Last month at MWC Barcelona, Red Hat and NTT announced a joint solution that enables real-time AI analysis of massive data sets while reducing power consumption and latency as part of the Innovative Optical and Wireless Network (IOWN) Global Forum PoC. Through optimizing AI inferencing at the edge area, we were able to realize a significant reduction in power consumption of large-scale AI data analysis by leveraging IOWN all-photonics network (APN) and data-centric infrastructure (DCI) with Red Hat OpenShift. IOWN Global Forum recognized this PoC as a significant step forward.
60% latency reduction and 40%-60% power save for AI analysis
Three years ago, Red Hat and NTT came together to share how NTT and Red Hat have built an edge offering to deliver new cloud-native AI platform services. Since then, we’ve progressed and with this latest IOWN PoC: Sensor Data Aggregation and Ingestion - we’ve been able to realize a 60% reduction in latency and about 40-60% reduction in power consumption of AI analysis.
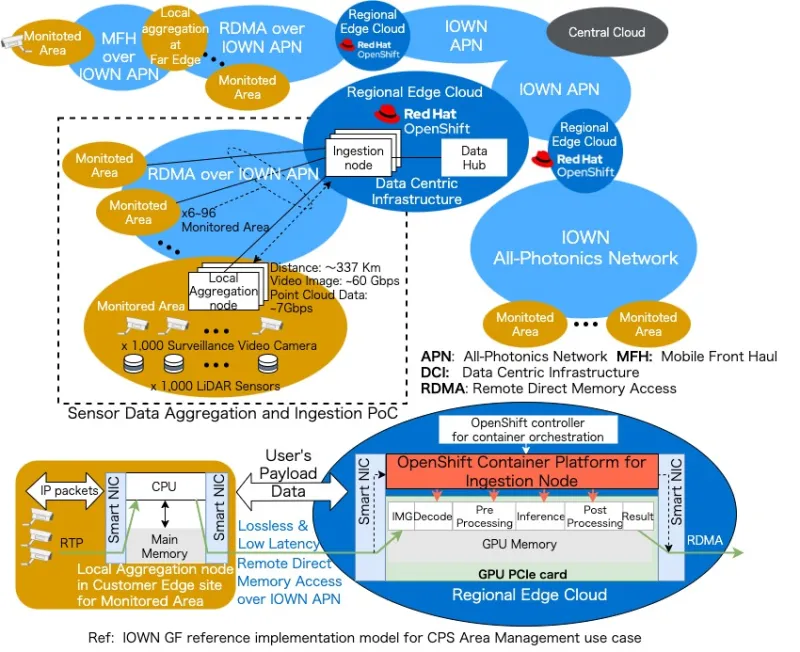
With this report, we’ve been able to explore the implementation for an energy efficient real time AI analysis that is powered by the GPU operators enabled in Red Hat OpenShift at the regional edge in Japan with IOWN infrastructure technology including IOWN APN and pre-IOWN DCI. The IOWN DCI is planned for composable, disaggregated infrastructure that can be powered by Red Hat OpenShift ingestion nodes running NTT’s AI inference engine on GPUs.
Highlighted in this PoC, we were able to demonstrate:
- The effectiveness of NTT's accelerated data pipeline by adapting GPUdirect Remote Direct Memory Access (RDMA) in Red Hat OpenShift over IOWN APN to efficiently collect and process large scale sensor data from many local aggregation nodes;
- A confirmation of significantly reduced power consumption with low latency in AI analysis at the regional edge cloud including telco edge data centers;
- Prove that even when a large number of cameras are used the latency required from aggregating sensor data to completing AI analysis can be reduced by up to 60% compared to conventional AI inference workloads;
- Power consumption required for AI analysis for each camera on a regional edge cloud can be reduced 40% from conventional technology.
- It is expected that the power consumption will be further reduced by 60% based on a trial calculation assuming that 1,000 cameras are accommodated, in case IOWN DCI enables this real-time AI analysis platform that allows the GPU to be scaled up for accommodating a larger number of cameras without the CPU becoming a bottleneck.
Regional Edge Cloud and Suburban in Japan
With major advancements in sensing technology, networking and AI, there will be new value created through AI analysis of vast amounts of data generated in real time. AI analysis performed on sites where sensors are installed can bring high maintenance costs due to the sheer number of installations and the amount of data aggregated in those AI platforms becomes smaller, making it difficult to obtain sufficient GPU utilization effects in terms of area management. Also it cannot keep up with the ever-evolving AI models and hardware due to difficulty of composing the compute node with many GPU/FPGA accelerators.
On the other hand, AI analysis using large-scale data centers such as the cloud intensively consumes a lot of power, which can produce a negative environmental impact. It also has high-latency and CPU overheads associated with collecting large amounts of data, making it difficult to provide services that require strict real time performance. In order to address these issues, we have worked to design a reference implementation model for an area management IOWN use case in Japan to support large scale data based on the following map of JPN48/JPN12 illustrated the photonics network model across 47 prefectures.
Ingestion nodes deploy Red Hat OpenShift to run NTT’s AI inference engine on GPUs for regionalized edge areas and suburbs in Japan to provide a regional edge cloud connected with the IOWN APN. The IOWN APN assumes All-Photonics Network deployment nationwide and brings advantage of a low latency and a lossless network eliminating many electric packet devices. The PoC conducted in the Kanto region where the Red Hat OpenShift based ingestion nodes placed at NTT Musashino R&D Center in Tokyo and Local aggregation nodes for a monitor area placed at NTT Yokosuka R&D Center in Kanagawa 100 km far from the ingestion nodes connected IOWN APN. As a result of comparing the results of applying conventional AI analysis processing in a state where many camera connections are simulated as sensors, we found that the latency of AI analysis processing can be reduced by up to 60%. The latency includes the delay time from receiving data in the sensor installation site to completing AI analysis processing on Red Hat OpenShift in NTT Musashino R&D center with NTT’s accelerated data pipeline over IOWN APN.

|

|
This reference implementation model of “Sensor and Data Aggregation and Ingestion” is not only for Area Management use case but also will be adaptable for Remote Controlled Robotics Inspection in Industry management use case and Interactive Live Music in AI integrated Communications Entertainment use case.
Note that IOWN DCI architecture is ongoing to develop with adapting latest technologies such as Composable Disaggregated Infrastructure (CDI). We have a session about "IOWN: An Efficient Infrastructure for AI Analysis'' in the OpenShift commons gathering to share our result of IOWN PoC, and have an IOWN BOF at CloudNativeCon+KubeCon EU 2024 to discuss Kubernetes/OpenShift Dynamic Resource Allocation on CDI.
Call to Action
- Check out the OpenShift Commons Gathering collocated at Cloud Native+KubeCon EU 2024
- Check out the IOWN BOF session at Cloud Native+KubeCon EU 2024
About the author
Hidetsugu (Hyde) Sugiyama is a Chief Architect at Red Hat, focused on the digital service provider and telecom sector in Japan. Sugiyama has been with Red Hat for over eight years, working on software-defined networking, network functions virtualization, edge computing solutions development, and joint go-to-market with technology partners and R&D customers. He has 34 years of experience in the information and communications technology industry. Sugiyama is also member of the Vision & Technology and Marketing steering committees in the Innovative Optical and Wireless Network Global Forum.
More like this
Building the foundation for an AI-driven, sovereign future with Red Hat partners
Simplifying modern defence operations with Red Hat Edge Manager
Technically Speaking | Build a production-ready AI toolbox
Technically Speaking | Platform engineering for AI agents
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
