Convert2RHEL is a Red Hat utility that converts operating systems that are similar to or derived from Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), such as CentOS Linux and Oracle Linux. For a full list of supported operating systems, please read this document. For more information, read Terry Bowling’s blog entries here and here on Oracle Linux.
Red Hat Satellite 6.10 first featured the capability of bulk Convert2RHEL operations. I wrote about it in a blog here. Satellite 6.11 builds on top of those capabilities in two ways:
-
An Ansible role automates Satellite server configuration/preparation for Convert2RHEL.
-
An Ansible playbook automates the host conversions.
The flowchart below presents a high-level overview of the tasks required to perform a bulk Convert2RHEL operation in Satellite 6.11.

When ready, register the Centos/Oracle Linux host(s) to Satellite and schedule a job to convert your hosts to RHEL.
Note that the Ansible role can be applied manually to the Satellite server, with a separate Ansible server.
Here we detail all of the steps required to implement this new automation.
Prepare the Satellite server
First, follow these instructions to import the included Ansible roles.
First, go to Configure > Roles.
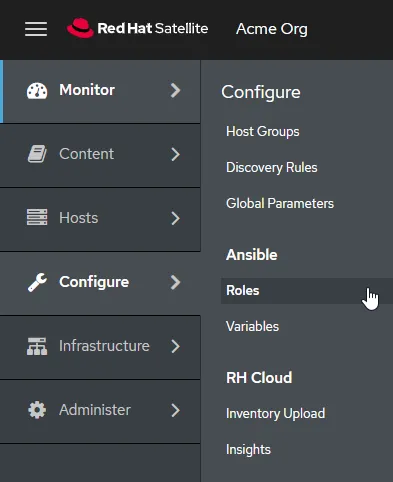
Click on "Import…".
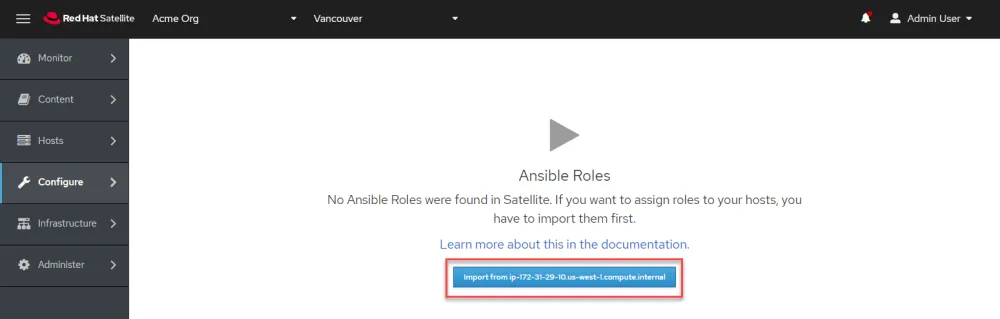
Click "Select All" and then "Submit".

Next, we’ll have to create variables for the Ansible role before we run it on the Satellite server. These variables will tell the Ansible role how you want to configure the bulk Convert2RHEL operation on your Satellite server. This includes specifying a subscription manifest, Organization, Location, admin credentials, etc.
I’ve found that the easiest and fastest way to configure the Ansible role variables is to use the hammer command line utility on the Satellite server. You can also configure the Ansible role variables through the Satellite web UI.
On this particular Satellite server, I am defining the following variables.
|
Variable |
Value |
|
satellite_rhel_wait_for_syncs |
true |
|
satellite_manifest_path |
/usr/share/satellite/manifest_satellite_20220815T193102Z.zip |
|
satellite_organization |
Acme Org |
|
satellite_password |
Ha ha no you don’t |
|
satellite_username |
myee |
|
satellite_server_url |
|
|
satellite_validate_certs |
true |
|
satellite_content_rhel_enable_rhel7 |
true |
|
satellite_content_rhel_enable_rhel8 |
true |
Here’s how to create the Ansible role variables with the hammer utility.
satellite_rhel_wait_for_syncs
The Ansible role configures and synchronizes repositories required to perform the bulk Convert2RHEL operation. The satellite_rhel_wait_for_syncs variable tells the operation to wait for the repositories to synchronize.
Enter the following on the command line interface of the Satellite server while logged in as root:
hammer ansible variables create --location "Vancouver" --organization "Acme Org" --ansible-role redhat.satellite.convert2rhel --variable satellite_rhel_wait_for_syncs --variable-type boolean --default-value false --override true
satellite_manifest_path
When the Ansible role is run, it uploads the subscription manifest, ensuring all your new hosts are appropriately licensed. If you have already uploaded a valid manifest, you’ll have to do it again, unfortunately.
hammer ansible variables create --location "Vancouver" --organization "Acme Org" --ansible-role redhat.satellite.convert2rhel --variable satellite_manifest_path --variable-type string --default-value "/usr/share/satellite/manifest_satellite_20220815T193102Z.zip" --override true
satellite_organization/usr
My Satellite organization is “Acme Org”.
hammer ansible variables create --location "Vancouver" --organization "Acme Org" --ansible-role redhat.satellite.convert2rhel --variable satellite_organization --variable-type string --default-value "Acme Org" --override true
satellite_password
The Ansible role will require Satellite admin credentials. Enter the password here.
hammer ansible variables create --location "Vancouver" --organization "Acme Org" --ansible-role redhat.satellite.convert2rhel --variable satellite_password --variable-type string --default-value "YOUR_ADMIN_PASSWORD" --override true
Note: To avoid using passwords, you can set up Personal Access Tokens instead.

