 This is a guest post from Redis Labs. Vick Kelkar is a Global Technology Manager on Partnerships team at Redis Labs. In the last few years, he has focused on developing product and partnerships for microservice and platforms like OpenShift, PCF, PKS, Docker, and Kubernetes.
This is a guest post from Redis Labs. Vick Kelkar is a Global Technology Manager on Partnerships team at Redis Labs. In the last few years, he has focused on developing product and partnerships for microservice and platforms like OpenShift, PCF, PKS, Docker, and Kubernetes.
During the last few releases of Kubernetes, the Kubernetes community has managed to optimize the running of stateful applications by releasing new core primitives. For instance, the general availability of StatefulSet allows users to run stateful applications like databases on a Kubernetes and or Red Hat OpenShift cluster. OpenShift, Red Hat’s enterprise distribution of Kubernetes, has also introduced persistent volumes, which allow users to persist data across pod and/or service restarts. The introduction of the new core primitives allows OpenShift users to bring different application workloads onto a single OpenShift cluster. However, running complex use cases and or stateful applications via the built-in Kubernetes primitives continues to be a challenge.
Enter the Operator Framework
This is where the Kubernetes Operators come into the picture. Operators allow users to extend the Kubernetes primitives using custom resources and custom controllers. In May 2018, Red Hat released the Operator SDK as part of the Operator Framework. The Operator Framework essentially focuses on deploying and managing a stateful application by extending the Kubernetes application programming interfaces (APIs). The Operator SDK allows an application developer, such as a database vendor, to embed the domain-specific logic into the operator and extend the Kubernetes API. Red Hat has also included a few custom resources and operators in OpenShift release 3.11.
Why an Operator?
Operators are becoming a standard way of deploying complex stateful applications in Kubernetes. Redis Labs adopted the Operator Framework to enable our users to more efficiently deploy and manage the lifecycle of their Redis Enterprise clusters. The Operator Framework allowed us to introduce a Custom Resource Definition (CRD) called redisenterprisecluster or rec. The custom controller, which is a Redis Enterprise operator written in the Go programming language, allows us to embed application-specific lifecycle management logic into the operator. Using the operator, we are able to validate the state of the Redis Enterprise cluster.
OpenShift Specific Features
We take advantage of the multi-tenancy features offered by projects in the OpenShift platform and use the security context constraint it provides. We have published our sample security context constraint (SCC) deployment files for the OpenShift platform. Additionally, our Redis Enterprise and operator images are in Red Hat’s OpenShift container registry.
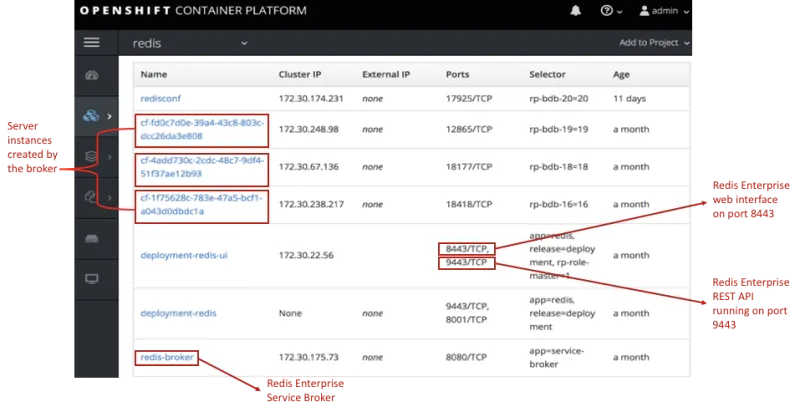 Figure 1: Redis Enterprise on the OpenShift container platform
Figure 1: Redis Enterprise on the OpenShift container platform
Since adopting the Operator Framework, we continued to work with Red Hat to continually improve and enhance solutions like an ingress controller, which we currently plan to integrate with the OpenShift router.
Resources:
- Download the Operator-based deployment files for OpenShift here
- Learn How to Install Redis Enterprise Clusters Using Operators on OpenShift here
- Learn More about the Operator Framework here
- Find more Community Operators here
If you have any further questions, please don’t hesitate to contact one of our Redis experts.
執筆者紹介
Red Hatter since 2018, technology historian and founder of The Museum of Art and Digital Entertainment. Two decades of journalism mixed with technology expertise, storytelling and oodles of computing experience from inception to ewaste recycling. I have taught or had my work used in classes at USF, SFSU, AAU, UC Law Hastings and Harvard Law.
I have worked with the EFF, Stanford, MIT, and Archive.org to brief the US Copyright Office and change US copyright law. We won multiple exemptions to the DMCA, accepted and implemented by the Librarian of Congress. My writings have appeared in Wired, Bloomberg, Make Magazine, SD Times, The Austin American Statesman, The Atlanta Journal Constitution and many other outlets.
I have been written about by the Wall Street Journal, The Washington Post, Wired and The Atlantic. I have been called "The Gertrude Stein of Video Games," an honor I accept, as I live less than a mile from her childhood home in Oakland, CA. I was project lead on the first successful institutional preservation and rebooting of the first massively multiplayer game, Habitat, for the C64, from 1986: https://neohabitat.org . I've consulted and collaborated with the NY MOMA, the Oakland Museum of California, Cisco, Semtech, Twilio, Game Developers Conference, NGNX, the Anti-Defamation League, the Library of Congress and the Oakland Public Library System on projects, contracts, and exhibitions.
類似検索
Ford's keyless strategy for managing 200+ Red Hat OpenShift clusters
F5 BIG-IP Virtual Edition is now validated for Red Hat OpenShift Virtualization
Can Kubernetes Help People Find Love? | Compiler
Scaling For Complexity With Container Adoption | Code Comments
チャンネル別に見る
自動化
テクノロジー、チームおよび環境に関する IT 自動化の最新情報
AI (人工知能)
お客様が AI ワークロードをどこでも自由に実行することを可能にするプラットフォームについてのアップデート
オープン・ハイブリッドクラウド
ハイブリッドクラウドで柔軟に未来を築く方法をご確認ください。
セキュリティ
環境やテクノロジー全体に及ぶリスクを軽減する方法に関する最新情報
エッジコンピューティング
エッジでの運用を単純化するプラットフォームのアップデート
インフラストラクチャ
世界有数のエンタープライズ向け Linux プラットフォームの最新情報
アプリケーション
アプリケーションの最も困難な課題に対する Red Hat ソリューションの詳細
仮想化
オンプレミスまたは複数クラウドでのワークロードに対応するエンタープライズ仮想化の将来についてご覧ください
