coming months.
- Telemetry/performance data - OpenShift provides some telemetry data to Nokia’s assurance platform in order for deployment decisions to be made.
More information here.
Converged access with open digital architecture
Current connectivity solutions for the small and midsize business (SMB) market do not include a method for guaranteeing a service level agreement (SLA) and software-defined wide area network (SD WAN) based solutions are cost prohibitive. A current solution for SMBs is to failover to cellular technologies from fiber, however, this is only a solution in the event of access failure, not a degradation of service. In this catalyst we address this issue by extending the converged access solutions from phase 1 to connect with the assurance systems and reconfiguring a customer premise equipment (CPE) if an access method needs to be changed to meet an SLA.
Platform capabilities:
- Core network and OSS Platform - The 5G Core network that sits under the Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) runs on OpenShift. This allows for the rapid scaling of the platform should resources be constrained when a number of customers are transitioned away from a poorly-performing fiber network. It then can scale down once the issue is resolved. Furthermore, the OSS Platform runs on OpenShift, which has allowed our partners, Incognito, to be onboarded.
More information here.
The benefit of using a Red Hat platform in catalysts is to innovate and develop new applications quickly. With Red Hat, you can develop once and deploy anywhere at scale when success kicks in. You can connect with Red Hat experts at any of our Catalyst booths, or booth #205 in the expo hall, at DTW in Copenhagen to discuss the projects in more detail. See you in Copenhagen!
Über den Autor
Chris Thornton is part of Red Hat's global telecommunications ecosystems team. He brings together partners with communications services providers to generate new revenue streams using an open platform approach. These include edge computing and private mobile networks where he brings over 10 years experience in edge computing, having contributed to the formation of ETSI MEC.
Thornton brings a blend of business development skills with a technical background, being a Distinguished Architect with the Open Group. He hold a BA(Hons) in Accounting and a MSc in Information Security.
Ähnliche Einträge
Ford's keyless strategy for managing 200+ Red Hat OpenShift clusters
F5 BIG-IP Virtual Edition is now validated for Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization
Can Kubernetes Help People Find Love? | Compiler
Scaling For Complexity With Container Adoption | Code Comments
Nach Thema durchsuchen
Automatisierung
Das Neueste zum Thema IT-Automatisierung für Technologien, Teams und Umgebungen
Künstliche Intelligenz
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die es Kunden ermöglichen, KI-Workloads beliebig auszuführen
Open Hybrid Cloud
Erfahren Sie, wie wir eine flexiblere Zukunft mit Hybrid Clouds schaffen.
Sicherheit
Erfahren Sie, wie wir Risiken in verschiedenen Umgebungen und Technologien reduzieren
Edge Computing
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von den Plattformen, die die Operations am Edge vereinfachen
Infrastruktur
Erfahren Sie das Neueste von der weltweit führenden Linux-Plattform für Unternehmen
Anwendungen
Entdecken Sie unsere Lösungen für komplexe Herausforderungen bei Anwendungen
Virtualisierung
Erfahren Sie das Neueste über die Virtualisierung von Workloads in Cloud- oder On-Premise-Umgebungen
