The state of edge security report: An overview
Edge computing is evolving from limited use in a few industries to the next generation of decentralized infrastructure supporting digital transformation and latency-sensitive workloads that require powerful and localized computation. Despite its critical nature, maintaining a cohesive strategy and resilient security posture can be a challenge for large enterprises expanding their infrastructure footprint beyond the security of the datacenter environment. The State of Edge Security Report provides a benchmark for current edge deployments in terms of the scale of projects, investments, use cases and endpoints, as well as possible efficiencies from scaling edge initiatives effectively and security challenges from this immense and expanding attack surface area. The report addresses the top security threats facing the edge with comprehensive insights into the edge security stack required to support edge projects and the need to develop an edge ecosystem.
3 key findings
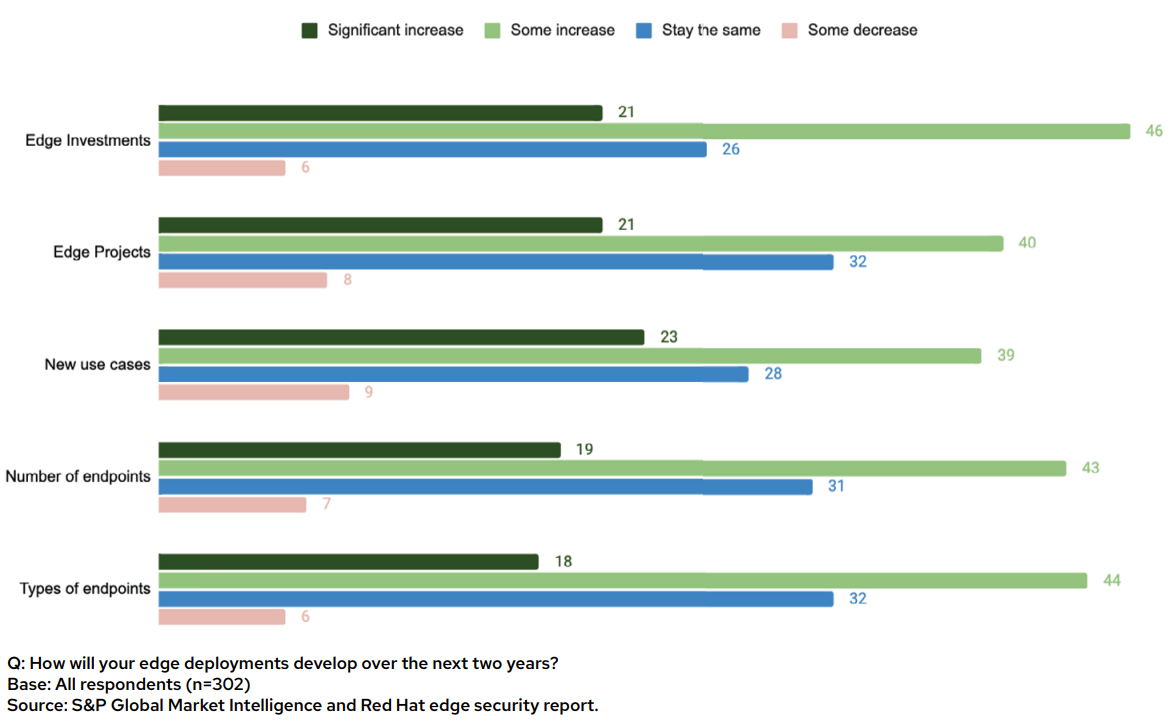
- Edge deployments are increasing in scale across investments, projects, use cases, endpoints and types of endpoints.
- Security is the top challenge cited by enterprises with edge deployments.
