In today's volatile and unpredictable business environment, IT continuity has become an indispensable pillar of business resilience. As organizations grapple with a multitude of threats, from escalating cyber-attacks and regulatory shifts to geopolitical uncertainties and the volatility of global markets, the ability to maintain IT operations in the face of disruptions is crucial for survival and growth.
This necessitates a comprehensive approach to IT service continuity , encompassing a deep understanding of the organization's IT infrastructure, risk assessment, and the implementation of robust recovery strategies. Amidst the complexities of legacy IT infrastructure, escalating workloads, the proliferation of shadow IT, and the intricacies of hybrid and multi-cloud environments, organizations need to embrace innovative solutions to navigate these challenges and ensure business continuity in the face of any unforeseen disruptions.
1. Challenges in the current landscape
The adoption of hybrid and multi-cloud architectures has revolutionized IT operations, opening up new avenues for businesses to achieve agility, scalability, resilience and cost optimization. However, effectively managing these complex environments also presents a unique set of challenges that organizations must effectively address to achieve optimal performance and resilience for their business.
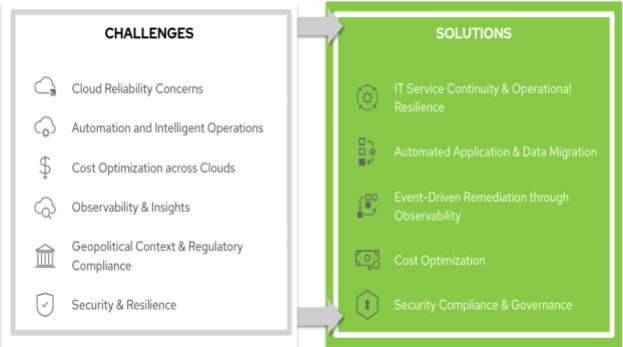
Figure 1 - IT Service Continuity & Operational Resilience Challenges / Solutions
2. Our solution: a holistic approach
Accenture’s Cloud First Innovation Center NAVAN came across a public sector customer facing several of the aforementioned challenges, specifically related to their Fishing Permit delivery application. The customer was facing increased scrutiny due to regulatory shifts and required a solution that would enable service continuity and provide optimal resilience for their application across any cloud.
This prompted the Accenture team to reach out across their partner ecosystem and carefully select trusted partners to define an innovative, comprehensive and fully automated solution to tackle these challenges head-on.
The resulting solution, driven by Dynatrace’s AIOps prowess and bolstered by Event-Driven Ansible (part of Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform) and Data Mobility by Trilio, provides a streamlined framework for resiliency and service continuity for GitOps-based cloud-native applications (running on Red Hat OpenShift) and their data across heterogeneous cloud environments as shown on the diagram below.

Figure 2 - Design Overview
Key ingredients - recipe for success:
More times than not, leveraging the power of the ecosystem is critical to achieving success with customers. This use case example perfectly illustrates a collaborative ecosystem approach, where each player contributes with their unique strengths in their respective areas of expertise, to create a synergistic solution tailored to meet the needs of customers in an evolving hybrid landscape.
- Accenture: Trusted planning, execution and advisory services and state of the art innovation center (NAVAN) for developing MVP and PoCs.
- Dynatrace: AIOps capabilities for intelligent, actionable insights for container based environments and infrastructure.
- Red Hat: Industry leading hybrid cloud container platform in Red Hat OpenShift coupled with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes and state of the art automation with Event-Driven Ansible.
- Trilio: Multi-cloud, multi-cluster data migration and policy-as-code for efficient control.
Leveraging the power of the ecosystem is ultimately the perfect recipe for success.
Design overview:
The following section outlines our solution design and use case workflow details.
Outline
- A government application (i.e. the Fishing Permit application) runs from Red Hat OpenShift cluster 1 hosted in GCP Cloud and has the ability to run from a second Red Hat OpenShift cluster, cluster 2 in a local sovereign cloud provider, when necessary.
- To facilitate this failover, the environment has been configured with centralized cluster management using Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management, Data Protection from Trilio and monitoring from Dynatrace. An Red Hat OpenShift Hub cluster has been implemented for this specific purpose.
- To allow for hands-off orchestration, Ansible Automation Platform, with the Event-Driven Ansible controller option has been implemented.
- Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management provides central governance and management of clusters, and manages the installation of operators like ArgoCD, Dynatrace and Trilio, and any additional configuration required such as verifying the backup storage that will be used can be accessed by both Red Hat OpenShift clusters.
- When Dynatrace intelligently infers a large enough anomaly that warrants a disaster recovery workflow, Event-Driven Ansible Playbooks will react to the event, triggering the failover steps. These steps will see the data backed up from cluster 1 being recovered to cluster 2 and triggering ArgoCD to redeploy the application to cluster 2 which will immediately utilize the recovered Persistent Volume Claim (PVC) provided by Trilio.
- Finally, an Ansible Playbook will reconfigure the load balancer to ensure traffic is moved from cluster 1 to cluster 2.
Workflow
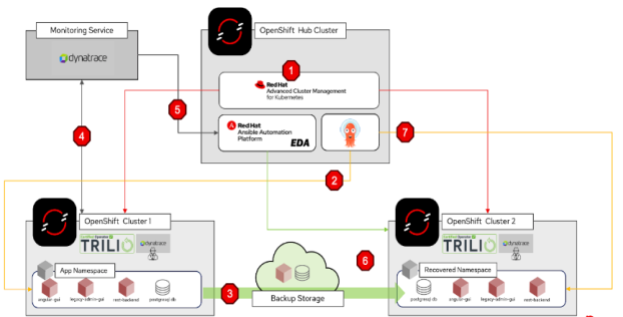
Figure 3 - Workflow Steps
- Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management helps ensure that Trilio and Dynatrace agents, as well as any other required operators are installed, configured and managed centrally on both Red Hat OpenShift cluster 1 and Red Hat OpenShift cluster 2.
- ArgoCD is used to initially deploy and update the Fishing Permit application in Red Hat OpenShift cluster 1.
- Trilio (using Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management Policies) enables the deployed application data on Red Hat OpenShift cluster1 to be backed up to the common storage backup (also configured via Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management Policies).
- Dynatrace detects a large, ongoing anomaly with Red Hat OpenShift cluster 1 (ex: cluster connectivity loss). This is achieved using Dynatrace Synthetic ClickPaths, which is an easy way to achieve proactive monitoring by simulating regular access to our application from various locations.
- Event-Driven Ansible Rulebooks are triggered as a reaction to the Dynatrace event, effectively triggering specific actions in the form of several Ansible Playbooks to trigger the move from Red Hat OpenShift cluster 1 to 2.
- Ansible is invoked to perform the data recovery of the Persistent Volume Claim backup to OpenShift cluster 2.
- Ansible directs ArgoCD to redeploy the application to Red Hat OpenShift cluster 2, which uses the recovered PVC Data.
Additionally, load balancing failover occurs as part of the Ansible actions so operations of the application continue between clusters + cleanup of the application namespace on Red Hat OpenShift cluster
Solution technical implementation guidelines
3. Environment specifications:
Our solution has been implemented in the Accenture Cloud First Innovation Center NAVAN with the following specifications:
- Red Hat OpenShift:
- Version 4.13 (stable) for all clusters
- Hub Cluster specifications: 3 master nodes and 7 worker nodes with 16 vCPU, 32GB memory. Located on the local cloud provider.
- Cluster 1 specifications: 3 master nodes and 3 worker nodes with 4 vCPU, 16GB memory. Located on GCP Cloud.
- Cluster 2 specifications: 3 master nodes and 7 worker nodes with 8 vCPU, 16GB memory. Located on the local cloud provider.
- Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management:
- Version 2.8
- Installed via Operator Hub on the Red Hat OpenShift hub cluster
- Automatic updates deactivated.
- CRD object MultiClusterHub created and remote clusters imported in the Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management as managed clusters.
- ArgoCD operator via GitOps:
- GitOps operator installed on Red Hat OpenShift hub cluster via operator hub
- Target clusters integrated with ArgoCD GUI
- Git repository containing the resource code integrated to the ArgoCD instance.
- Through ArgoCD dashboard two separate applications have been created – one for the application and one for application database.
Figure 4 – ArgoCD applications
- Fishing Permit application:
- Deployment method: GitOps with ArgoCD
- 2 separate namespaces (one for the application and one for database) deployed by ArgoCD (with Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management integration configured https://www.redhat.com/architect/multi-cluster-deployment-kubernetes-gitops)
- The application is visible in Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management
Figure 5 – Application topology
Figure 6 – Application database topology
App needs to be visible in Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management GUI through ArgoCD integration leveraging application sets.
- Ansible Automation Platform:
- Version 2.4 (required for Event-Driven Ansible).
- Ansible Automation Platform and Event-Driven Ansible are both installed on two separate servers following the official documentation steps.