satellite_username
Enter the admin username here.
hammer ansible variables create --location "Vancouver" --organization "Acme Org" --ansible-role redhat.satellite.convert2rhel --variable satellite_username --variable-type string --default-value "myee" --override true
satellite_server_url
The satellite server URL is the URL that the hosts will need to access with the curl utility.
hammer ansible variables create --location "Vancouver" --organization "Acme Org" --ansible-role redhat.satellite.convert2rhel --variable satellite_server_url --variable-type string --default-value "https://ip-172-31-29-4.us-west-1.compute.internal" --override true
satellite_validate_certs
This value should be set to true.
hammer ansible variables create --location "Vancouver" --organization "Acme Org" --ansible-role redhat.satellite.convert2rhel --variable satellite_validate_certs --variable-type boolean --default-value true --override true
satellite_content_rhel_enable_rhel7
This variable specifies that you would like the Ansible role to synchronize RHEL7 content to enable the conversion of Centos 7 (or Oracle) hosts to RHEL7. If you do not want RHEL7 content synchronized, use this variable to specify false.
hammer ansible variables create --location "Vancouver" --organization "Acme Org" --ansible-role redhat.satellite.convert2rhel --variable satellite_content_rhel_enable_rhel7 --variable-type boolean --default-value true --override true
satellite_content_rhel_enable_rhel8
This variable specifies that you would like the Ansible role to synchronize RHEL8 content to enable the conversion of Centos 8 (or Oracle) hosts to RHEL8. If you do not want RHEL8 content synchronized, use this variable to specify false.
hammer ansible variables create --location "Vancouver" --organization "Acme Org" --ansible-role redhat.satellite.convert2rhel --variable satellite_content_rhel_enable_rhel8 --variable-type boolean --default-value true --override true
You can check if your variables are set correctly in the web UI. Go to the Ansible Variables sub-menu.

Page over the variables until you find the ones you just created.

Now we have to configure Satellite to enable the running of remote execution jobs against itself.
Note: This step is unnecessary if you can already run remote execution jobs against the Satellite server.
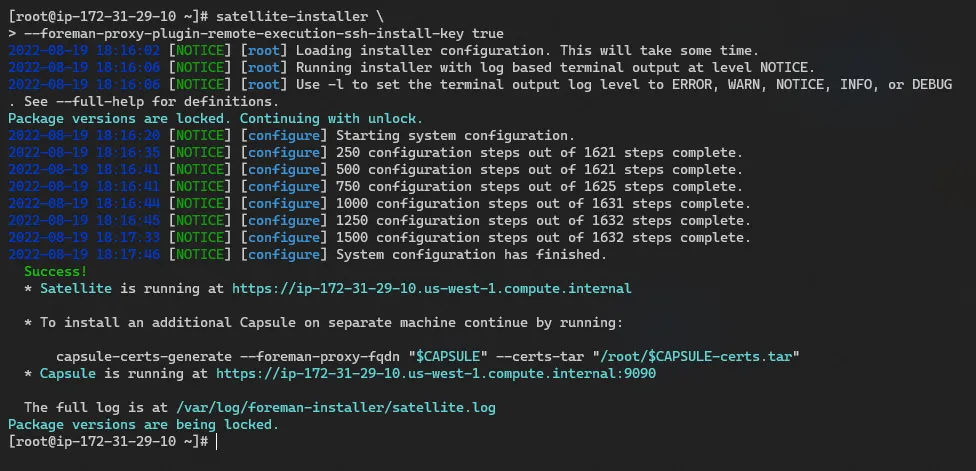
Log into the Satellite server as root and run the following command:
satellite-installer \ --foreman-proxy-plugin-remote-execution-ssh-install-key true
The output will look like the following.
Next, we’ll apply the Ansible role to the Satellite server.
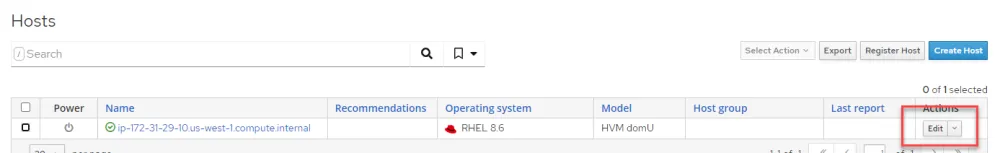
Click on Hosts > All Hosts.

