One of the most important aspects of system security is keeping systems up to date with patches. Many organizations have hundreds or thousands of Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) servers in their environments, so keeping track of patches on servers can be challenging. If critical patches are missed on systems, it could result in the systems being compromised, having unscheduled downtime, or other issues.
Red Hat Insights is a software-as-a-service (SaaS) offering that is included with your Red Hat Enterprise Linux subscription. It includes several capabilities to help with various aspects of management. The Patch capability can help customers understand which advisories are applicable in their environments, and can help automate the process of patching via Ansible playbooks.
For example, if a Red Hat Security Advisory were issued, you could go into the Insights Patch dashboard to see a list of systems in your environment that are impacted. With a few clicks from within the Patch dashboard, you can generate an Ansible Playbook that can automate the advisory installation.
If you have Red Hat Smart Management, the Cloud Connector functionality lets you run the Ansible playbook right from the Insights web interface. Smart Management, Satellite and Cloud Connector are not required for use with Insights, and if you are in an environment without Satellite you can still utilize Insights Patch and generate Ansible playbooks that can be downloaded and manually run.
Prerequisites
The first step to using any of the Insights services, including Insights Patch, is to register your RHEL servers with Insights. See the Red Hat Insights Get Started documentation for information on how to register RHEL servers. And now there's an intuitive and interactive capability to register systems right on the Insights dashboard, under the left menu item called Register Systems.
If you have a large number of hosts to register, there are options to automate the Insights client registration process, and the previous two links contain more information on this.
If you would like to use the optional Smart Management Cloud Connector functionality, which allows you to initiate Ansible Playbook runs on your hosts from Insights via your Satellite 6.7 and above servers, follow the documentation to configure it.
Viewing applicable advistories
To view the applicable advisories on your systems, go to Insights Patch. Insights Patch offers two different views into patches, one from the advisory level, and one from the system level. You can select your preference in the menu on the left (see figure 1).
Figure 1. Partial view of the menu on the left
We’ll start in the Advisories section, which will show a list of advisories that impact one or more of the servers in the environment (see figure 2). You can optionally filter by the type of advisory, or the publish date by clicking on the filter dropdown. Clicking on any of the advisories will bring up its details, including a description, and a list of affected systems.
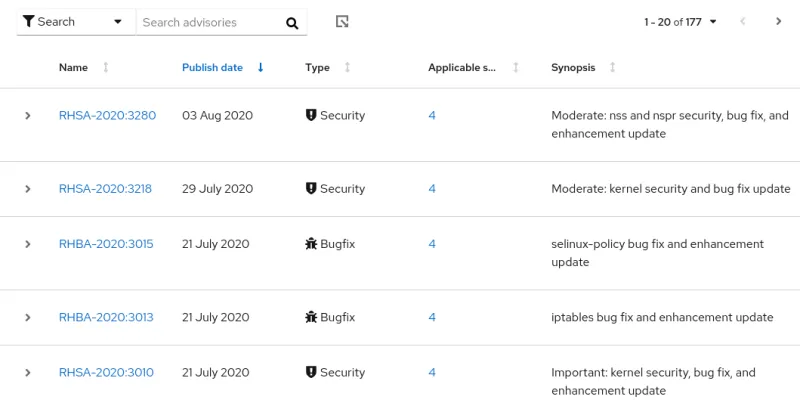
Figure 2. The view from the Advisories section
In this example, I clicked on the RHSA-2020:3010 advisory, and a list of systems that are affected by this advisory are shown, as shown in figure 3.
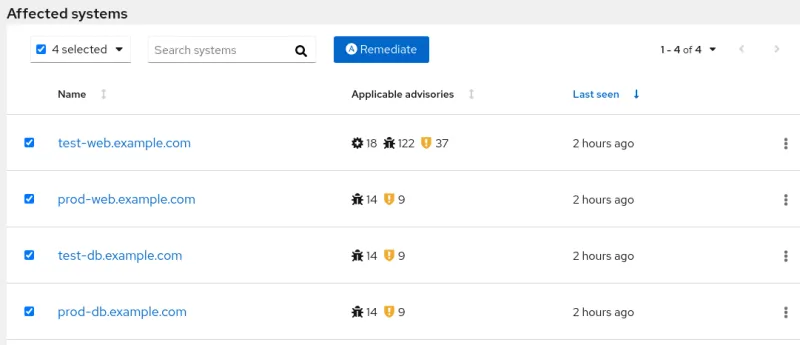
Figure 3. List of systems affected by the RHSA-2020:3010 advisory
To build an Ansible playbook to install this advisory, select the systems that should be patched (in this example, I selected all four systems), and click on the Remediate button. If you have any existing playbooks, you can either add to that playbook, or choose to create a new playbook, as shown in figure 4.
