Redhat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA) is a joint venture between Red Hat and AWS, providing a managed way to run OpenShift for organizations. This way the development teams can focus on innovation, and quickly build, deploy and scale applications. Learn more on ROSA homepage and ROSA on AWS marketplace.
Today’s post is on how to deploy a JBoss EAP application on a ROSA environment, using the Red Hat Container registry base image. Let’s get started!
Prerequisite
Once you provision the ROSA cluster via AWS Management console, you will get access to Redhat OpenShift console, it will look similar to the below screenshot.
Connect and configure OpenShift environment
- Go ahead , and login to OpenShift via terminal using the “oc login” command.
- Create new project/namespace for the demo
$ oc new-project eap-demo
- For any https-enabled features, go ahead and create a secret out of the Keystore file.
Use keytool command to generate keystore using below command.
$ keytool -genkey -keyalg RSA -alias eapdemo-selfsigned -keystore keystore.jks -validity 360 -keysize 2048
- Create an OpenShift secret from the above keystore file.
$ oc create secret generic eap7-app-secret — from-file=keystore.jks
Authenticate Red Hat Container Registry
In order to use JBoss EAP for OpenShift image, we need to configure authentication to the Red Hat Container Registry.
- Follow this link, to get your access set up, and create a yaml file pull secret.
- Once you get to the Token Information screen, select the “OpenShift Secret” tab, as we want to pull the container images for our OpenShift namespace.
- Download the yaml file, which will be in “<<serviceaccount>>-secret.yaml” format.
- Create the Auth token secret, with the above file.
$ oc create -f <<1234567_serviceaccount>>-secret.yaml
- Above command will result in a secret being created, let us link this secret for pull
$ oc secrets link default <<1234567-serviceaccount>>-pull-secret — for=pull
$ oc secrets link builder <<1234567-serviceaccount>>-pull-secret — from=pull
Import latest JBoss EAP OpenShift Image streams and templates
- Now you are ready to import the JBoss EAP Image resources into your OpenShift namespace, or if you are a cluster admin, you can choose to import into all of your OpenShift Projects.
- Go ahead and run below script in your terminal
for resource in \
eap72-image-stream.json \
eap72-amq-persistent-s2i.json \
eap72-amq-s2i.json \
eap72-basic-s2i.json \
eap72-https-s2i.json \
eap72-mongodb-persistent-s2i.json \
eap72-mongodb-s2i.json \
eap72-mysql-persistent-s2i.json \
eap72-mysql-s2i.json \
eap72-postgresql-persistent-s2i.json \
eap72-postgresql-s2i.json \
eap72-third-party-db-s2i.json \
eap72-tx-recovery-s2i.json \
eap72-sso-s2i.json
do
oc replace — force -f \
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/jboss-container-images/jboss-eap-7-openshift-image/eap72/templates/${resource}
done
- To import images across projects, please replace with below command, in above script, for
$ oc replace ……
……
oc replace -n openshift — force -f \
……….
Deploy JBoss EAP application (s2I) to OpenShift
It’s time, let’s deploy the kitchensink app, from this github repo.
- Run below oc command from your terminal.
$ oc new-app — template=eap72-basic-s2i \
-p IMAGE_STREAM_NAMESPACE=eap-demo \
-p SOURCE_REPOSITORY_URL=https://github.com/jboss-developer/jboss-eap-quickstarts \
-p SOURCE_REPOSITORY_REF=openshift \
-p CONTEXT_DIR=kitchensink
- In the OpenShift console, you should see Build pod running at this time, creating the final S2I image. You can also follow logs from the terminal.
$ oc get bc -o name
- You should see the Build , and Deploy pods finished as shown below, and the container running.
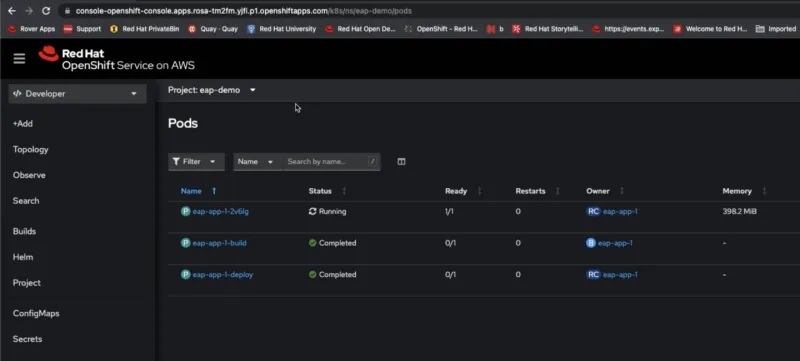
- Provide the Build config name from above step
$ oc logs -f buildconfig/BUILD_CONFIG_NAME
Check Service and Route
- Check the service created for the application
$ oc get service
- Templates should have already exposed a route, if not , go ahead and expose.
$ oc expose service/SERVICE_NAME — port=8080
Access the deployed application
Go to the OpenShift console, and navigate to Projects -> Routes, and click the URL.


Feel free to play around with the deployed app, and try to access the /rest/members REST API, to see the app in action.
Conclusion
Hopefully this article is helpful for you to get a quick start on how to deploy JBoss EAP using OpenShift container templates, and deployed on Red Hat OpenShift Service on AWS (ROSA), a managed cloud service.
Reference
About the author
More like this
Introducing OpenShift Service Mesh 3.2 with Istio’s ambient mode
How DTCC uses GitOps to accelerate customer value and security
Heroes in a Bash Shell | Command Line Heroes
Bad Bosses | Compiler: Tales From The Database
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
