Automating repeatable tasks is a core part of a sysadmin's daily routine. Increasingly, this automation involves interacting with web-based APIs to orchestrate activities across devices, cloud providers, or software-as-a-service (SaaS) tools. You must thoroughly test your code, whether you're writing shell scripts or Ansible playbooks that interact with web services.
The ability to mock an API is an important part of this testing process. A mock API mimics a real API, allowing you to develop and test your API interactions. While some tools and vendors provide live sandbox environments, being able to mock an API locally is useful for advanced testing scenarios, such as modifying a response's body or HTTP status code. If you are in the initial stages of developing your own API, you also want a quick way to build endpoints before writing code.
One option for doing so is Mockoon. Mockoon is a wonderful open source tool with a rich user interface for quickly building mock APIs and running them on your local machine.
Install Mockoon
You can install Mockoon on Windows, macOS, and Linux via official packages, including AppImage and RPM formats. Once Mockoon is installed, the official documentation has an excellent tutorial for new users.
[ Learn your options by downloading this guide to installing applications on Linux. ]
Mockoon features both a graphical interface and a command-line interface (CLI) utility, and this article focuses on using the graphical interface.
Create an environment
The first step when working with a new project in Mockoon is to create a new environment. Environments allow you to separate your API endpoints into logical groups. Each environment can also run on its own port, enabling you to mock multiple APIs on the same host. Environments are saved as JSON files, and they can be easily imported, exported, and saved alongside your code.
An environment is created by clicking the New environment icon shown below. It will prompt you for a location to save the environment's JSON file. Once you create the environment, you can begin adding routes to it.

Add a basic API route
Most API interactions involve a simple request-and-response cycle, which often returns a JSON object. Setting up a simple API route is also the easiest way to get started with Mockoon. Add routes to an environment by clicking the + sign in the interface.
I added a route at /api/v1/healthcheck that returns a 200 OK status code, as you can see in the example below. This example also returns a JSON response that contains information about the healthcheck:

Once you add the route and start the server (or restart, if it is already running), the endpoint is accessible:
Generate random response data
Static values in an API response body cover many basic testing use cases. However, Mockoon can also generate random data in a response body for more realistic testing. The Faker.js library generates random data. The randomly generated values can be templated within a response body and returned to the requestor.
[ Free eBook: Manage your Linux environment for success. ]
In the example below, I've added another endpoint: /api/v1/hosts/:id. The :id indicates that this is a URL parameter. The response body returns a JSON object containing several fields with randomly generated data.

With this configuration, each call to the API endpoint reveals a different set of fake data:
Caution: The version of Faker.js implemented by Mockoon may not be the latest, so always ensure that you are looking at the correct version of the Faker documentation when writing templates.
Add authentication and rules
Most API endpoints require authentication, often in the form of an HTTP header that contains an API token. Ensuring that your tools can properly handle authentication failure from an endpoint is important for developing robust automation. Mockoon allows you to define rules, such as header requirements, that you can use to return different responses.
Rules are defined on the Rules tab for a route. The example below extends the /api/v1/hosts/:id endpoint with two rules. The first rule (Response 1) returns an HTTP 401 Unauthorized. The first rule is used if no other rules match a request.
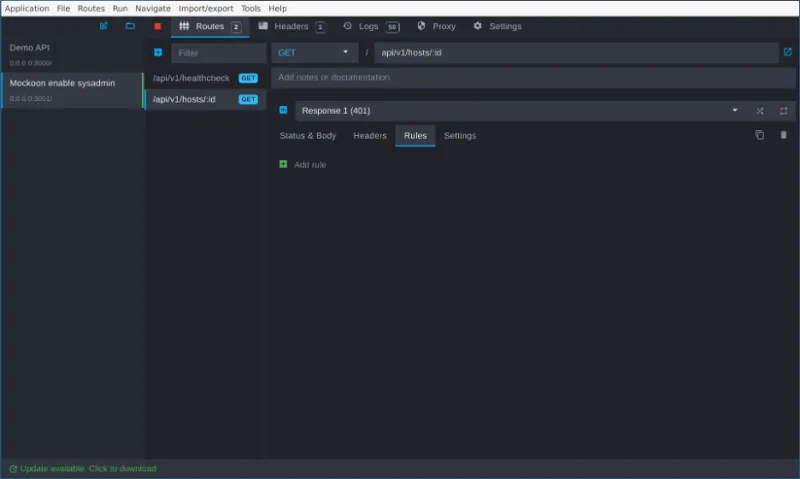
The second rule (Response 2) requires that a request contain the X-Auth-Token HTTP header with a value equal to 40650a76. Any request that matches this rule will receive a 200 OK and the JSON response from the previous example.

These rules cause any request that does not contain the correct value in the X-Auth-Token header to fail with an HTTP 401 Unauthorized. Requests that have the correct token will continue to receive data, as shown below:
This is a basic example of using rules to control response behavior based on request attributes.
Mockoon's rule engine is powerful and capable of creating very advanced scenarios, and it can be best understood by reviewing the official documentation.
Wrap up
Mockoon provides a simple and powerful way to locally mock API responses. This article shows how to create basic responses with static and dynamic data and how response rules can be leveraged to return different responses based on request attributes. It barely scratches the surface of Mockoon's capabilities, and I encourage you to look at Mockoon's website to learn more.
About the author
Anthony Critelli is a Linux systems engineer with interests in automation, containerization, tracing, and performance. He started his professional career as a network engineer and eventually made the switch to the Linux systems side of IT. He holds a B.S. and an M.S. from the Rochester Institute of Technology.
More like this
Manage clusters and applications at scale with Argo CD Agent on Red Hat OpenShift GitOps
Data-driven automation with Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
Creating JavaScript | Command Line Heroes
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
