Tracking and controlling activities across a large environment is challenging in any IT environment. Adding requirements like HIPAA compliance makes life even more challenging for IT teams, and takes time away from addressing higher-level business problems. In this post, we'll look at how teams can use OpenSCAP in Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) to help with Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) compliance and focus on work that delivers real value for the business.
Meet OpenSCAP in RHEL 8.3
Delivering a more secure platform has been front-and-center for RHEL since its first releases. When it comes to security, timely inspection to identify vulnerabilities is critical for Red Hat customers. They are frequently looking for tools to evaluate and improve the security of their environments quickly.
OpenSCAP, included in your RHEL subscription, can perform compliance and vulnerability scanning on RHEL systems and help teams identify and remediate problems as they crop up. OpenSCAP is a SCAP compliant scanner. SCAP scanners are driven by several different industry policies, profiles, and rules. The SCAP Security guide has content that is Red Hat’s interpretation of the policies, rules, and related Ansible playbooks for remediation to facilitate automation of configuration and auditing. In RHEL 8.3, we added support for the Center for Internet Security (CIS) and the HIPAA benchmarks.
Although there is a bit of overlap between the security controls that cover HIPAA and those that cover CIS, when you pull back the curtain, these compliance regulations are different in the way they are implemented. HIPAA is a subjective standard that is very focused on policies, training, and processes. This means that HIPAA does not precisely define the technical specifications or methods needed to achieve compliance. Instead, a consensus-driven approach is used to map security checks to various HIPAA requirements. Some of the key elements of HIPAA include enabling the audit service, disabling root login using SSH, and enabling FIPS mode.
On the other hand, CIS provides prescriptive guidance to establish a security baseline configuration, including detailed recommendations for auditing, logging, monitoring, identity management, and access control. This post’s focus will be on HIPAA compliance in RHEL 8.3, and if you’d like to learn more about CIS, check the following post about OpenSCAP and CIS.
The OpenSCAP ecosystem is rich, offering multiple tools to assist administrators and auditors in assessing, measuring, and enforcing security baselines. Several hardening guides and configuration baselines are developed by the open-source community, allowing you to choose a security policy that best suits your organization’s needs, regardless of its size.
In RHEL 8.3, here are the key steps to scan against the HIPAA profile:
# yum install openscap-scanner scap-security-guide # oscap xccdf eval --fetch-remote-resources --profile xccdf_org.ssgproject.content_profile_hipaa --results /tmp/scan.xml /usr/share/xml/scap/ssg/content/ssg-rhel8-ds.xml # oscap xccdf generate report /tmp/scan.xml > /tmp/report.html
OpenSCAP scans the system against the HIPAA profile and saves the result in the /tmp/scan.xml file.
Being compliant from the get-go
In some scenarios, it might be essential to be compliant right from when the system is first installed. With RHEL’s installer (based on Anaconda), you can dynamically feed the security policy into the installation process, helping the system be compliant from the very first boot.
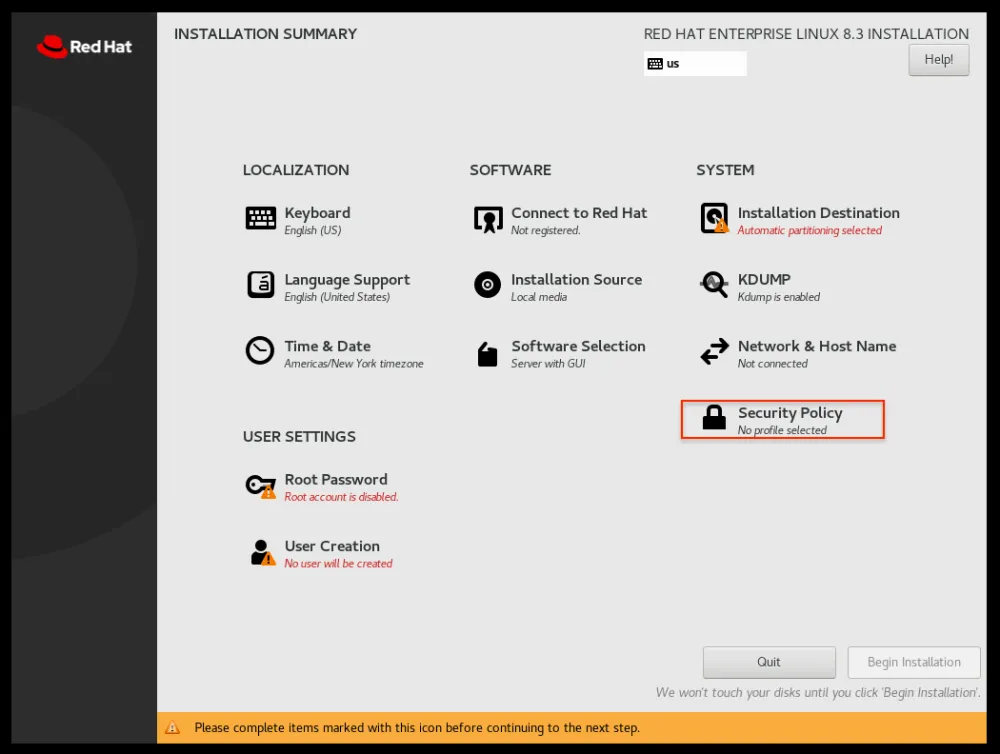 Setting this up is pretty simple — before you begin the installation, you select “Security Policy” in the installation wizard and then pick the “HIPAA” profile.
Setting this up is pretty simple — before you begin the installation, you select “Security Policy” in the installation wizard and then pick the “HIPAA” profile. 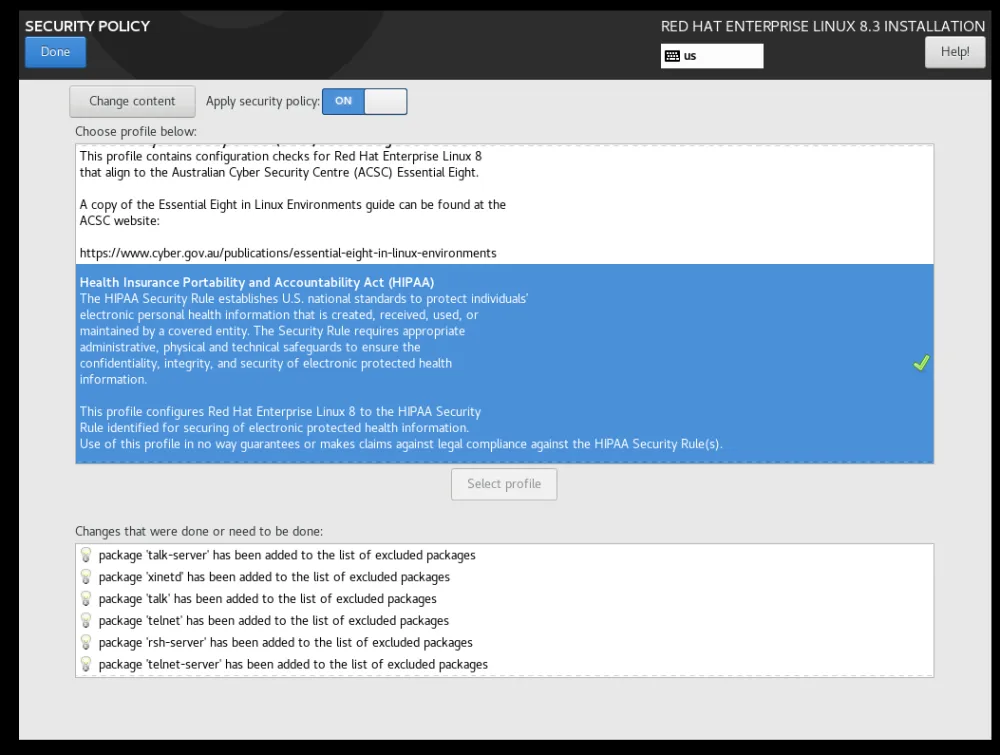
Automating your scans to help remain compliant
We understand that scanning for a compliance standard is not just a one-off task. You need to scan your systems regularly to ensure that you are maintaining compliance with the standard. Any deviation from the policy will need to be remediated.
With OpenSCAP and Red Hat automation platform, you can take control of your organization’s exposure by automating security scans and compliance at scale in hybrid environments. This means that you can use OpenSCAP using several products in Red Hat’s Management portfolio, including Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform, Red Hat Smart Management with Satellite, and Red Hat Insights to scan across your deployment portfolio.
Want to try OpenSCAP in Red Hat Enterprise Linux? Check out our live demo here.執筆者紹介
Don Pinto is a Technical Product Marketing Manager at Red Hat focused on helping customers understand why Red Hat Enterprise Linux is an ideal operating system platform for modern application workloads. Pinto is passionate about data management and operating systems, having authored several technical blogs and white papers on various tech topics. Pinto holds a Masters degree in Computer Science and a Bachelor's degree in Computer Engineering from the University of Toronto, Canada.
John Spinks is a Senior Principal Technical Marketing Manager for Red Hat. He acts as a subject matter expert for Red Hat Management products including Satellite and Insights. Previous experience includes almost 10 years as a Technical Marketing Engineer for NetApp in RTP, NC.
Marek Haičman is a Product Owner of the Security Compliance subsystem, dealing mostly with the SCAP ecosystem shipped with RHEL. He started at Red Hat as a Quality Engineer. He later exchanged catching bugs for features, priorities and deadlines, while still preserving quality and user experience as the guiding principle of his work. When not dealing with compliance, he enjoys preparing cocktails for his friends and reading thought-provoking sci-fi stories.
Alan Scott is a Chief Architect, specializing in solutions for our healthcare customers.
類似検索
Red Hat to acquire Chatterbox Labs: Frequently Asked Questions
From incident responder to security steward: My journey to understanding Red Hat's open approach to vulnerability management
What Is Product Security? | Compiler
Technically Speaking | Security for the AI supply chain
チャンネル別に見る
自動化
テクノロジー、チームおよび環境に関する IT 自動化の最新情報
AI (人工知能)
お客様が AI ワークロードをどこでも自由に実行することを可能にするプラットフォームについてのアップデート
オープン・ハイブリッドクラウド
ハイブリッドクラウドで柔軟に未来を築く方法をご確認ください。
セキュリティ
環境やテクノロジー全体に及ぶリスクを軽減する方法に関する最新情報
エッジコンピューティング
エッジでの運用を単純化するプラットフォームのアップデート
インフラストラクチャ
世界有数のエンタープライズ向け Linux プラットフォームの最新情報
アプリケーション
アプリケーションの最も困難な課題に対する Red Hat ソリューションの詳細
仮想化
オンプレミスまたは複数クラウドでのワークロードに対応するエンタープライズ仮想化の将来についてご覧ください



