This is the second post of our blog series on Red Hat OpenShift and Splunk Integration. In the first post, we showed how to send application and system logs to Splunk. The second part is focused on how to use Splunk Kubernetes Objects.
Prerequisites
The prerequisites are the same as defined in the first part.
Architecture
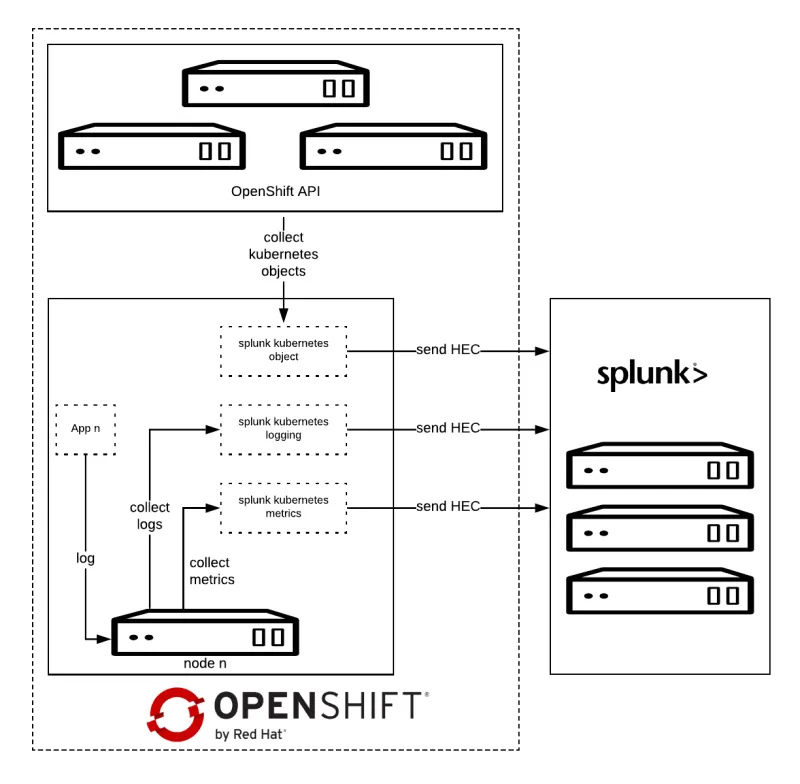
Splunk Connect for Kubernetes deploys:
- One DaemonSet on each OpenShift node for collecting log.
- One DaemonSet on each OpenShift node for collecting metrics.
- One Deployment to collect OpenShift Objects changes.
Installation
Before starting, please make sure you have already configured the Splunk Connect project as described in the first part.
Download the latest Helm Splunk Connect Helm package, which at the time of writing is 1.2.0.
wget <a href="https://github.com/splunk/splunk-connect-for-kubernetes/releases/download/1.1.0/splunk-kubernetes-objects-1.1.0.tgz">https://github.com/splunk/splunk-connect-for-kubernetes/releases/download/1.2.0/splunk-kubernetes-objects-1.2.0.tgz</a>
Download the source code as well; it is necessary to setup fine-grained permission.
wget https://github.com/splunk/splunk-connect-for-kubernetes/archive/1.2.0.zip
unzip 1.2.0.zip
cd splunk-connect-for-kubernetes-1.2.0/
Configure the variables for Helm; you can find sample values for the Splunk Connect on GitHub:
Minimal value example:
global:
splunk:
hec:
host: splunk.openlab.red
port: 8080
token: xxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxx-xxxxxxxxx
protocol: https
rbac:
create: false
Splunk Kubernetes Objects
Splunk Kubernetes Objects collect Kubernetes objects that can help users access cluster status. Splunk collects the object data by calling the Kubernetes API. This supports two modes:
- Watch mode: the Kubernetes API sends new changes to the plugin. In this mode, only the changed data is collected.
- Pull mode: the plugin queries the Kubernetes API periodically. In this mode, all data is collected.
Setup
1: Assign cluster-reader permission.
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user cluster-reader -z splunk-kubernetes-objects --rolebinding-name=splunk-kubernetes-objects
Or Add fine-grained permission, check objects clusterRole manifests.
oc apply -f manifests/splunk-kubernetes-objects/clusterRole.yaml
oc adm policy add-cluster-role-to-user splunk-kubernetes-objects -z splunk-kubernetes-objects --rolebinding-name=splunk-kubernetes-objects
2: Install Helm package.
helm install --tiller-namespace=splunk-connect --name splunk-kubernetes-objects -f objects-value.yml splunk-kubernetes-objects-1.2.0.tgz
Verify on Splunk
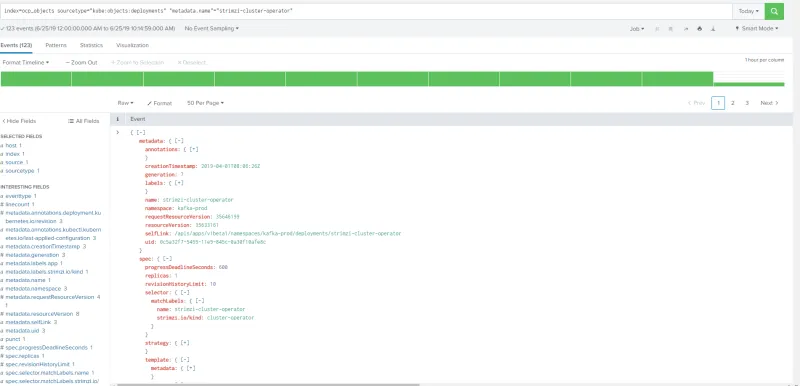
Conclusion
In this article we have explored how we can capture and send to Splunk the entire definition of Kubernetes objects, once they get created or modified.
In the next post will see how to collect OpenShift/Kubernetes metrics to Splunk.
執筆者紹介
チャンネル別に見る
自動化
テクノロジー、チームおよび環境に関する IT 自動化の最新情報
AI (人工知能)
お客様が AI ワークロードをどこでも自由に実行することを可能にするプラットフォームについてのアップデート
オープン・ハイブリッドクラウド
ハイブリッドクラウドで柔軟に未来を築く方法をご確認ください。
セキュリティ
環境やテクノロジー全体に及ぶリスクを軽減する方法に関する最新情報
エッジコンピューティング
エッジでの運用を単純化するプラットフォームのアップデート
インフラストラクチャ
世界有数のエンタープライズ向け Linux プラットフォームの最新情報
アプリケーション
アプリケーションの最も困難な課題に対する Red Hat ソリューションの詳細
仮想化
オンプレミスまたは複数クラウドでのワークロードに対応するエンタープライズ仮想化の将来についてご覧ください
