Smart Inventory is a feature that was added to Red Hat Ansible Tower 3.2. The feature allows you to generate a new Inventory that is made of up hosts existing in other Inventory in Ansible Tower. This inventory is always-up-to-date and is populated using what we call a host filter. The host filter is a domain specific query language that is a mix of Django Rest Framework GET query language with a JSON query syntax added in. Effectively, this allows you create an Inventory of Hosts and their relational fields as well as related JSON structures.
The ansible_facts field is a related field on a Host that is populated by Job Template runs (Jobs) that have fact caching enabled. Ansible Tower bolts on an Ansible fact cache plugin with Job Template that have fact caching enabled. Job Templates of this kind that run playbooks that invoke Ansible gather_facts will result in those facts being saved to the Ansible Tower database when the Job finishes.
A limitation of the Smart Inventory filter is that it only allows equality matching on ansible_fact JSON data. In this blog post I will show you how to overcome this limitation and add hosts to a Smart Inventory using, for example, a range query on if a host is part of a subnet.
Ansible Tower Objects
Enough talking about it, let's see an example. We are going to have to create objects in Ansible Tower. Specifically, the objects in the table below.
| Resource | Value |
| Organization | Transformers |
| Inventory | Autobots |
| Project | Facts |
| Hosts | optimus, bumblebee, jazz |
| Job Templates | gather, clear, subnet, set_fact_cacheable |
Enable fact cache for all the job templates
1. Fact Cache
Now, let's make something happen. Run the gather job template. Then look at the resulting facts that got gathered in the UI for the Inventory Autobots.

Above is an example of how you view the results from the fact gathering process in the UI. Now let's see how we can create a Smart Inventory from the facts gathered.
2. Our First Smart Inventory
We will create a smart inventory that contains only Red Hat hosts. In my example, optimus and bumblebee are both Red Hat hosts while jazz is an Ubuntu host.

Create a smart inventory with host filter: ansible_facts.ansible_distribution:RedHat
My new smart inventory, Red Hat Autobots, contains 2 hosts (see below image).
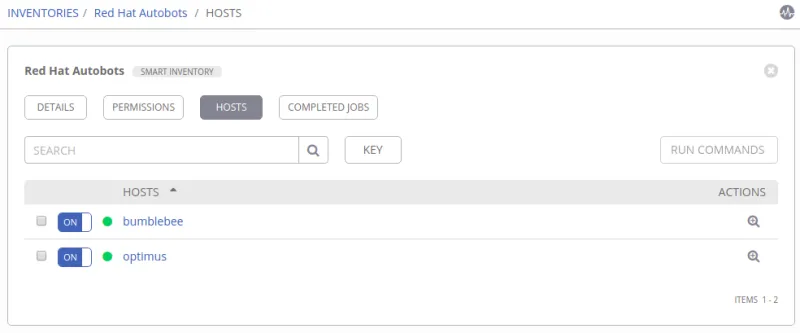
3. Inject playbook facts
We are now going to leave the Smart Inventory feature and go back to fact caching. Specifically, I am going to show you how to set_fact in a playbook and have that fact stored in Ansible Tower.
Run the job template set_fact_cacheable. Below is the result of that run.

Now, let's look at the facts for any of the 3 hosts that this playbook ran against. Notice how bumblebee now has a new set of facts (see below image).

Specifically:
a:
b:
c:
- a
- b
These facts were set by this playbook which uses the set_fact Ansible module with cacheable: true set.
Create a Smart Inventory
I've showed you all the pieces you are going to need to create a Smart Inventory based on host facts that aren't simple equality matching. The pieces are:
- Fact Cache
- Smart Inventory
- Inject playbook facts
Now I'll show you an example using all these pieces to construct a Smart Inventory of hosts within a subnet. This is a good example because selecting hosts based on subnet is a range query, it is not a simple equality query. Therefore, we are going to need to leverage 3. Inject playbook facts to accomplish creating a Smart Inventory to group these hosts.
The overall goal is to set is_subnet on a host to True if the host is in the desired subnet, or False if the host is not in the subnet. Then, we can construct a Smart Inventory host filter like ansible_facts.is_subnet:true to get hosts in the subnet. The below playbook accomplishes this.
- hosts: all
vars:
subnet: '172.18.0.0/16'
tasks:
- name: "Presume host to not belong to subnet"
set_fact:
is_subnet: False
cacheable: True
- name: "Figure out if host belongs to subnet"
set_fact:
is_subnet: True
cacheable: True
when: ansible_all_ipv4_addresses | ipaddr(subnet)
Future
Currently, all traditional relational database fields on Ansible Tower objects can be used in a Smart Inventory host filter query (i.e. Host name, Inventory name, Organization description, etc); the only JSON searchable field related to Hosts is the ansible_facts field. We hope to expand the searchable JSON fields in the future as well as the operators supported (right now we only support equality). However, much consideration must be given to the performance characteristics as well as the storage requirements in doing so.
About the author
More like this
Friday Five — February 6, 2026 | Red Hat
AI insights with actionable automation accelerate the journey to autonomous networks
Data Security And AI | Compiler
Data Security 101 | Compiler
Keep exploring
- The automated enterprise
E-book - Try Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform with self-paced, hands-on labs
Interactive lab - Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform: A beginner’s guideE-book
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
