The Remote Host Configuration (rhc) command helps you connect Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) systems to the Red Hat Hybrid Cloud Console for configuration and management. This article is intended to provide information and knowledge to RHEL system administrators, and also discusses how rhc relates to existing tools, such as insights-client and subscription-manager.
When I started my journey with RHEL, it was version 7 and there was no talk of Simple Content Access (SCA). To run RHEL, systems had to be registered with Red Hat Subscription Management (RHSM), a Satellite server, or through an offline process to assign subscription entitlements using subscription-manager.
Over time, the Red Hat Insights service evolved. I wrote an introduction to it back in 2020. The insights-client command was developed for easy enrollment into the Red Hat Insights service. This later became the Hybrid Cloud Console, home to many other services related to RHEL, Red Hat OpenShift, and Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform.
A lot has happened since then. SCA eliminates the need to assign entitlements to hosts. Subscription management has moved to Hybrid Cloud Console.
Hybrid Cloud Console with Insights and Ansible remediation playbooks
Hybrid Cloud Console is a web-based, unified management interface for Red Hat solutions. With the Hybrid Cloud Console, you can connect to your disparate platforms and then centrally manage and automate your hybrid cloud and the systems within it.
Use the Hybrid Cloud Console to manage your RHEL infrastructure, Red Hat OpenShift clusters, Ansible Automation Platform, and application services.
The Hybrid Cloud Console provides a single view of operations, security, and subscriptions for RHEL.
With tools, rules-based analysis models, and support from Red Hat, you can use the console to streamline many of the tasks and analyses required to build and deploy a stable and secure environment for applications running on RHEL.
In the following sections, I describe how to create an activation key in the Hybrid Cloud Console and how to use rhc to register RHEL systems in the console. Then I'll demonstrate how rhc allows Ansible remediation playbooks to run directly from the console on connected RHEL systems.
Create an activation key
To create an activation key, log into the Hybrid Cloud Console and type "create activation key" into the search field at the top.

Completed search mask in the Hybrid Cloud Console
The first result takes you to a screen where an activation key can be created. Click the Create activation key button to get started.
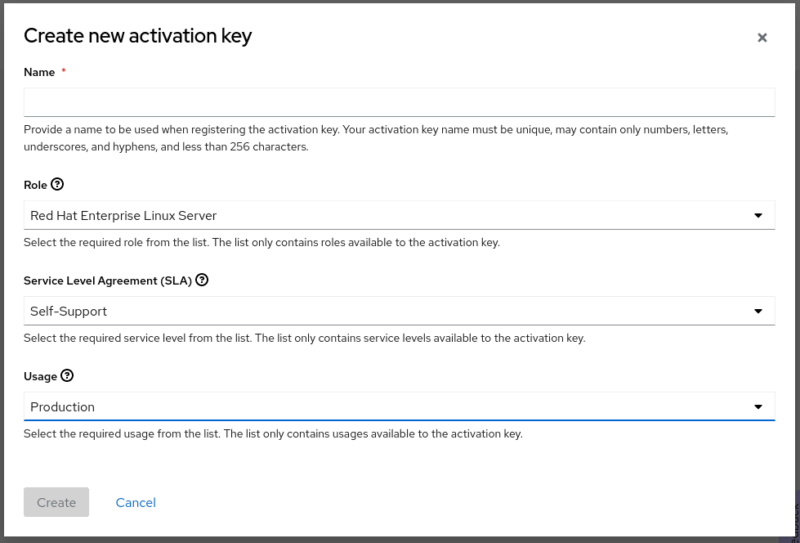
Dialog for creating the activation key with the forms Name, Role, Service Level Agreement (SLA), and Usage
The options available for Role, Service Level Agreement (SLA), and Usage depend on the existing subscriptions in the account. They're used to determine the purpose of the system. The name of the key is for your own reference only, and appears in the overview.
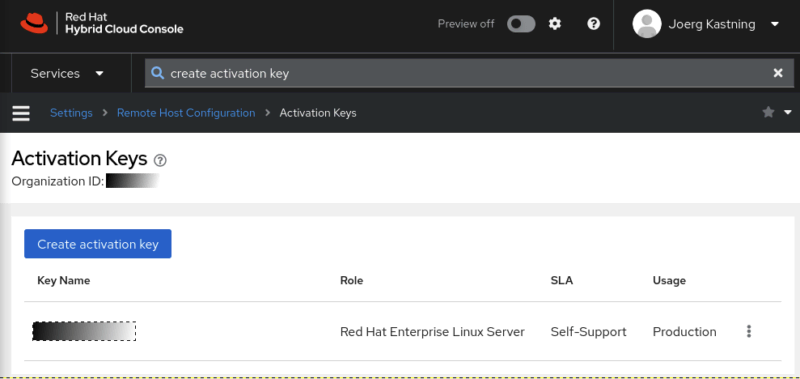
Overview of the existing activation keys
The Organization ID and Activation Key name must be kept confidential! This information can be used to register systems with Hybrid Cloud Console.
