Red Hat: Transform your organization's edge operations with AI
Enhance edge computing for faster decision making
The rapid evolution of edge technology presents opportunities and challenges across various industries, from manufacturing to retail. As organizations increasingly deploy internet of things (IoT)-devices and applications at the edge of their networks, the need for real-time data processing and intelligent decision-making capabilities grows. This shift necessitates a robust platform that can manage the complexities of edge computing while supporting quick and accurate decisions.
Technological shifts
Advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) are transforming the landscape of industrial technology, coupled with advancements in software management and even the proliferation of lower-cost, lower-power hardware, increasing the ability for decision making to occur directly at the source of the data. This capability is crucial in edge computing, where immediacy and speed are paramount. By analyzing data locally, companies can dramatically reduce latency, minimize data transmission costs, and enhance operational efficiency. For example, in manufacturing, real-time analysis of equipment data can trigger immediate maintenance actions that prevent costly downtime and enhance productivity. In sectors such as retail, local data processing allows personalized customer experiences through instant analytics and responses based on customer behavior observed in-store.
Furthermore, the integration of AI at the edge optimizes the capabilities of IoT devices, making them more autonomous. This evolution allows devices to make decisions on the fly without waiting for instructions from a central server, which is critical in scenarios where every millisecond counts, such as autonomous vehicle navigation and emergency response systems in healthcare.
Regulations, compliance, and overall security
The increase in data processing capabilities at the edge also brings to the forefront the challenges posed by stringent regulatory requirements, particularly in industries handling sensitive information. Certain sectors are governed by strict data privacy and security regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States, however, the overall cost and negative ramifications of a breach are a concern for all industries.
The successful deployment of edge computing solutions depends not only on technological advancements but also on a keen understanding of the regulatory and security environment. The convergence of these elements fosters new business models and operational methodologies that capitalize on the benefits of edge computing while mitigating the risks associated with data privacy and security.
