How to implement Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS
Reduce Kubernetes platform complexity with Red Hat OpenShift
Red Hat® OpenShift is a common platform to develop and run applications. Companies like Verizon and Siemens use Red Hat OpenShift to build, manage, and secure applications consistently across complex environments like mobile edge networks and hybrid clouds.
By using Red Hat OpenShift, organizations avoid the burden of managing heterogeneous, complex environments. Red Hat OpenShift not only helps teams build and run new cloud-native applications; they can also migrate and containerize legacy apps with it.
OpenShift gives developers an advantage because they only need to learn one interface, while the underlying details of the Kubernetes app platform are abstracted away. This can result in significant productivity increases.
Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS
Some organizations who adopt Red Hat OpenShift simplify further by running managed OpenShift on Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud infrastructure. Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA) is a supported, reliable Kubernetes platform that runs natively on AWS. This turnkey application platform—managed by Red Hat and AWS—lets teams focus on being productive and developing applications from day one instead of worrying about providing cloud infrastructure or managing clusters.
ROSA is hosted completely on the AWS public cloud. It is maintained jointly by Red Hat and AWS, which means that the control plane and compute nodes are fully managed by Red Hat Site Reliability Engineers (SREs) with joint Red Hat and Amazon support. This covers installation, management, maintenance and upgrades on all the nodes.
What are the foundations of a Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS architecture?
As you consider implementing ROSA for running OpenShift on AWS, it is important to have clarity about the major components involved in this architecture. We will start by defining the foundational components for deployment and implementation.
What is Site reliability engineering (SRE)?
Site reliability applies the principles of software engineering to define the structure of IT operations and infrastructure teams. The purpose of SRE methods is to create scalable, stable environments—without sacrificing reliability or sustainability. This often involves automating operations tasks that were historically manual. Ultimately, SRE helps teams focus on adopting new technologies, features, and practices while avoiding downtime and system failures.
What is a virtual private cloud (VPC)?
A virtual private cloud provides a defined, hosted, and virtually isolated network, compute and storage environment. VPCs closely resemble traditional networks that would be hosted in a private datacenter. VPCs unlock the scalability of AWS infrastructure, in-line with the other components defined in the rest of this architecture for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS.
What is a load balancer?
A load balancer is a set of integrated software components that balance IP traffic across a set of real servers. These systems offer a highly available and scalable solution for production services and applications.
What’s the difference between multicloud and hybrid cloud?
A multicloud solution includes multiple cloud services, where each performs a separate function for the business. This can be because one cloud provider or hyperscaler is better equipped to handle a specific function, while another is better for other functions. The result is an environment where each function lives in a different cloud, seamlessly operating irrespective of the other functions.
A hybrid cloud is a solution in which applications run in a combination of different environments, including physically on-premise and virtually in the cloud. Hybrid clouds are designed to be flexible and prevent lock-in, so users can blend public or private cloud infrastructure, and each application can operate across a common platform, regardless of location or cloud provider.
For example, Red Hat customers often run a development or testing environment in a public cloud, their quality engineering environment in a private cloud, and finally, host their production environment on-premise. A hybrid cloud solution spans this entire estate, providing versatility and simple application management, despite the complexity of the environment.
What is an open hybrid cloud?
Open hybrid cloud is Red Hat's recommended strategy for architecting, developing, and operating a hybrid mix of applications, delivering a truly flexible cloud experience with the speed, stability, and scale required for digital business transformation.
Red Hat’s open hybrid cloud strategy is built on the technological foundation of Red Hat Enterprise Linux®, Red Hat OpenShift, and Red Hat Ansible® Automation Platform. This strategy gives developers a common application environment to develop, orchestrate, and run their applications, while giving system administrators and operations teams a common operating environment to manage their infrastructure. With this consistency across environments, you can deliver automated IT infrastructure.
What is Red Hat OpenShift?
OpenShift is a unified platform powered by Kubernetes for building, modernizing, and deploying applications at scale. It delivers a consistent experience across public cloud, on-premises, hybrid clouds, and even edge architectures.
What is AWS?
Amazon Web Services (AWS) is a cloud provider with over 200 fully featured services from data centers globally. AWS helps organizations lower costs, become more agile, and innovate faster, with infrastructure technologies (ie. compute, storage, and databases) to emerging technologies (ie. AI/ML, data lakes and analytics, and IoT). This enables faster, simpler, and cost effective migration of existing applications to the cloud.
What is Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS?
Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS is a turnkey application platform that provides a managed Red Hat OpenShift service running natively on AWS, allowing organizations to increase operational efficiency, refocus on innovation, and quickly build, deploy, and scale applications.
What deployment options are available for Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS?
There are two main ways to deploy ROSA: in a public cluster and in a private link one. In both cases we recommend deploying them in multiple availability zones for resiliency and high-availability.
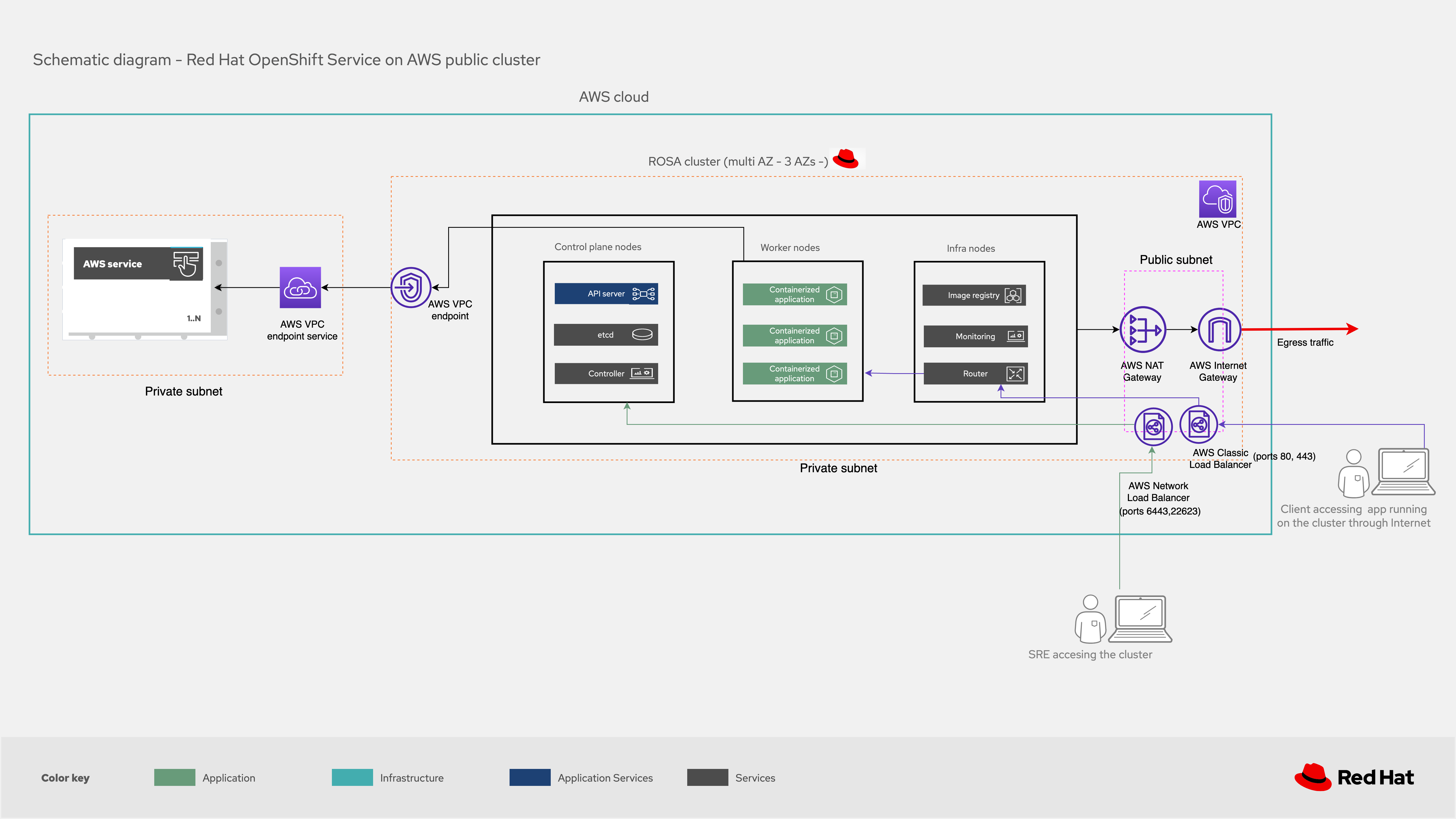
Deploying ROSA in a public cluster
Public clusters are mostly used for workloads without stringent security requirements. The cluster is deployed in a VPC inside a private subnet. The private subnet contains the control plane nodes, the infrastructure nodes, and the worker nodes where the applications run. It still needs to be accessible from the internet, however—so a public subnet is needed in addition to the VPC.