Important — Review and test any recommended actions in the playbook, and if you deem appropriate, deploy on your systems running Red Hat software. Red Hat is not responsible for any adverse outcomes related to these recommendations or Playbooks.
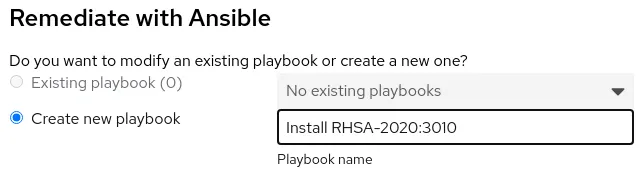
Figure 4. Menu to select if an existing playbook should be modified, or a new playbook created
In this example, I’ll create a new playbook, name it Install RHSA-2020:3010, then click Next.
On the next screen, it will be indicated if the advisory installation requires a system reboot, and you can specify if the playbook should automatically reboot the hosts or not, as shown in figure 5.
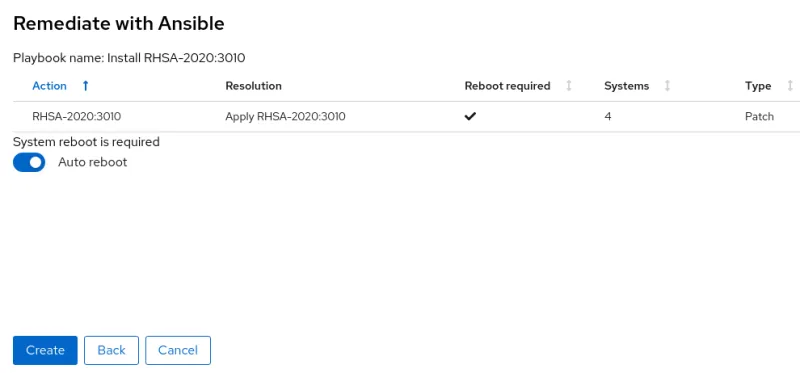
Figure 5. Menu showing if the patch requires a reboot, and if the playbook should auto reboot or not
After clicking the Create button, the playbook will be created.

Figure 6. Playbook was successfully created
Next, go to Remediations in the menu on the left part of the Insights web interface. From here, you can view the playbooks you’ve created, and can either download the playbooks, or if you have Smart Management's Cloud Connector configured, you can execute the playbooks right from Insights.
In this example, I have the Cloud Connector configured, so I will click on the Install RHSA-2020:3010 playbook, and then click on the Execute playbook button (see figure 7).
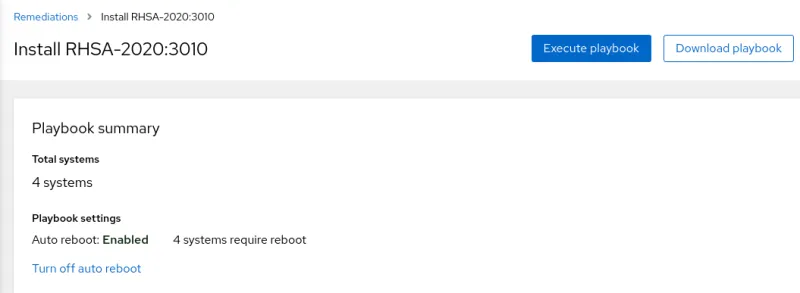
Figure 7. Option to execute playbook
After confirming the information presented, I’ll then click on Execute playbook on 4 systems, as shown in figure 8.
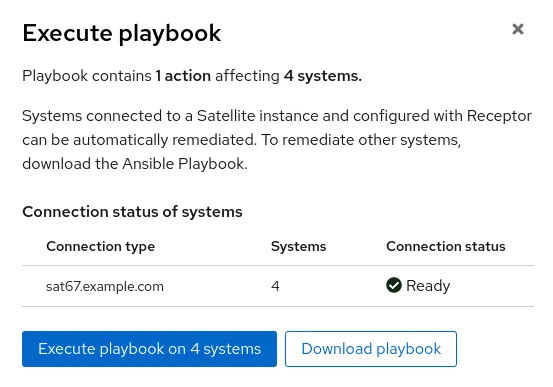
Figure 8. Executing the playbook on the systems
At this point, the playbook is run on the hosts via the sat67.example.com Satellite server’s Cloud Connector and the advisory is installed.
Progress of the Playbook execution is shown from the Insights web interface, as shown in figure 9.
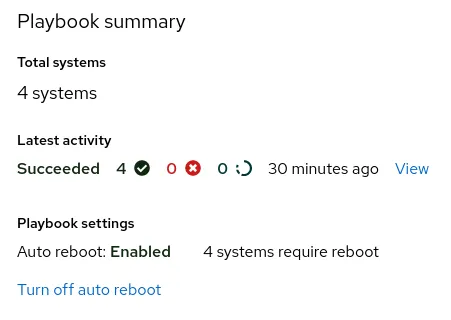
Figure 9. Playbook summary and progress
Viewing Patches from the System Level
In the previous example, we used the Advisories section of Patch which shows a list of advisories that are applicable to one or more hosts in the environment. It is also possible to see patches at the system level by going to the Systems menu option under Patch in the menu on the left side of the Insights interface, as shown in figure 10.
Figure 10. Partial view of the menu on the left
From here, a list of systems will be displayed, along with a summary of the number of advisories that are applicable to the system, as well as the last time it was seen by Insights (see figure 11).
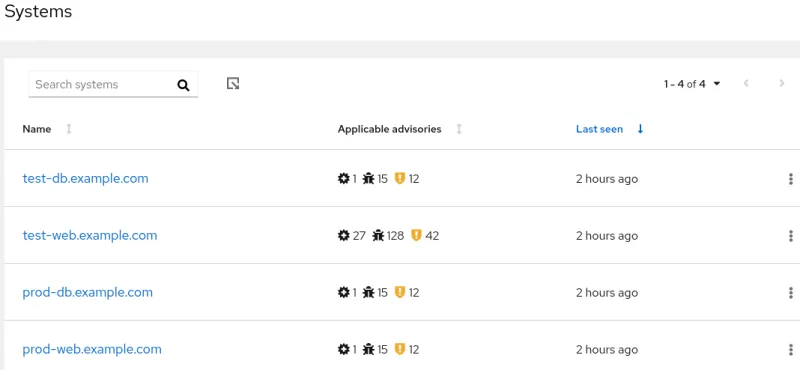
Figure 11. The view from the Systems section
If you would like to install all applicable advisories on a system, click on the dots on the right side of the table, and click on Apply all applicable advisories.
Or if a system is clicked on, a list of advisories applicable to that specific system are shown (see figure 12).
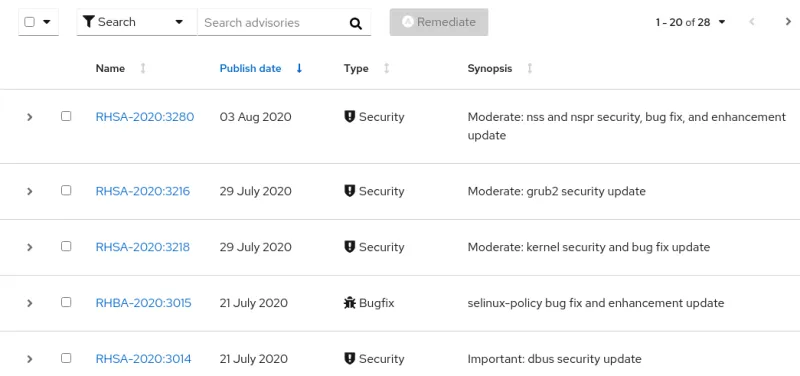
Figure 12. List of advisories applicable for a specific system
From here, advisories can be selected, and an Ansible playbook can be generated by clicking on the Remediate button.
Summary and Closing
Insights Patch is a useful way to keep track of which systems in your environment need to be patched. The ability to generate Ansible playbooks to install patches can also automate these tasks and save System Administrators time, especially when used with the optional Smart Management Cloud Connector functionality.
You can see a short presentation and live demo of the Patch capability from a recently recorded “Ask Me Anything” webinar. This webinar is part of a full series of technical webinars to help you get started with the new Red Hat Insights capabilities.
About the author
Brian Smith is a product manager at Red Hat focused on RHEL automation and management. He has been at Red Hat since 2018, previously working with public sector customers as a technical account manager (TAM).
More like this
Redefining automation governance: From execution to observability at Bradesco
AI insights with actionable automation accelerate the journey to autonomous networks
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
A composable industrial edge platform | Technically Speaking
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