Edit your Satellite server.
Click on the Ansible Roles tab.
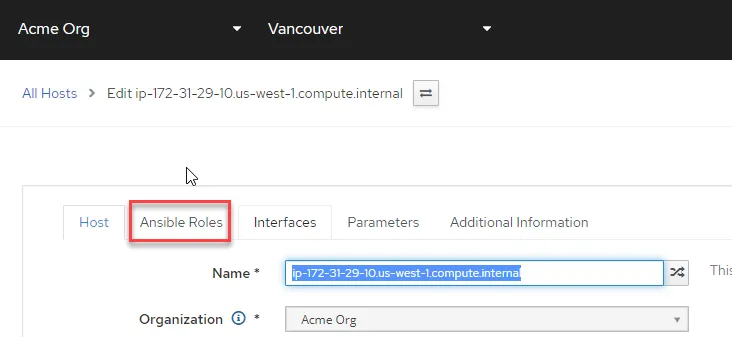
The Convert2RHEL role is on the second page of the sub-menu. Click on the + sign to assign the redhat.satellite.convert2rhel role to your Satellite server.

Then click "Submit".

You’ll then be redirected to the host information page. Click on the “Schedule Remote Job” button and select “Run Ansible roles”.

You’ll be redirected to a page displaying the status of the job. Click on the Satellite host to see the real-time status of the job.
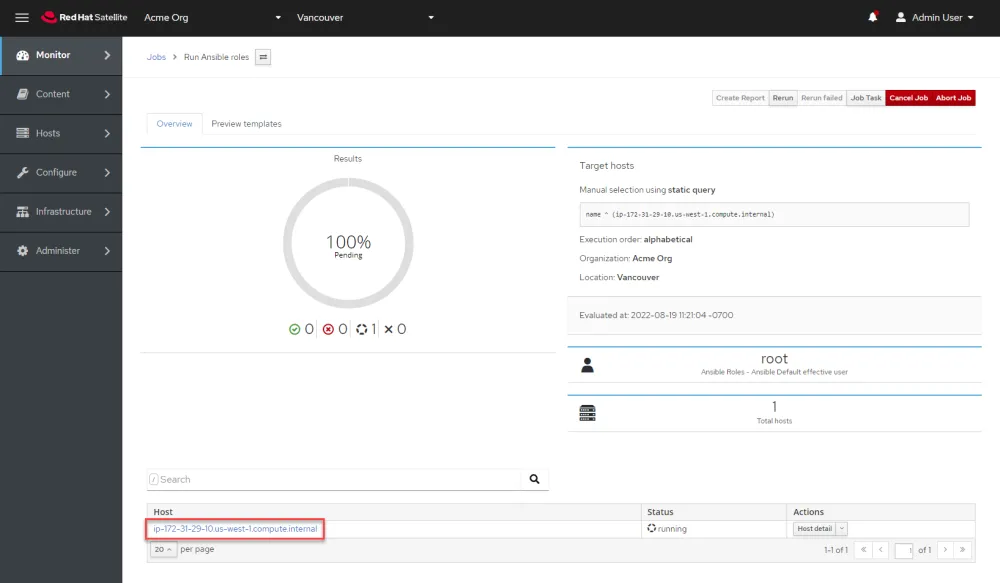
Here you can see each task in the job being executed.

