Communications service providers are increasingly delivering 5G offerings through hyperscalers' public cloud infrastructures. Their goal is making 5G available, accessible, and affordable for consumers and providing a consistent, best-in-class user experience.
While there are common elements to creating a 5G solution, each service provider is pursuing its own approach with its own partner ecosystem (including cloud infrastructure providers). There is a real-world need to build an open 5G solution blueprint that leverages common solution elements and open source technologies and is compatible with any hyperscaler's infrastructure.
[ Learn why open source and 5G are a perfect partnership. ]
This article presents a way to architect an open 5G solution built with open source technologies at its core, operable across any hyperscaler.
A formula for expanding 5G
5G adoption rates vary across offerings, including fixed wireless access (FWA) for consumers and businesses, edge deployments for latency-sensitive applications, dedicated infrastructure offerings for enterprises using network slicing, and so forth. The full catalog of 5G offerings is not yet available, accessible, or affordable to many consumers, depending upon their geographic location.
To expand 5G coverage to a wider consumer base, communication service providers need visibility into the return on investment (ROI) for the capital expenditure (CapEx) investments to acquire, deliver, and build 5G, as well as the ongoing maintenance and operational expenditures (OpEx). Collectively, these place a significant financial burden on service providers.
Telco service providers could benefit from adaptable, on-demand, and pay-as-they-consume infrastructure services—from 5G Core (5GC), to enterprise/consumer network edge, and even towards 5G radio access network (RAN)—that address diverse use cases while minimizing CapEx and OpEx.
Meeting these goals requires a value chain consisting of cloud-native technologies, complementary service capabilities, creative business model capabilities, and an extensive partner ecosystem. No less important are talented and empowered engineering teams that can quickly create solution prototypes, evolve them to mature production implementations, and support the complete end-to-end solution.
Coincidentally, communications service providers' own digital (cost and service) transformation will require some of these same ingredients. As with all new technology offerings, some use cases are likely not guaranteed business opportunities but entail a degree of risk, particularly in approaching or emergent business areas.

The role of open source
Open source software has long driven the business and technology transformation of communication service providers into digital service providers. We have seen significant success stories with increased business agility, adaptability to changing business needs and environments, and cost reductions from those who transform successfully.
Open source's flexibility allows communication operators to select and combine on-premises infrastructure with public cloud infrastructure, all monitored and managed through a single control plane with an abstracted application programming interface (API) layer.
A 5G solution using hyperscalers allows dynamic scaling to meet demand and other changes based on time, location, cost, and earnings. Cloud-native technology enables operators to adopt consumption-based, geographically distributed technology stack implementations on cloud infrastructures, using automation to minimize risk and increase customer coverage.
[ Boost security, flexibility, and scale at the edge with Red Hat Enterprise Linux. ]
5G solution stack components
The 5G solution stack can be broadly categorized into several components:
- Infrastructure: Provides necessary compute, network, and storage resources to the application platform
- The application platform: Accommodates applications with declarative desired state consistency and facilities for scaling, healing, and monitoring
- 5G applications: Provide the business logic to deliver desired outcomes in a homogenous, performant way (for example, wider, stronger, faster 5G)
- Management and orchestration: Allow dynamic scaling of end-to-end 5G solutions across multiple locations with automation
[ Hiring enterprise architects? Learn how to find great telco candidates. ]
The following conceptual diagram shows the common architectural elements in a 5G solution stack.