AWS load balancers (Elastic and Network Load Balancers) deployed on the public subnet allow both the SRE team and users accessing the applications (which is to say, ingress traffic to the cluster) to connect.A load balancer redirects user traffic to the router service, running on the infrastructure nodes, and from there it is forwarded to the desired application running on one of the worker nodes. The SRE team uses a dedicated AWS account to connect to the control and the infrastructure nodes through different load balancers.
Red Hat OpenShift is the clear leader in enterprise Kubernetes. And while the virtualization market leaders can run Kubernetes on their virtualized infrastructure, only Red Hat OpenShift can run our whole virtualization environment within its Kubernetes container platform.
sabhibidin.com reduced reliability incidents by
97% and adopted DevOps with Red Hat OpenShift. Read the sahibidin.com success story. >>
Deploying in a private cluster
For production workloads with stringent security requirements, Red Hat recommends deploying a PrivateLink cluster. In this case, the VPC where the cluster resides has only a private subnet and cannot be accessed at all from the public internet.
The SRE team uses a dedicated AWS account that connects to an AWS Load Balancer via an AWS PrivateLink endpoint. The load balancer redirects the traffic to the control or infrastructure nodes as needed. Once the AWS PrivateLink is created, the customer needs to approve access from the SRE team’s AWS account. The users connect to an AWS Load Balancer, which redirects them to the router service on the infrastructure nodes. From there, users are sent to the worker node that’s running the application they want to access.
In PrivateLink cluster implementations, it is common for customers to want to redirect the egress traffic of the cluster to their on-premise infrastructure or other VPCs in the AWS cloud. To do so, they can use an AWS Transit Gateway or AWS Direct Connect so that there is no need to deploy a public subnet in the VPC where the cluster resides. Even if they need to direct egress traffic to the internet, they can connect (via the AWS Transit Gateway) to a VPC that has a public subnet with an AWS NAT Gateway and an AWS Internet Gateway.
Compare 4 options for running OpenShift on AWS public cloud infrastructure.
Red Hat OpenShift on AWS (ROSA): What architects need to know >>

In both public and PrivateLink implementations, the cluster can interact with other AWS services by using AWS VPC Endpoints to communicate with the VPC—and the cluster that provides the desired services.
How to connect to the cluster
Red Hat recommends using AWS Security Token Service (STS) for the SRE team to log on to the ROSA clusters and carry out administration tasks. Teams should apply the concept of least privilege so that only the roles that are strictly necessary to accomplish a task are assigned and permitted. The token is temporary and single use, so if a similar task needs to be done again after it has expired, a new token has to be requested.
The use of STS is extended to the connection of the ROSA cluster to other AWS services such as EC2 (for example, if new servers need to be spun up for the cluster) or EBS (when persistent storage is needed).
Conclusion: Simplify OpenShift on AWS with ROSA
Adopting DevOps methodologies and modernizing application deployment using an enterprise Kubernetes platform like OpenShift is applicable to all types of organizations and use cases. They can choose to host it on-premise and manage it themselves, but, if they prefer not to, one option is ROSA. The large number of AWS services that can interact with ROSA clusters helps customers make the most of their platform.
Learn more about this solution, including a video summary and downloadable architecture diagrams:
Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS implementation >>
Check out more solutions built with Red Hat products at the Portfolio Architecture Center, where we have documented successful customer deployments and laid the groundwork for innovation in your organization.
Ready to create a ROSA cluster? Red Hat’s self-guided learning path will show you how.
Getting started with Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA) >>
Evaluating Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS for your organization?