Note: The Ansible role synchronizes the required content, creates host groups and activation keys, among other tasks. Satellite 6.11 has a bug where the activation key created to register CentOS 7 hosts, "Convert2RHEL7" enables the Convert2RHEL8 repository. To work around this bug, you must override this repo in the "convert2rhel_centos7" activation key.

Run the conversion
IMPORTANT: Before running the conversion, the candidate hosts must be up to date and rebooted with the latest kernel.
First, we’ll need to register our hosts to be converted. In this case I am converting CentOS7 hosts. Click on Hosts > Register Host.

On my test CentOS hosts, I have not copied the certificate authority files from the Satellite server. You can learn more about how to do this here.
In the register host menu, select 1) "CentOS 7 converting" host group, then 2) "Insecure", then 3) "Advanced". The "Insecure" option enables the script to run at first without verifying the self-signed certificate. Subsequent communication is fully secured. If you would like to avoid using the "Insecure" method, read more about importing certificates here.

Next, click on "Advanced".
Perform the following tasks in the "Advanced" context of the "Register Host" menu.
-
Check that the "Activation Keys" is inherited from the host group "convert2rhel_centos7". You should not have to click on anything here.
-
Click on "Generate". This will generate the curl script you will copy and paste into the CLI of the CentOS host.
-
Click on the copy button to copy the curl script.

Now log into one of your candidate hosts. Export the correct locale of your host.
export LANG=en_US.UTF-8
Paste the curl script and run it. Here’s some example output.
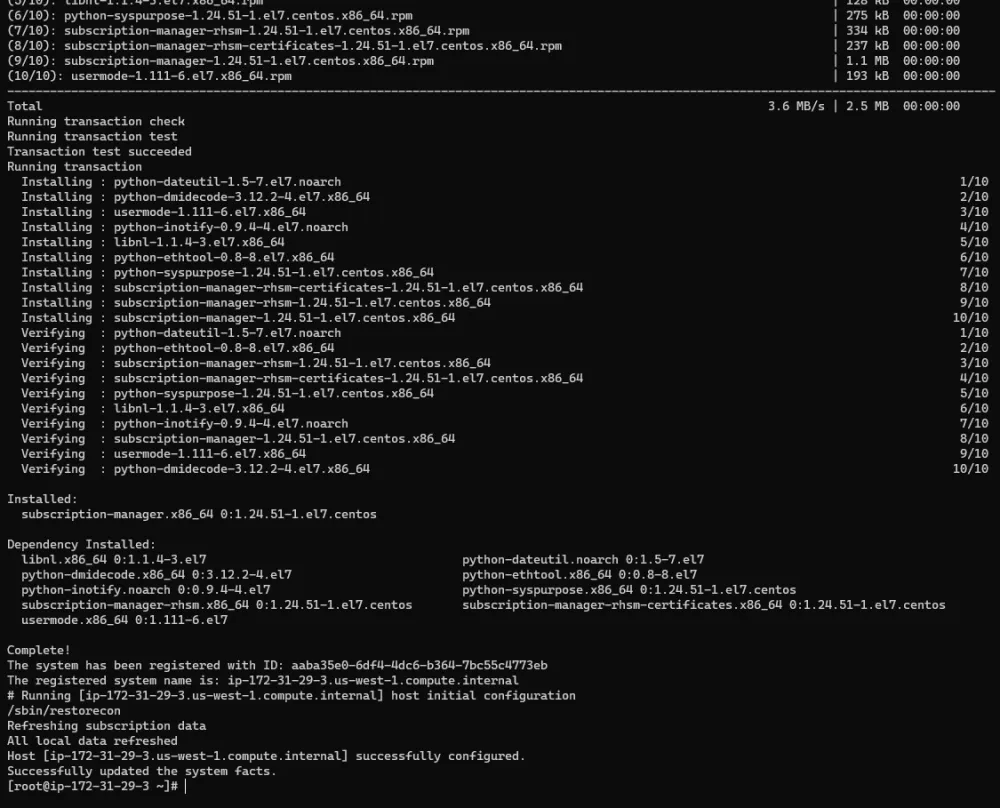
Repeat this task for all your candidate hosts.
In the Hosts menu, you see all your CentOS hosts registered to Satellite.
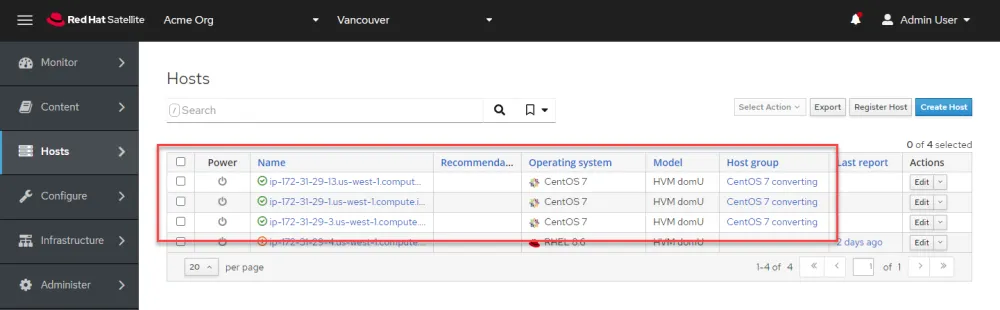
To start the Convert2RHEL operation, perform the following tasks.
-
Select the candidate hosts.
-
Click on "Select Action" and select "Schedule Remote Job".