Companies leading the way in edge computing are those that not only equip their platforms with innovative technology, but also embed comprehensive compliance and security processes into their solutions. This holistic approach is necessary to provide immediate, intelligent, and compliant decision making at the network edge.
A security focus at the edge requires a continuous, comprehensive approach that goes beyond just setting up perimeter defenses. Approaches such as zero trust address architectural gaps, safeguarding IT environments and organizations.
Zero trust principles are essential for securing edge devices, which often lack the firewalls and security infrastructure found in datacenters. These devices are frequently located in unsecured, remote areas, making them more susceptible to physical attacks and needing to be managed as untrusted nodes.
An overview of Red Hat solutions for the edge
Red Hat® edge solutions can support organizations in delivering operational efficiency and decision-making processes in several key industries. Below are detailed scenarios illustrating how Red Hat technology is applied in real-world environments.
Red Hat OpenShift
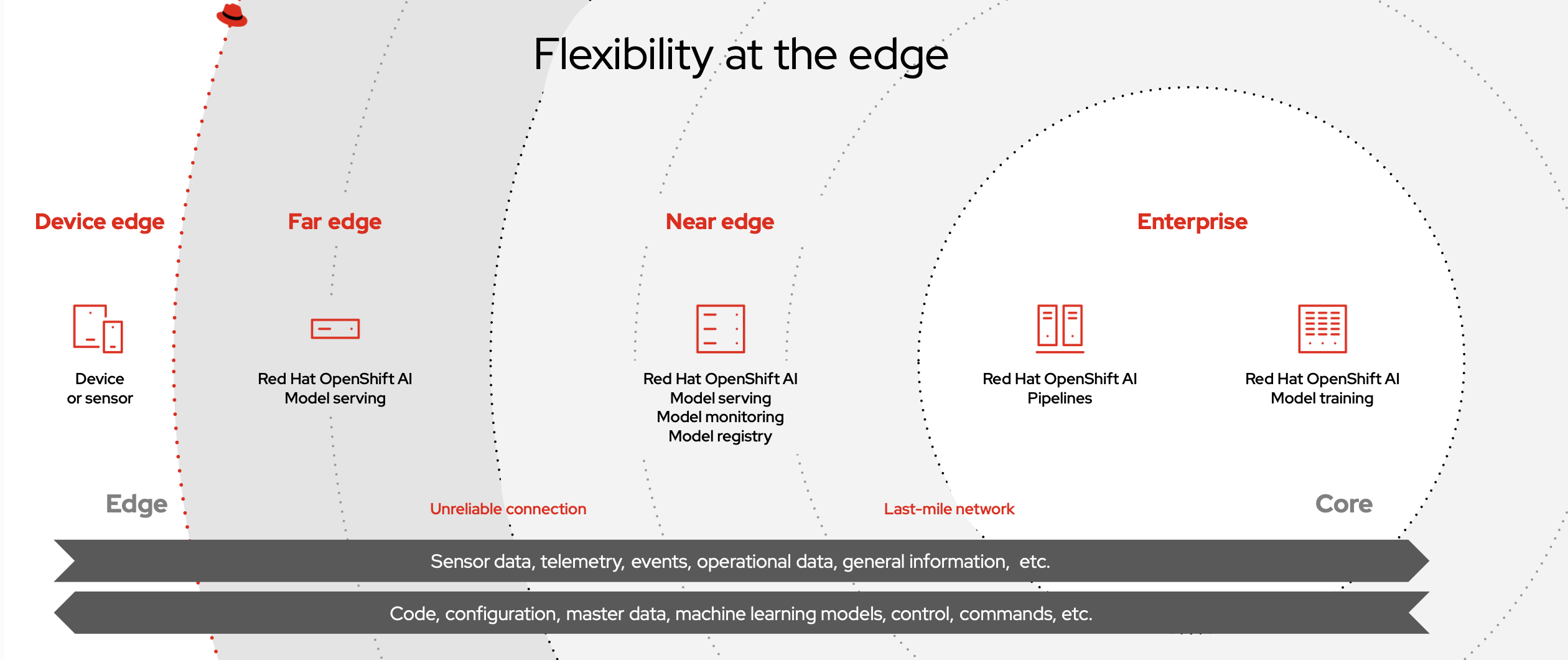
Red Hat OpenShift® allows organizations to extend Kubernetes capabilities from their core and clouds and out to edge computing environments, all while using existing tools and processes. Thanks to Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes and features like zero touch provisioning, it reduces the challenges of configuring, deploying, provisioning, managing, tracking metrics, and monitoring large-scale containerized environments. Red Hat OpenShift provides a consistent experience across various deployment sites—on-premise, in a cloud, at remote offices, at the far edge, and beyond. Red Hat OpenShift is a scalable platform ideal for AI workloads, equipped with access to popular hardware accelerators, like those from partners such as Nvidia and Intel.
Red Hat Device Edge
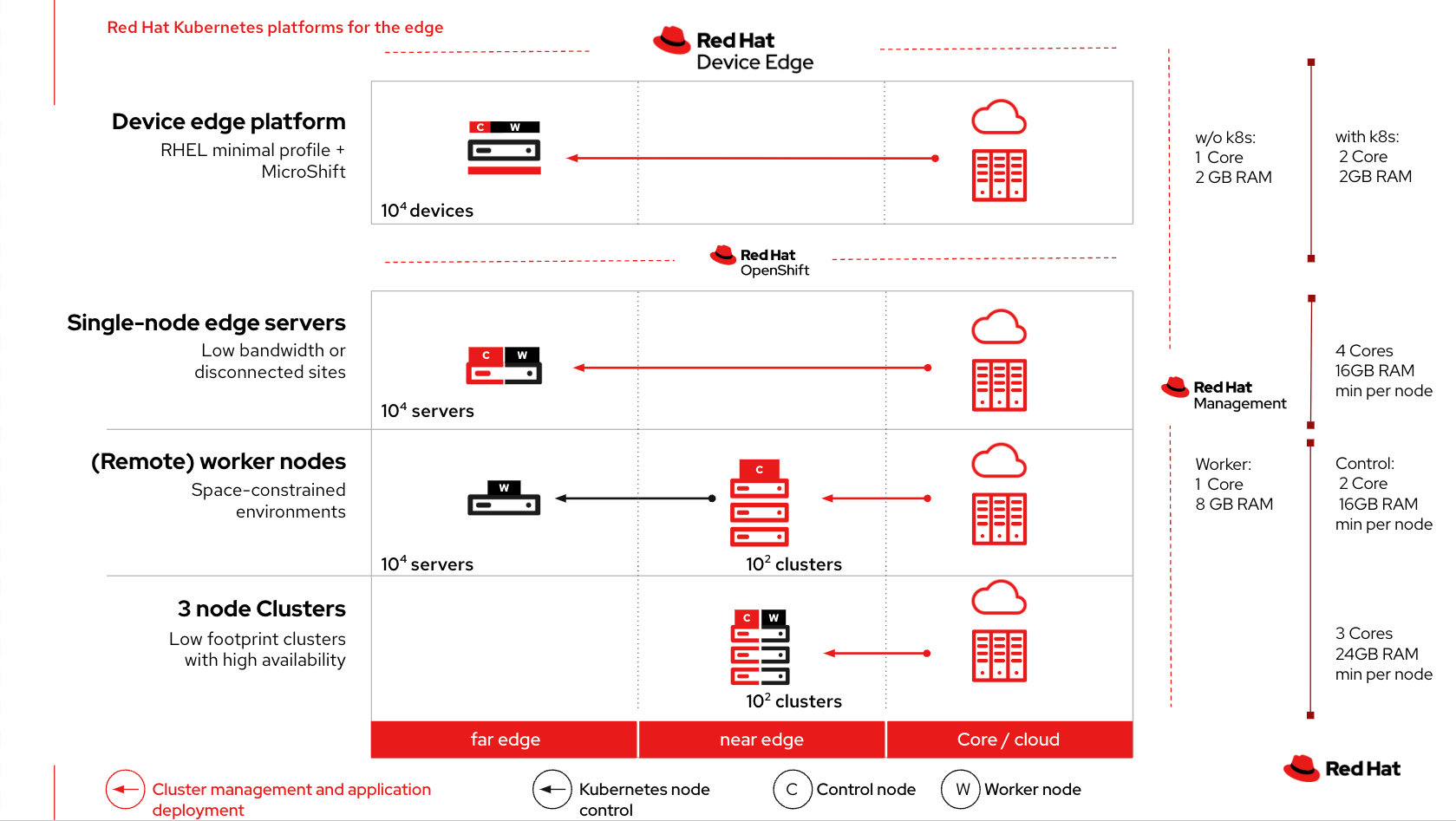
Red Hat scales the platform to the size of edge devices through Red Hat Device Edge. While standard multinode and single-node configurations manage the core network and near-edge nodes, Red Hat Device Edge provides a lightweight orchestration solution that extends Kubernetes operations to the farthest edge of hybrid and multicloud deployments.
Red Hat OpenShift AI
Red Hat OpenShift AI powers data acquisition and preparation, model training and fine-tuning, model serving and model monitoring, and hardware acceleration, and works alongside Red Hat OpenShift to combine into an enterprise-ready AI application platform. This combined platform offers consistent capabilities for teams to test, deploy, and scale AI-driven applications, crucial for tasks such as computer vision.
At the heart of this system lies Red Hat Enterprise Linux®, the core operating system that connects the entire environment. It provides edge-optimized OS images designed to manage diverse use cases and workloads efficiently.
Scaling operations to the edge involves numerous steps and configurations, posing significant challenges. Red Hat Ansible® Automation Platform helps efficiently scale up capacity for both local and remote automation workloads. It includes built-in health checks to select the best nodes for running automation tasks, thereby integrating and boosting the security of the infrastructure.
Edge-specific capabilities important for decision making
Development consistency
Red Hat OpenShift maintains consistency across various computing environments, from traditional datacenters to edge locations. This approach allows developers to use the same tools and processes they are accustomed to, regardless of the deployment location.
Red Hat OpenShift makes managing your environment consistently whether they are deployed in a cloud environment, on-premise, or at the edge. This uniformity is crucial for simplifying the management of applications and services across the dispersed infrastructure, which is particularly beneficial for organizations looking to streamline operations and enhance efficiency without needing to retool for different environments or train multiple teams on multiple tools and environments.
Multiple topologies for every environment
While Red Hat OpenShift maintains consistency from the cloud to the edge, not every deployment is the same—however the combination of flexibility and consistency allows environments and teams to scale. To better support edge implementations and to facilitate rapid decision making at the edge, Red Hat OpenShift is offered in multiple topologies. These include minimal footprint multinode clusters for the near edge, single-node edge servers for smaller or disconnected sites, and Red Hat Device Edge for the absolute smallest, lowest power deployments. Red Hat Device Edge includes the Red Hat build of MicroShift which is a lightweight Kubernetes distribution derived from Red Hat OpenShift—bringing the best orchestration to the further reaches of the edge.
AI model training
The training of AI models is especially important in situations where intelligent decisions need to be made in less time and closer to the data.
