Introduction
Modern datacenters are evolving rapidly to optimize workload performance, security and efficiency. A key innovation that enables this transformation is the data processing unit (DPU). DPUs are specialized hardware accelerators that offload networking, security and storage tasks from the host CPU, improving overall system efficiency, enhancing workload isolation and bolstering security capabilities.
With Red Hat OpenShift, DPUs can be integrated into existing infrastructure. The key advantage is a cloud-native extension: any workload that runs on OpenShift or Kubernetes today can smoothly extend to DPUs, enabling organizations to optimize performance without requiring application modification. Some workload containers can be moved from the host system down to the DPU.
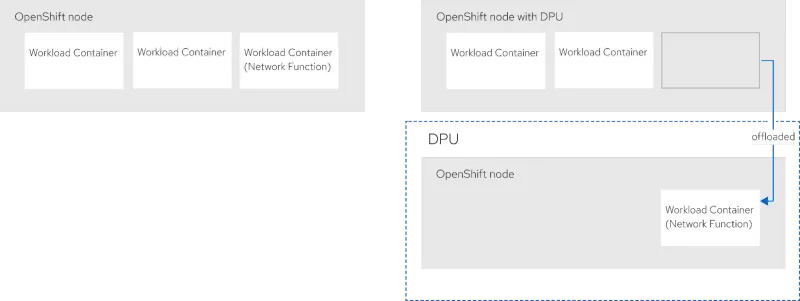
Deploying and managing DPUs in OpenShift
The OpenShift DPU operator extends OpenShift’s built-in management capabilities to DPUs in a vendor-agnostic way, making deployment and configuration as streamlined as possible while reducing the maintenance burden for software engineers. With user-friendly custom resources (CRs), administrators can manage DPUs without needing deep expertise in specific vendor hardware.
The operator automates DPU discovery, workload scheduling and lifecycle management through vendor-neutral APIs aligned with the Open Programmable Infrastructure (OPI) Project. A primary design goal is optimizing data flow between the host system and the network, significantly reducing bottlenecks and accelerating network-bound workloads.
By using a standardized API, the DPU operator enables clusters to integrate DPUs from multiple vendors, allowing organizations to take advantage of their unique advantages. Administrators can define node affinity rules, offload workloads and monitor performance with OpenShift-native tools like Prometheus and Grafana, ensuring harmonious integration with existing infrastructure.
Supported DPUs rely on in-tree open source components and are integrated across all layers of the Red Hat product stack, removing the need for custom components that add complexity and friction. This ensures smooth integration, long-term maintainability and robust enterprise support.
The Red Hat OpenShift DPU operator is available in the OpenShift catalog today and the source code can be found on GitHub.
Advantages of DPUs in OpenShift
Integrating DPUs into an OpenShift environment unlocks a new tier of operational excellence. The benefits ripple through the infrastructure, creating a more robust, responsive and security-focused platform.
One of the most significant gains is network acceleration. DPUs, with their specialized hardware, take over the heavy lifting of network traffic processing. This direct hardware acceleration dramatically improves network throughput, allowing more data to flow and significantly reduces latency. For data-intensive applications, real-time communications or financial trading platforms where every microsecond counts, DPUs provide the necessary speed and efficiency.
From a security perspective, DPUs offer enhanced security isolation. By creating a separate, hardware-isolated domain for security functions, DPUs minimize the attack surface on the host system. Critical security tasks like firewalling and encryption can run directly on the DPU. This means that even if a host were compromised, these security mechanisms could continue to operate independently, providing a resilient defense layer. Furthermore, these enforcement mechanisms operate transparently to the workloads, meaning applications don't need to be rewritten to benefit from this heightened security posture.
This offloading strategy naturally leads to host CPU optimization. When infrastructure tasks like networking and security are managed by the DPU, the host CPU is liberated from these computationally intensive processes. These conserved CPU cycles can then be dedicated to running core business applications, leading to improved performance and the ability to accommodate more workloads on existing hardware, potentially lowering infrastructure costs.
Finally, DPUs deliver substantial storage performance improvements. For workloads heavily reliant on fast storage access, such as databases or big data analytics, DPUs can manage storage I/O operations. This not only accelerates these storage-heavy workloads but also further alleviates the host CPU. A key capability here is the ability for DPUs to dynamically expose NVMe (Non-Volatile Memory Express) devices to the host, allowing for flexible and efficient allocation of high-speed storage resources.
Use cases for DPUs in OpenShift
The unique capabilities of DPUs, when combined with the orchestration power of Red Hat OpenShift, enable a wide array of compelling use cases, allowing organizations to reimagine how they architect and deploy critical services. These use cases demonstrate the practical application of the aforementioned advantages.
Building upon the network acceleration advantage, DPUs facilitate true high-performance networking by transforming into dedicated network control points. Offloading entire software-defined networking (SDN) stacks, including virtual switching, routing, firewalls and load balancers, allows OpenShift environments to implement sophisticated traffic management policies and fine-grained network segmentation for enhanced security. This also enables high-fidelity telemetry directly at the server edge, all without siphoning resources from application workloads, resulting in a highly agile and programmable network fabric.
The rapidly expanding field of artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) also stands to benefit significantly. AI/ML offloading to DPUs, particularly for tasks like AI inference, can dramatically accelerate processing times. As AI models grow in complexity, the computational demand for inference (using a trained model to make predictions) increases. DPUs efficiently handle these inference workloads, freeing up valuable host CPU and even GPU resources for other tasks, including model training or other application logic. This allows organizations to deploy AI-powered services more broadly and cost-effectively.
Taking advantage of their inherent security isolation, DPUs provide a robust platform for advanced security enforcement. The DPU's isolated execution environment can serve as a root of trust. This enables the deployment of sophisticated measures such as in-line deep packet inspection for intrusion detection and prevention systems (IDS/IPS) or the enforcement of complex, data-centric security policies like microsegmentation directly in the data path. Security thus becomes an integral, high-performance component rather than a host-based bottleneck, capable of operating effectively even if the host system is under duress, with policies applied transparently.
Finally, the storage performance gains from DPUs revolutionize storage access, particularly for demanding applications. In scenarios involving distributed databases or AI/ML training pipelines, DPUs excel at storage acceleration. By handling storage protocols and offloading tasks like data reduction or encryption at wire speed, DPUs enable direct, low-latency access to disaggregated storage pools. This not only speeds up I/O operations but also fosters more flexible and scalable storage architectures within OpenShift, where storage resources can be dynamically provisioned and managed independently of compute nodes, leading to faster data processing and improved application responsiveness.
Conclusion
DPUs in Red Hat OpenShift redefine cloud-native infrastructure by enabling streamlined workload extension, improved performance and stronger security capabilities. By treating DPUs as compute nodes, Red Hat OpenShift users can move tasks from the host to the DPU while maintaining operational simplicity. As DPUs become more prevalent, Red Hat OpenShift will continue to evolve by adding support for more DPUs and by enabling more acceleration capabilities.
Now is the time for organizations to explore DPUs and elevate their cloud-native deployments.
Product trial
Red Hat OpenShift Data Foundation | Product Trial
About the author
Balazs Nemeth is a Senior Principal Software Engineer at Red Hat. He's the tech lead and team lead of the Hardware Enablement Team specializing in end-to-end enablement of DPUs in Openshift.
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