- Ansible Automation Platform is installed on a RHEL 9.2 VM with following specifications: 8 CPUs, 16GB RAM, disk 150 GB.
- Event-Driven Ansible is installed on a separate server with the exact same specification as Ansible Automation Platform.
- Event-Driven Ansible has been installed by running the installer setup script following the Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform 2.4 Installation Guide (you can find this in the Red Hat Customer Portal).
Figure 7 – Event-Driven Ansible Controller interface
- Trilio:
- Version 4.0.0
- An install policy has been created on Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management in the hub cluster to deploy Trilio Operators onto Red Hat OpenShift clusters 1 and 2. (https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/deploying-triliovault-for-kubernetes-with-openshift-red-hat-advanced-cluster-management-policies)
- A backup policy has been created on Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management in the hub cluster to continuously backup the Fishing Permit application persistent volume claim and data into our shared S3 storage. (https://www.redhat.com/en/blog/deploying-triliovault-for-kubernetes-with-openshift-red-hat-advanced-cluster-management-policies)
Figure 8 – Trilio Policies in Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management
- Storage:
- A shared S3 storage bucket has been implemented in our local cloud provider environment, leveraging a standard service similar to AWS S3.
- Dynatrace:
- We are leveraging a SaaS based Dynatrace instance (This can be ordered at: https://www.dynatrace.com/trial)
- To deploy the Dynatrace operator in cluster 1 and cluster 2, we have chosen a guided installation method and obtained the dynakube.yaml file from Dynatrace UI.
- On the target clusters, run the necessary commands from the documentation - https://docs.dynatrace.com/docs/setup-and-configuration/setup-on-k8s/installation/classic-full-stack
- Two Red Hat OpenShift clusters are being monitored using Dynatrace.
Figure 9 – Monitoring of Red Hat OpenShift in Dynatrace
- Synthetic Clickpaths are used to test our application with simulated access from multiple locations, that can be easily started as described in the following website using a chrome browser with the Dynatrace recorder plugin installed: https://docs.dynatrace.com/docs/platform-modules/digital-experience/synthetic-monitoring/browser-monitors/record-a-browser-clickpath
- We have defined a custom alert following guidelines found here https://docs.dynatrace.com/docs/platform/davis-ai/basics/events/event-types/custom-alerts. The scenario in this case is to simulate a complete network outage for the application thus it becomes unavailable. If this event occurs, the alert is set to create a problem that is detected by the Event-Driven Ansible which in turn redeploys the application and recovers the data on a target cluster.
Figure 10 – Dynatrace Clickpaths
- Ansible Rulebooks and Playbooks:
- We create an Ansible Rulebook that listens to the event from Dynatrace (https://github.com/Dynatrace/Dynatrace-EventDrivenAnsible).
- We have created a decision environment for the rulebook execution.
- Created an Ansible Playbook, which is triggered by the Event-Driven Ansible rulebook. The playbook contains following plays - restore of the data and PV into a new namespace through the TVK operator API then redeploy the application in the target cluster with ArgoCD and perform a cleanup in the source cluster.
Figure 11 – Ansible Rulebook
Conclusion
In an environment marked by uncertainties, it’s paramount to maintain service continuity for cloud native applications, observability, and operational resilience with automation. The collaborative solution presented here stands as a testament to the industry's commitment to addressing these challenges collectively. By leveraging the strengths of each player in the ecosystem, organizations can embark on a transformative journey towards optimal IT service continuity and operational resiliency.
Special thanks to the following contributors:
- Usman Mir, CTO Cloud First Innovation Center NAVAN - Accenture
- Zane Grandi, Lead Software developer NAVAN - Accenture
- Neelam Ganapathy, Lead Infrastructure engineer NAVAN - Accenture
- Tasos Chalvatsiotis, Lead Infrastructure engineer NAVAN -Accenture
- Kevin Jackson, Director of Solution Architecture - Trilio
- Steve Weinert, EMEA Partner Solution Architect - Dynatrace
About the author
Jan is a Senior Solutions Architect at Red Hat, working closely with Accenture as part of the EMEA Eco Tech team. He previously worked for 10 years at Accenture being a part of the Accenture - Red Hat Business Group where he held the position of EMEA Technology & Architecture Lead and was also one of the original members of the first Red Hat team at Accenture in 2016. He currently lives in Toulouse, France with his wife and 2 small boys.
More like this
Strategic momentum: The new era of Red Hat and HPE Juniper network automation
Redefining automation governance: From execution to observability at Bradesco
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
Adventures In Automation | Compiler
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