Training AI models is handled by Red Hat OpenShift, which is an ideal platform for training using edge data. While the configuration of Red Hat OpenShift is different between the minimal profile version running on far edge devices, single-node servers running on near-edge devices, and larger multinode clusters running in the core network, together all of these different versions combine into a single platform to process information.
Red Hat OpenShift AI is an MLOps platform that works in conjunction with Red Hat OpenShift to rapidly develop, train, serve, and monitor ML models on site, in a public cloud, or at the edge. With tools such as model serving, data science pipelines, and model monitoring, data scientists can use similar DevOps principles honed by application developers on the same Red Hat OpenShift platform.
Operationalize AI at the edge
Operationalizing AI is still a challenging process. Half of the respondents in a 2023 Gartner survey said their average AI/ML timeline from idea to operationalization is 7 to 12 months. An MLOps platform, with workflows inspired by DevOps and GitOps principles, integrates AI models into the software development process.
Since Red Hat OpenShift and Red Hat OpenShift AI are integrated from the network core all the way to the device edge, operationalizing AI models at the edge becomes part of a unified MLOps process.
Data management
Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation based on Red Hat Ceph® Storage provides a robust, terabyte-scale storage management system already used by large organizations such as CERN for handling extensive data from experiments. Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation integrates with Red Hat OpenShift, offering a cohesive solution for data storage and management that ensures data remains manageable even at the edge. This system facilitates the smooth transition and storage of data across systems, which is essential for maintaining the integrity and availability of data in edge computing environments.
Industry use cases
Manufacturing: Enhance quality control with AI
In manufacturing, maintaining high quality and efficiency is paramount. Implementing AI-driven visual inspection systems on manufacturing lines can enhance quality control processes, especially in environments with limited computational resources.
Environment: These edge systems deploy directly on manufacturing lines, analyzing products in real time. By operating close to the data source, they minimize latency and maximize responsiveness, working to make sure no defective product moves far down the line undetected.
Hardware and data needs: To support these systems, manufacturers employ small-form-factor edge devices. These devices are powerful enough to process high volumes of visual data on site. Despite their compact size, they perform complex computations required for detailed image analysis and defect detection without needing to send data back to central servers for processing.
Red Hat solutions: Red Hat application platforms offer robust container orchestration that allows these AI-applications to run efficiently and consistently across various devices. Red Hat OpenShift and Red Hat Device Edge facilitate real-time data processing by deploying containers that can scale dynamically with the workload, making sure the visual inspection applications receive the computational resources they need, exactly when they need them.
Integration and benefits: Integrating these AI-systems with existing manufacturing operations works with Red Hat OpenShift, which can handle and connect the AI-systems, modern microservices, and even more traditional monolithic applications. Early defect detection allows manufacturers to rectify issues before they escalate, significantly reducing waste and downtime. Over time, this leads to enhanced production efficiency, which can positively influence the bottom line. Additionally, consistent product quality boosts customer satisfaction and brand reputation, which are critical for business success in any market.
Example implementations
Zero touch provisioning for factory workflows
Zero touch provisioning (ZTP) allows for a set deployment to be rolled out across a large number of disparate devices in a uniform way. This is especially useful for high numbers of devices that need to be deployed outside of the datacenter.
Building on ZTP, Red Hat’s ZTP for Factory Workflows solution allows customers to order high numbers of edge nodes and clusters that can arrive from the factory preprovisioned for onsite configuration. This means that customers not only save time traditionally lost to repetitive manual deployments, but also reduce the chances of errors due to those same manual deployments.
Retail: Transform customer experiences
In the retail sector, implementing AI-systems at store locations can revolutionize inventory management and enhance customer interactions directly at the point of sale. By deploying edge computing solutions, retailers can process data on site, triggering immediate responses to inventory changes and customer behaviors without the latency associated with data transmission to distant servers.
Environment: Effective implementation in retail requires edge devices equipped to handle robust security protocols to protect sensitive customer data. These devices must also support AI-hardware acceleration to process large volumes of data swiftly. Such capabilities help the systems perform complex analyses in real time, from tracking inventory levels to providing personalized shopping recommendations based on customer preferences and purchase history.
Red Hat solutions: Red Hat Device Edge offers a streamlined, lightweight orchestration solution ideal for these environments. It facilitates operational consistency across devices with data management and real-time analytics. This solution integrates with existing retail systems, which can also run on Red Hat OpenShift, allowing for a unified approach to edge computing that enhances the efficiency of retail operations.