Register system with rhc
The command rhc -h provides a description of how the Organization ID and Activation Key are used to register the system with Red Hat:
To connect the system using an activation key: rhc connect --organization ID --activation-key KEY
Run the command as specified:
Connecting host.example.com to Red Hat. This might take a few seconds. ● Connected to Red Hat Subscription Management ● Connected to Red Hat Insights ● Activated the Remote Host Configuration daemon ● Enabled console.redhat.com services: remote configuration, insights, remediations, compliance Successfully connected to Red Hat! Manage your connected systems: https://red.ht/connector
Open a browser and navigate to the Remote Host Configuration Manager at the URL https://red.ht/connector. The current settings are displayed there.
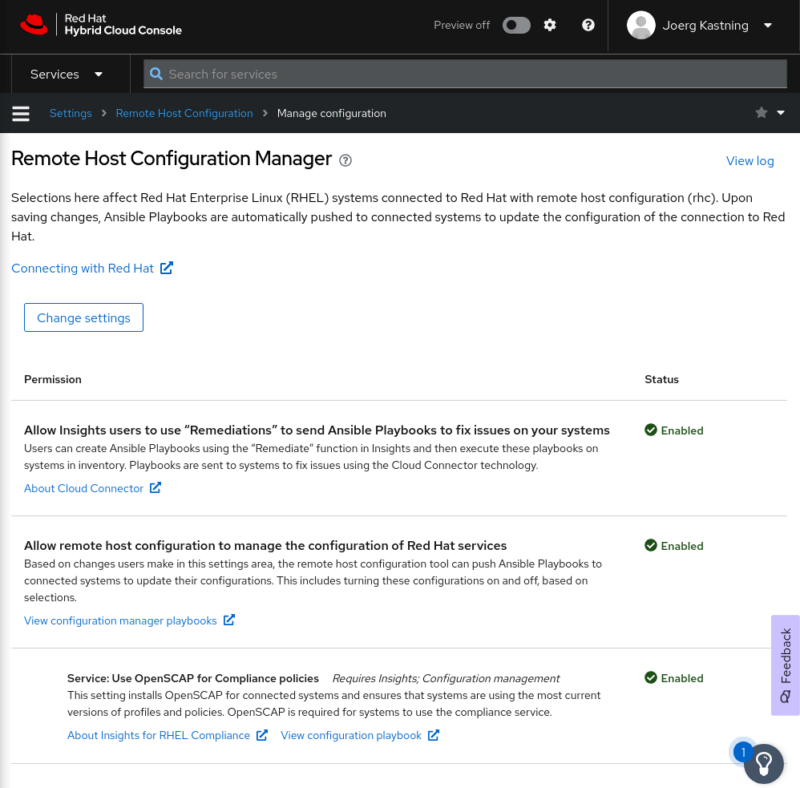
Appearance of the Remote Host Configuration Manager page
The client configures the rhc service on the RHEL host, which initiates the connection to the Hybrid Cloud Console and listens for instructions over a MQTT connection.
This completes the registration and integration with the Hybrid Cloud Console.
If you want to register multiple systems, I recommend using RHEL System Role rhc.
Build and run Ansible remediation playbook
With that set up, you can create a remediation playbook using Ansible to quickly resolve known vulnerabilities on all your systems at once. I have chosen a system that has not yet been updated and therefore has some vulnerabilities.
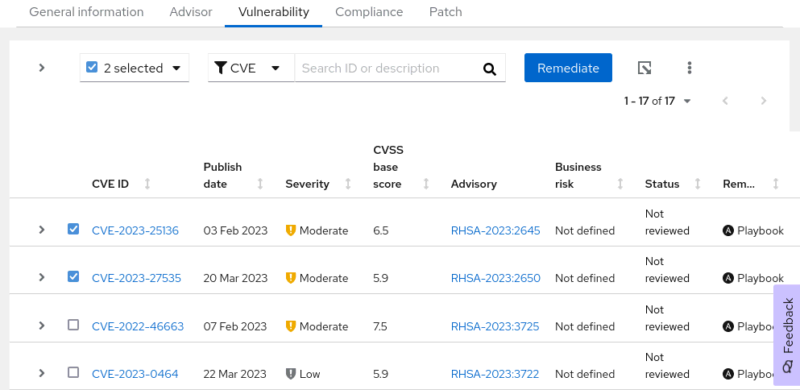
Overview of the existing CVE. Two entries were selected for remediation with Ansible.
In the overview, you can select a CVE to close with the help of an Ansible remediation playbook. Click the Remediate button to start creating the playbook.
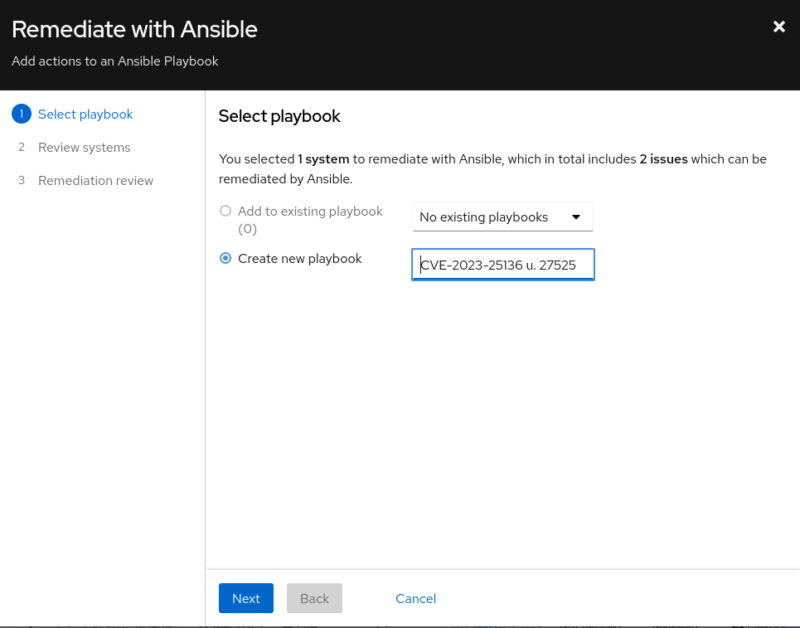
Choose a name for your playbook. This is for your reference only.

In step two, select the vulnerable system you want to fix.

Review of the settings, and note that the target system is automatically restarted by the playbook.

The playbook has been created, but remediation has not yet been carried out.
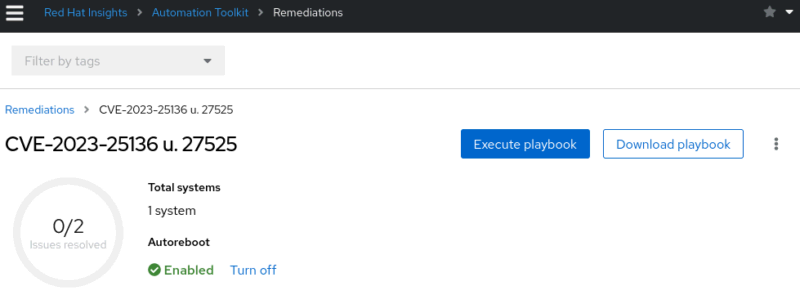
The playbook can be found in the menu under Red Hat Insights > Automation Toolkit > Remediations. At this point, you can only download the playbook to run on automation controller or locally on the system when it has the ansible-core package installed. To run these playbooks directly from the Hybrid Cloud Console, the user logged into the console must be a member of a group with the Remediations administrator role.
Hybrid Cloud Console roles and permissions is beyond the scope of this article, but here are the basics:
- Create a group and add the Remediations administrator role to it. See Managing group access with roles and members for details.
- Add your user to the group you just created. See Adding a user to a group for details.