What is 5G Open HyperCore?
The 5G Open HyperCore technology stack is an assembled collection of functional components that include infrastructure, an application platform, 5G applications, and management and orchestration elements.
Infrastructure
The infrastructure encompasses the services and resources provided by the cloud service provider, including core services such as compute, network, storage, infrastructure subutilities (NTP source), and additive network functions (firewalls and load balancers). It also includes add-on software services, such as identity management, infrastructure automation, and base image catalogs.
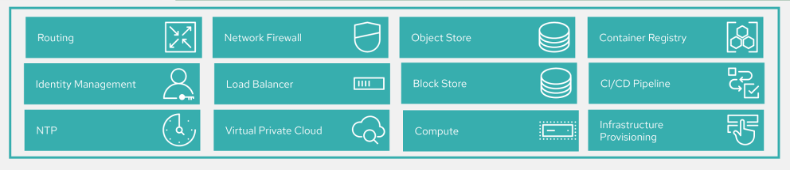
Although each hyperscaler might offer similar stacks with equivalent components, their access methodology (the API) varies. This brings overhead to the 5G engineering team to adopt and manage different stacks with continuously changing catalogs and costs. However, the application platform installers and management toolboxes can cloak this complexity by introducing infrastructure neutrality.
[ Learn more about creating an event-driven architecture for a hybrid cloud blueprint. ]
Application platform
The application platform is the core "engine" that runs the 5G application or function stack. The key components include the container execution and orchestration platform, application subutilities (dashboards, APIs, pluggable resources, etc.), additive DevOps, and platform-management toolboxes. The application platform is not necessarily a singular instance but a distributed, highly available, and resilient open source software stack.
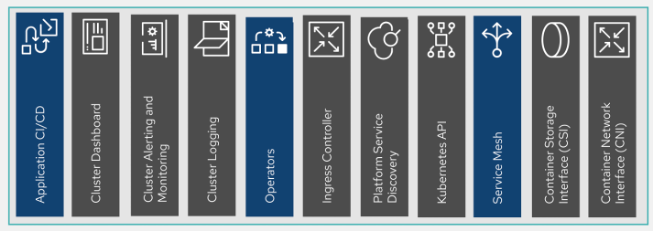
Applications
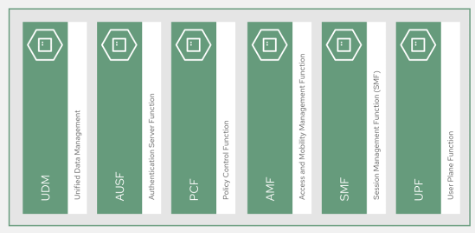
5G applications can be subcategorized into the following functions, which all span various application platforms for resilience and higher availability.
Main functions that deliver 3GPP 5G Core functionality for device/user registration and session management.
Supplementary functions that deliver device or user subscription and value-added services.
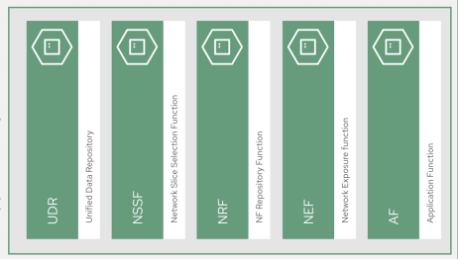
Management function(s) that deliver operations support system (OSS) and business support systems (BSS) duties.

Platform management and application orchestration
Similar to many other communication solutions, 5G Core's availability can be enhanced with multilocation deployment, as well as location-aware access to allow dynamic resource allocation and management.
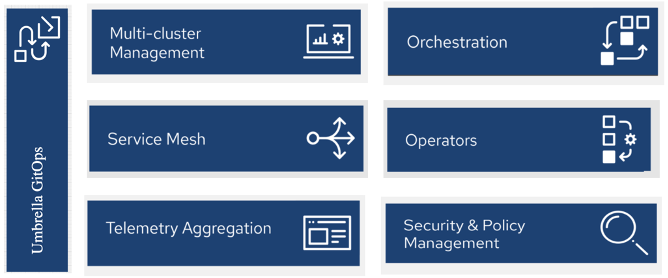
To achieve this, multiple platform instances need to host 5G application stacks. The best practice to achieve smooth and consistent platform creation, management, and application stack delivery is using the GitOps pattern. Using Git as a single source of truth, both for platform configurations and application and function stacks, is the only way to achieve homogeneous and scalable 5G Core across on-premises and hyperscaler deployments.
What's next?
This introduction provides an overview of the common elements that make up the 5G Open HyperCore architecture blueprint. Follow-up articles will look into other aspects of 5G HyperCore. In the meantime, you can learn more about Red Hat OpenShift, the enterprise Kubernetes application platform that can enable solutions on top of hybrid and multicloud. You can also explore more about the future of 5G and edge computing on our telecommunications blog.
Check out Red Hat Portfolio Architecture Center for an entire catalog of solutions that are all built off of successful customer deployments for telecommunications, media, and entertainment (TME) service providers.
This article is adapted from the authors' post Open 5G HyperCore on Medium.
About the authors
Fatih, known as "The Cloudified Turk," is a seasoned Linux, Openstack, and Kubernetes specialist with significant contributions to the telecommunications, media, and entertainment (TME) sectors over multiple geos with many service providers.
Before joining Red Hat, he held noteworthy positions at Google, Verizon Wireless, Canonical Ubuntu, and Ericsson, honing his expertise in TME-centric solutions across various business and technology challenges.
With a robust educational background, holding an MSc in Information Technology and a BSc in Electronics Engineering, Fatih excels in creating synergies with major hyperscaler and cloud providers to develop industry-leading business solutions.
Fatih's thought leadership is evident through his widely appreciated technology articles (https://fnar.medium.com/) on Medium, where he consistently collaborates with subject matter experts and tech-enthusiasts globally.
Ishu Verma is Technical Evangelist at Red Hat focused on emerging technologies like edge computing, IoT and AI/ML. He and fellow open source hackers work on building solutions with next-gen open source technologies. Before joining Red Hat in 2015, Verma worked at Intel on IoT Gateways and building end-to-end IoT solutions with partners. He has been a speaker and panelist at IoT World Congress, DevConf, Embedded Linux Forum, Red Hat Summit and other on-site and virtual forums. He lives in the valley of sun, Arizona.
More like this
AI in telco – the catalyst for scaling digital business
Metrics that matter: How to prove the business value of DevEx
Press Start | Command Line Heroes
How Should We Handle Failure? | Compiler
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds

