We revolutionized the operating system (OS) with Red Hat Enterprise Linux more than two decades ago. Over that time, Red Hat has become the enterprise open source technology leader, offering a broad portfolio of hybrid cloud platforms and open source technologies—including artificial intelligence (AI), virtualization, edge computing, application development and automation solutions. Now, as we introduce the Red Hat In-Vehicle Operating System to the automotive sector, our dedicated automotive product team is forging a focused developer solution based on these companion productivity solutions to help customers optimize and scale an efficient “software factory” operation.
Key components of our automotive development platform
We can utilize the following key solutions to build a comprehensive development platform:
- Red Hat OpenShift provides the foundation for cloud-native development and testing
- Red Hat Developer Hub provides a centralized portal for managing development project tools
- Red Hat OpenShift DevSpaces enable collaborative development via a cloud-based integrated development environment (IDE) for writing and debugging software code without requiring local hardware setup
- Red Hat OpenShift AI delivers a flexible, scalable platform for AI and machine learning (ML), empowering enterprises to create and deploy AI-enabled applications at scale across hybrid cloud environments
- Automated CI/CD pipelines streamline build, test and deployment processes, as part of Red Hat OpenShift
The platform's cloud-native architecture facilitates scalable, collaborative development, streamlines workflows and helps ensure consistent testing environments throughout the development lifecycle, reducing time to market and enhancing software quality for software-defined vehicles.
This simplified architecture helps automotive manufacturers modernize development practices while maintaining high reliability and security standards.
Solution overview
The foundation of the solution includes the development platform and its integrated test and validation support. In addition to these, several components contribute to or influence the design of the solution.
The diagram below provides an overview of the solution architecture:
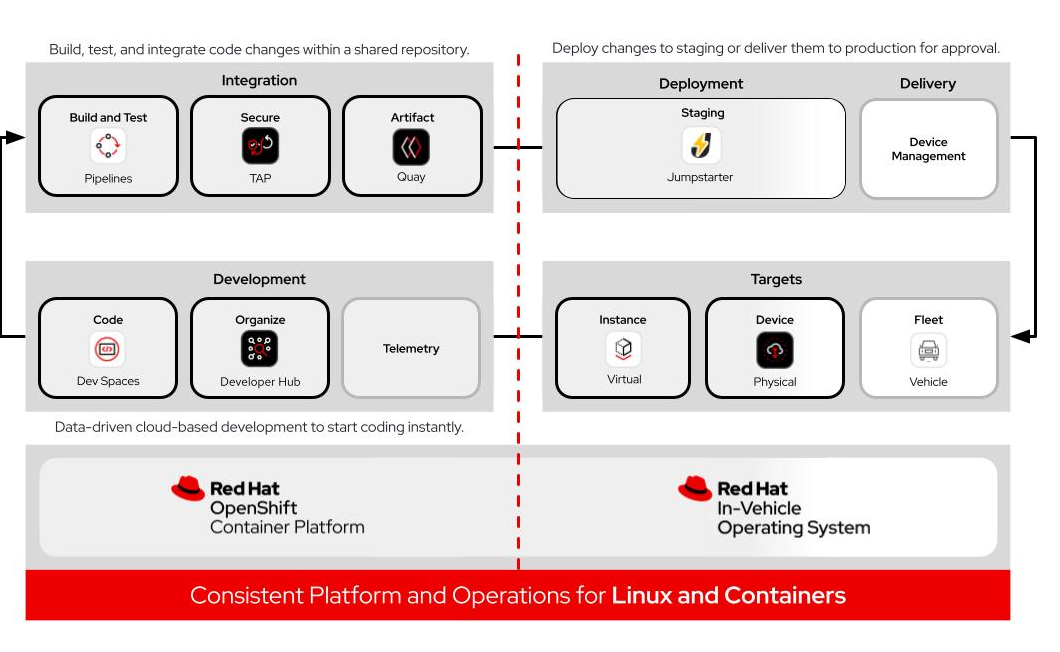
Red Hat Developer Hub and Red Hat OpenShift DevSpaces form the solutions’ core, consolidating tools and workflows for software-defined vehicle development. They provide a centralized environment where development teams can access standardized tools, automated testing pipelines and preconfigured components. This internal development platform (IDP), built on the open source Backstage project, comes pre-loaded with essential tools, extensions and configurations via a unified dashboard. It simplifies common tasks through automation and allows developers to work with familiar Linux-based tools. Cloud integration supports scalable development and testing, enabling rapid prototyping and deployment of automotive software components.
Virtual testing allows developers to validate vehicle systems through simulation—reducing reliance on physical prototypes and cutting both costs and time. This is particularly valuable with cloud-based virtual platforms building on upstream, open source platforms such as the Automotive Stream Distributions (AutoSD), which feeds the downstream, commercially-supported and functional safety-certified Red Hat In-Vehicle Operating System. Developers can begin prototyping immediately on AutoSD with no requirements for commercial access or support agreements before deciding to move up to the commercial product. This can save considerable time and expense, using a shift-left strategy.
Red Hat partners with multiple virtual platform providers, including new high-performance cloud platforms that use advanced techniques to map execution onto the latest high-performance server instances—sometimes exceeding the performance of the target automotive hardware system-on-chip (SoCs).
Hardware-in-the-loop (HIL) testing is essential to modern automotive software development. HIL testing is now typically the follow-on phase to hardware-agnostic virtual testing, integrating real vehicle hardware components (such as ECUs, sensors and actuators) into the simulation platform, creating controlled and realistic test environments. This is typically begun in a lab mock-up of in-vehicle systems, before moving on to test vehicles in the final proving ground phase of development.
Integration and delivery refers to the continuous process of merging code changes into a shared repository and automating the deployment pipeline. This includes automated testing, security scanning and deployment orchestration to help ensure that code is thoroughly validated before release. The automotive development platform automates repetitive tasks, enforces security policies and provides developers with the tools and workflows needed to deliver code efficiently and safely.
Monitoring, logging and security features built into Red Hat’s products are used to support developer workflows and operational excellence.
By deploying a consistent foundational layer across cloud, virtual and physical environments, automakers can accelerate innovation and reduce total cost of ownership, while continuing to maintain the stringent demands of software-defined vehicles development.
The future of software-defined vehicles and Red Hat technologies
About the authors
Bob Monkman is the Sr. Principal Product Marketing Manager for Automotive, at Red Hat, as part of the Edge Business Unit. Bob has been active in open source and embedded software industry for over 35 years. Bob has held leading roles in product management, product and segment marketing, open source strategy, strategic alliances, technical marketing, as well as applications and software engineering, primarily in mission critical and safety critical sectors. Bob has held leadership roles in many open source, open collaboration consortia over 25 years in communications infrastructure, medical and automotive industry consortia.
Paul Wallrabe, a former consultant, boasts expertise in Kubernetes-backend development and the elimination of toil through automation in developer toolchains. With a solid background in the automotive industry, he has turned his attention to the unique challenges that this sector presents to Linux.
More like this
Simplifying Windows Licensing with OpenShift Virtualization on ROSA
Simplifying modern defence operations with Red Hat Edge Manager
SREs on a plane | Technically Speaking
Compute confidential: In hardware we trust | Technically Speaking
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds