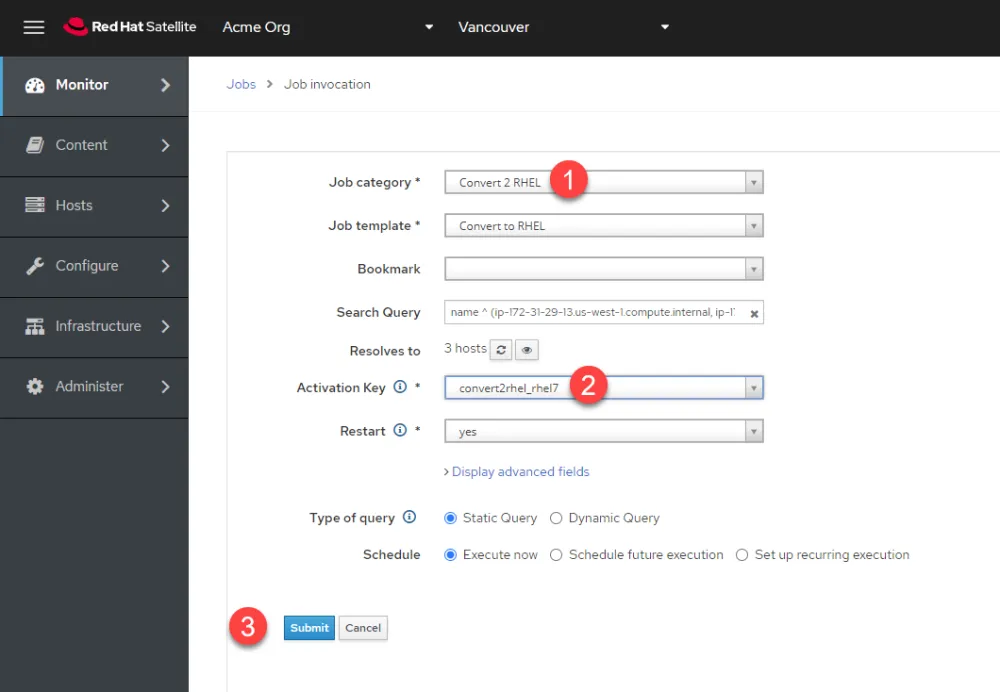
In the Job invocation menu, perform the following tasks.
-
In the "Job category" dropdown, select "Convert 2 RHEL".
-
In the "Activation Key" dropdown, select "convert2rhel_rhel7".
-
Click "Submit" to start the bulk Convert2RHEL operation.
You’ll be redirected to the "Job Overview" menu where you can choose to view the real-time status of the job on each host by clicking on the host.

Here’s the real-time view of the job.

The final result, all hosts converted to RHEL at once!

For more information, please refer to the official Convert2RHEL documentation here.
About the author
As a Senior Principal Technical Marketing Manager in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux business unit, Matthew Yee is here to help everyone understand what our products do. He joined Red Hat in 2021 and is based in Vancouver, Canada.
More like this
IT automation with agentic AI: Introducing the MCP server for Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
How Banco do Brasil uses hyperautomation and platform engineering to drive efficiency
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
You Can't Automate The Fire | Code Comments
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