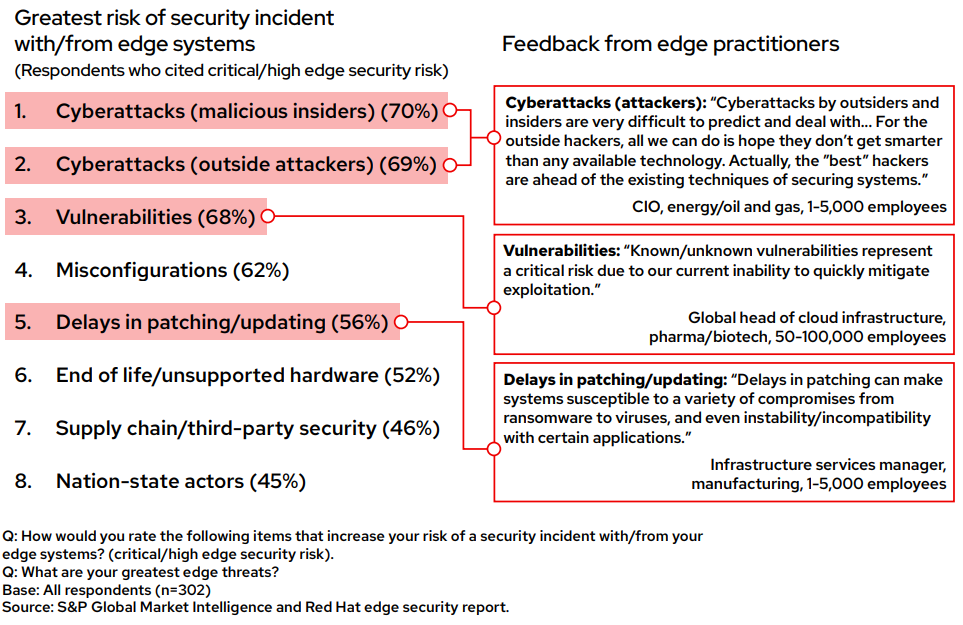
- Risks to edge systems such as cyberattacks and from edge systems due to vulnerabilities and misconfigurations are on the rise.
Edge deployments are expanding and maturing quickly
The edge is a strategic growth pillar for enterprises to generate new revenue and reduce costs. More than two-thirds (68%) of companies surveyed plan to increase their edge investments by “some” or “significant” amounts in the next 2 years. These investment dollars are funding growth for existing and new edge projects, use cases and endpoints.
Security is the top edge deployment challenge
Our research further supports the notion that there is a paradox in edge security; it is deemed a massive technical challenge and threat for enterprises but also an opportunity. Maintaining a resilient cybersecurity posture with this edge infrastructure buildout creates challenges in both physical and digital systems.
Nearly half of decision-makers (47%) say that data, network and device physical and digital security are among their biggest challenges in edge deployments. As with broader IT, cybersecurity has become the top enterprise challenge in edge deployments as digitalization continues to open the attack surface. Enterprises are wrestling with a need to expand their infrastructure footprint and effectively focus on securing not only the infrastructure itself, but also the larger number of IoT endpoints that are connected to it. This is an area where many believe the adoption of new operational patterns, such as cloud-native and DevOps, can improve their security posture alongside their operational efficiency.
Risks both to and from edge systems are on the rise
Criminal organizations and attackers funded by nation-states see the industrial base, critical infrastructure and companies of all forms as highly valuable targets. Being composed of hundreds of remote servers and thousands of IoT devices, the edge presents an attractive target for cybercriminals to expand their armies of bots for activities such as denial-of-service attacks and crypto mining. The data itself is a valuable target, as is the ability to hold an operational control environment for ransom, potentially costing millions for recovery and impact on operational downtime.
Many conventional edge systems are approaching the end of their life cycle or may not have the compute resources or cost efficiencies to support frequent software updates and patches. These older edge systems with outdated operating systems or vulnerable applications are a possible attack path for cybercriminals. Even short gaps in updates can expose vulnerabilities and misconfigurations because edge systems often have minimal access to central IT governance and policies.
Incorporating security earlier into the application development pipeline, or “shifting security left,” is a possible solution but also brings challenges. These include a lack of security gates at the development stage, meaning that security issues aren’t caught until an application is close to deployment, when it’s too late or too costly to fix (cited by 63% of respondents as a top-three challenge). Respondents are also concerned that developers are not equipped with security tools, and traditional tooling fails to protect cloud-native apps at the edge (61%).
Enterprises value a comprehensive set of edge security capabilities
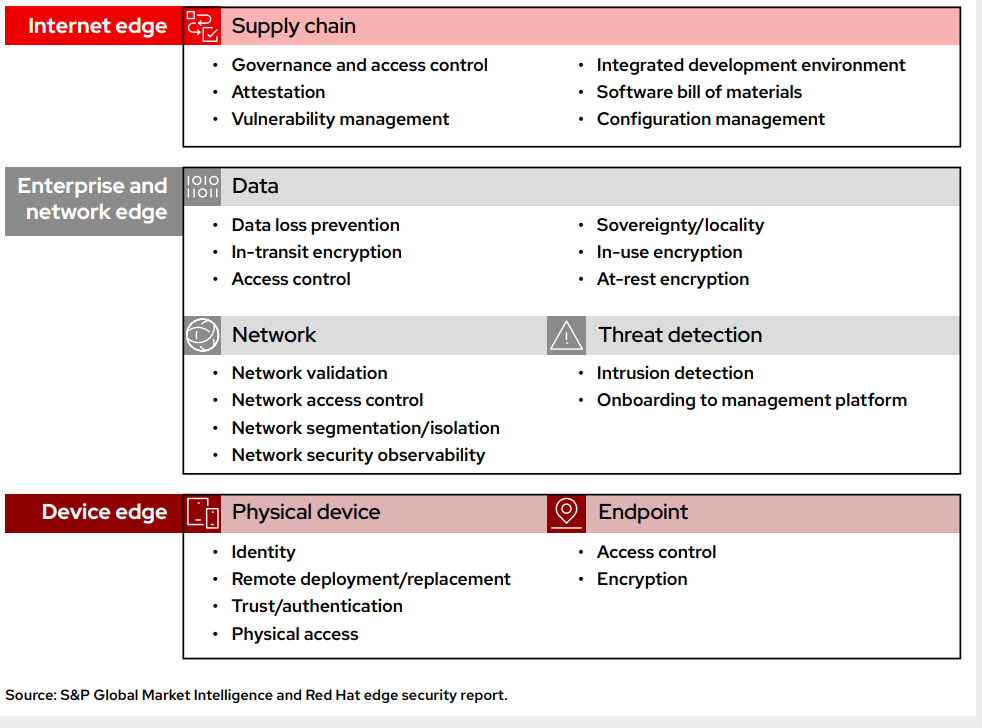
The emerging edge security stack boasts both new and existing security technologies purpose-built for this decentralized infrastructure. Six pivotal edge security areas for IT teams to consider are supply chain, data, network, threat detection, endpoint and device. When our survey asked for respondents’ priorities, there was minimal statistical significance across these six categories. This supports the notion that decision makers believe they all play a critical role and are required to safeguard a complex and growing edge infrastructure.
To reiterate, the ever-growing and increasingly connected digital and physical supply chain presents a sizable risk to edge sites, such as those in close proximity to suppliers upstream or to customers downstream. Systems that maintain governance and access control are key to ensuring the integrity of digital and physical touchpoints across edge systems. The ability to provide device and data attestation across the supply chain can reduce the risk of tampering and mitigate configuration errors. Tools are emerging that better identify and manage vulnerabilities across networks and assets, which increasingly include parts from external software suppliers and open-source projects. The software bill of materials (SBOM) is an emerging concept being driven by federal mandates for companies to start understanding the linkage of vendor components that make up software they use and the associated risks from using it. Software build of materials (SBOMs) can help enterprises comprehend the full set of software components that are used in their environments and prioritize remediation when new vulnerabilities are identified.
Conclusion
Simply put, it takes an edge ecosystem to scale edge deployments and ensure a resilient security posture that can support it. As with an iceberg, enterprises can see what’s “above the water line” in terms of orchestrating internal stakeholders and necessary investments in their edge strategies. However, many overlook what’s “below the water line”: initial and ongoing investments in external partners and technologies that support scaling. Aligning with sound edge security principles, embedding repeatable processes and investing in best-in-class security capabilities from modern and trusted providers are necessary initial investments that will advance an even greater long-term effect when at scale.
Discover more
Read the full report for more ideas to achieve better edge security
Edge capabilities are being put into real-world use by organizations on a massive scale, presenting an opportunity that they can’t ignore. But this impetus comes with challenges, particularly in security, and that’s an area where organizations see the ability to use new, more efficient technologies, such as cloud-native, to gain a competitive advantage. Partnering with leading providers to help manage this rapidly expanding and critical edge environment is paramount to maintaining security across it.