Integration and benefits: Using these solutions helps retailers respond to changing market conditions or create differentiated offerings as needs arise, in less time and limit the need for on-site tech staff with single touch updates, upgrades, and application deployment across remote sites.
Example implementations
AI for computer vision
Computer vision is an implementation of AI at the edge that is important for intelligent decision making in many industries, including manufacturing, retail, and healthcare. Using Red Hat OpenShift and Red Hat Device Edge as a platform, users can access Red Hat’s extensive partner ecosystem to implement a solution.
For example, a partnership between Guise AI and Red Hat offers a Manufacturing Visual Inspection solution. Guise AI Visual Inspection for Manufacturing solution is a proprietary technology built to address the need to automate quality control on manufacturing and assembly lines at the far edge. The machine vision and anomaly detection model is optimized on Intel® Distribution of OpenVINO™ toolkit, which reduces the power consumption needed for machine vision use cases.
The entire system runs on Red Hat Device Edge, which allows the flexibility to implement the system using the specific hardware required.
Healthcare: Real-time medical diagnostics
In healthcare, the implementation of edge computing is crucial for conducting immediate diagnostics in various settings, including remote locations. A critical application is the use of AI to interpret medical data, which allows for accelerated responses where traditional hospital resources may be absent.
Environment: Devices employed in these scenarios must handle high-compute tasks such as image processing and real-time data analysis. They must also comply with stringent health data security standards to protect patient information. This dual requirement means that the devices must be both powerful and have a security focus, capable of operating under the healthcare industry’s unique constraints.
Red Hat solutions: Red Hat OpenShift serves as a robust platform supporting AI-applications necessary for these diagnostic tasks. It offers a platform for the processing of sensitive medical data using established security protocols directly at the edge, working to make sure that the confidentiality and integrity of patient data is maintained. By deploying AI-models directly on edge devices, healthcare providers can use advanced diagnostics without the latency that comes from cloud processing.
Integration and benefits: The integration of real-time data processing capabilities into healthcare operations allows for swift decision making, which is often critical in medical emergencies. The ability to process data on site without needing to send it to a distant datacenter is vital for timely patient care and can have a significant effect on outcomes. Red Hat OpenShift facilitates this swift data processing, even in environments with limited or intermittent connectivity. This capability helps make sure that patient data is always up-to-date and accessible when needed, enhancing the ability to make informed medical decisions rapidly.
Example implementations
Edge devices to detect skin cancer
Another implementation example is how edge detection technology can help detect skin cancer by enhancing the way images are captured and analyzed.
Different devices, such as smartphones, tablets, or computers, can capture images of the skin. An application specifically designed for this purpose can be installed on these devices to manage the image capture process. Once a device captures an image, it sends it to the image upload application. This application not only stores the image but also its metadata in a secure database. The images themselves are stored separately in object storage managed by IBM Storage Ceph, while the metadata is saved on Ceph’s block storage for added security.
Once the image is uploaded, the image upload application places a message in the AMQ (Kafka) queue, signaling IBM watsonx model (an AI model that is compatible with Red Hat OpenShift and Red Hat OpenShift AI) to process the image. IBM watsonx model analyzes the image and sends the results back to the doctor through a notification service.
Doctors use these processed images, along with biopsy results when available, to diagnose skin cancer. These diagnoses help to continually train and refine the AI/ML models used in this process, enhancing both their accuracy and precision over time.
The development of these applications and models, along with the monitoring dashboards and the underlying infrastructure, are continuously updated by developers and operations teams. They use GitOps practices for deployment and management of all architectural elements. Furthermore, the entire setup, including installation and management of components, is automated using Ansible Automation Platform, working to establish a consistent, predictable, and auditable environment that supports the critical task of skin cancer detection.
Summary
Red Hat’s edge computing solutions help organizations process data directly where it is generated. Red Hat OpenShift and Red Hat Device Edge offer flexible deployments from cloud to edge, ensuring consistent and swift data handling.
Red Hat OpenShift extends Kubernetes capabilities to edge environments, providing a consistent operational experience across all deployment sites. This uniformity simplifies the management of applications and services, helping organizations to maintain efficiency without extensive retraining or retooling. Red Hat’s approach to edge computing supports diverse needs with solutions like multinode clusters for near-edge scenarios and lightweight orchestration for remote deployments, facilitating rapid and informed decision-making across various industries.
Discover how Red Hat can transform your organization’s edge operations with enhanced visibility into your network, a focus on security processes, and accelerated decision-making at the edge. Contact Red Hat to learn how to get started.