Once the requirements for running remediation playbooks are met, you can run the playbook directly in the remediation job view:
Here's what happens in the background:
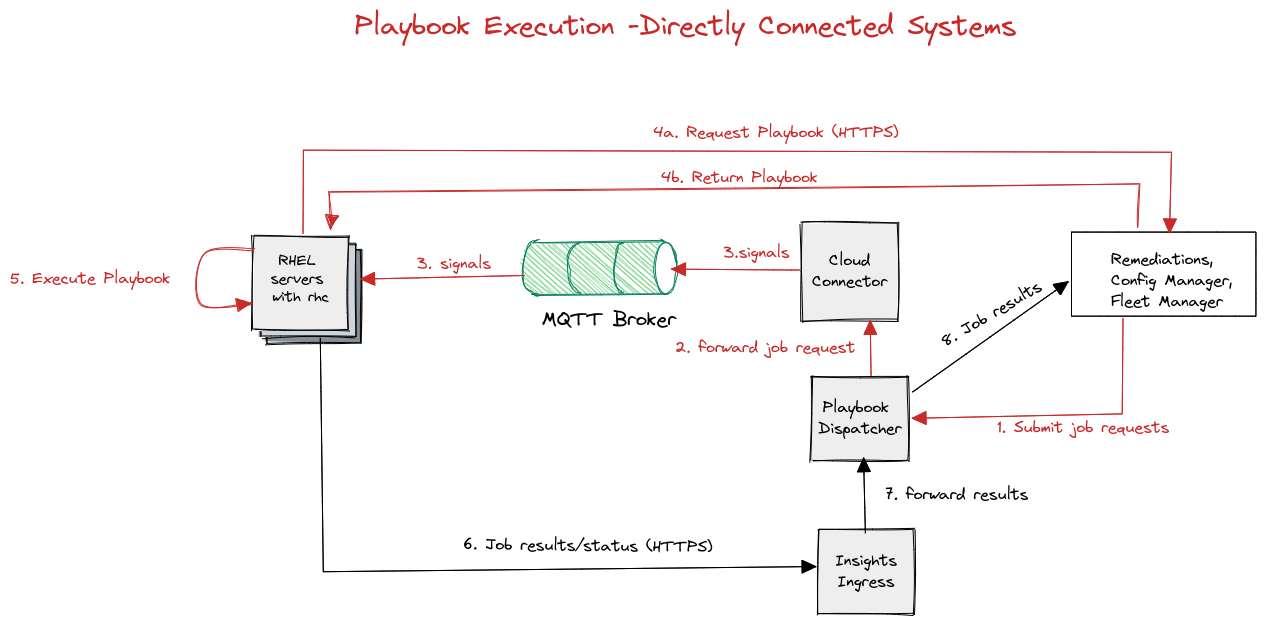
- The playbook is transferred to the hosts
- Targeted hosts receive a signal from MQTT that a playbook is available
- Hosts download the playbook over HTTPS
- The playbook is executed on the hosts by the locally installed Ansible (ansible-core)
- The host reboots afterwards according to the playbook requirements (you can disable autoreboot during playbook creation)
- The status of the playbook is reported over HTTPS to the Insights service
- The console displays results of playbook execution
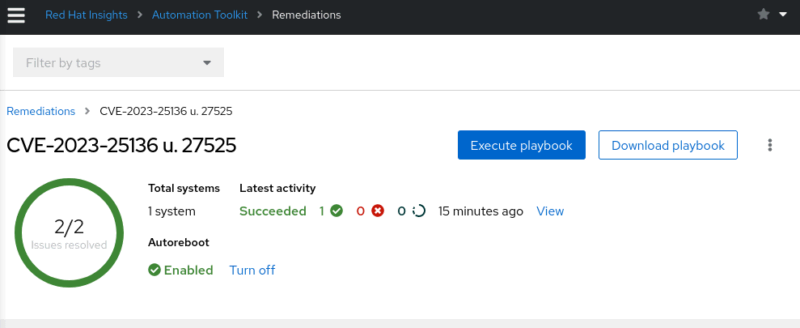
In my simple example, the playbook ran successfully.
More than just rhc
The rhc command lets you register a RHEL host with Hybrid Cloud Console and run the Ansible remediation playbooks. However, rhc is not a substitute for insights-client, which sends Insights reports to your Hybrid Cloud Console. The diverse options of the subscription-manager are also not available with rhc.
The rhc client is an addition, not a replacement for existing commands! Of course, be sure to talk to your security and compliance team first before using it. Not every environment allows the management of core servers and infrastructure from a cloud service.
The rhc client is ideal for RHEL 8.8 and greater and for RHEL 9.2 and greater when you want to connect RHEL systems to Hybrid Cloud Console for management through Insights and centralized execution of Ansible remediation playbooks.
Links for further reading
Sull'autore
Jörg Kastning is a Senior Technical Account Manager (TAM), TAM Ambassador, Open Culture Advocate, Sudoer, and 1x Engineer. He joined Red Hat in March 2023 and enjoys it to work with Fedora and RHEL all day long.
Altri risultati simili a questo
Redefining automation governance: From execution to observability at Bradesco
How Banco do Brasil uses hyperautomation and platform engineering to drive efficiency
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
You Can’t Automate Collaboration | Code Comments
Ricerca per canale
Automazione
Novità sull'automazione IT di tecnologie, team e ambienti
Intelligenza artificiale
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che consentono alle aziende di eseguire carichi di lavoro IA ovunque
Hybrid cloud open source
Scopri come affrontare il futuro in modo più agile grazie al cloud ibrido
Sicurezza
Le ultime novità sulle nostre soluzioni per ridurre i rischi nelle tecnologie e negli ambienti
Edge computing
Aggiornamenti sulle piattaforme che semplificano l'operatività edge
Infrastruttura
Le ultime novità sulla piattaforma Linux aziendale leader a livello mondiale
Applicazioni
Approfondimenti sulle nostre soluzioni alle sfide applicative più difficili
Virtualizzazione
Il futuro della virtualizzazione negli ambienti aziendali per i carichi di lavoro on premise o nel cloud
