Living on the far edge
The edge can be a wild place. It's where the physical world tightly meets the digital world, and it's where the most innovative and cutting-edge applications are being built. But the edge is also a challenging place, with limited resources, minimal environments, and often unreliable connectivity.
To thrive on the edge, businesses need solutions that are lightweight, resilient, and flexible while still easy to manage. That's where Red Hat Device Edge comes in.
Red Hat Device Edge is a new modular edge computing solution designed to help businesses overcome the challenges at the farthest reaches of the edge. It enables them to build and deploy innovative applications while accommodating the constraints of small, low-power, or resource constrained hardware, thanks to its lightweight,low-resource footprint.
It's resilient and supports a stronger security profile, even in harsh and unpredictable environments. It's also easy to configure and manage so that organizations can focus on developing workloads without worrying about the environment where they will run.
In this article, we take a closer look at Red Hat Device Edge and see how it can help businesses thrive on the edge.
Introducing Red Hat Device Edge
Red Hat Device Edge is a modular solution based on a proven and reliable OS, Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL), that also delivers an enterprise-ready and supported distribution of the Red Hat-led open source community project, MicroShift. MicroShift is a lightweight Kubernetes container orchestration solution built from the edge capabilities of Red Hat OpenShift.
Purpose-built for resource-constrained devices, Red Hat Device Edge utilizes Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform for consistent Day 1 and Day 2 management of hundreds to thousands of sites and devices. Users choose what to deploy and when, ensuring the necessary resources are deployed to process workloads and support the underlying platform.
Red Hat Device Edge delivers:
- A minimal footprint that supports the deployment of workloads on small, resource-constrained devices in challenging environments by prioritizing system resources for workloads thanks to tailored system images that can be built minimizing unnecessary components.
- A consistent operational experience from small edge devices all the way to large IT systems in the datacenter and cloud.
- Simplified management to deploy on baremetal, virtual or containerized workloads with ease.
- Proven Red Hat support including documentation, solutions and the expertise of Red Hat’s professional services.
- Versatility for a variety of edge use cases, including industrial automation, retail, healthcare, telecommunications, transportation, smart cities and more.
What's in Red Hat Device Edge?
Red Hat Enterprise Linux
RHEL is the foundation at the edge for enterprise-grade Linux, and it comes with relevant features that make it ideal for edge use cases. In fact, it leverages rpm-ostree and implements the concept of immutability, and efficient atomic over-the-air updates to boost consistency,
Using RHEL Image Builder, it is possible to create a bootable installer or working virtual machine (VM)/Instance image with only the packages and configurations that are needed, bringing your devices up to speed in minutes.
Device onboarding and provisioning, even in disconnected environments, can be performed at scale using the simplified installation. RHEL can use the FIDO Device Onboarding (FDO) specification to streamline and scale the onboarding process for newly provisioned devices.
On top of the setup process, due to the immutable nature of RHEL, updates are optimized for over-the-air delivery, transferring the minimum possible amount of data to perform ad hoc updates of consolidated baselines, just for the bits and pieces that are changed on the devices. Image updates are applied in a mirrored space on the edge device to retain the previous working image. When systems are rebooted to the new updated image, a health check mechanism implemented with Greenboot, can perform an automatic rollback of the configuration easily reverting the changes if things are not working as expected, keeping the system operational and reducing the need to send resources to get it back online.
Red Hat's build of MicroShift
On top of RHEL, the solution includes the option to deploy MicroShift, a lightweight CNCF-certified Kubernetes solution with the minimal set of components that are needed to spin up run and orchestrate applications taking advantage of the flexibility and consistency of a single platform.
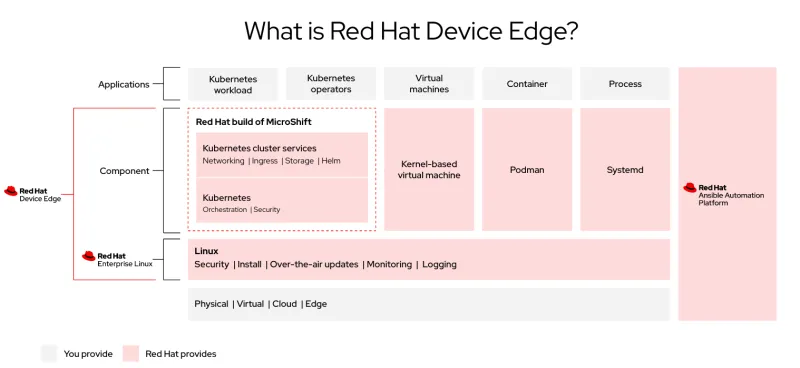
Despite its low-resource footprint, MicroShift comes with all the features that applications need to be fully operational:
- Networking: MicroShift comes with container networking capabilities as well as an ingress controller to manage the exposure of the services inside the cluster and to the outside world.
- Storage: Leveraging Logical Volume Management CSI, MicroShift can provide persistent storage to stateful workloads deployed on it, including volume snapshots and thin provisioning.
- Application deployment: MicroShift supports deploying applications using standard Kubernetes deployment resources and also advanced templating using Helm.
- Container orchestration: All Kubernetes APIs are available in MicroShift, which relies on cri-o as container runtime.
In addition, MicroShift can be embedded into a RHEL image to automate the deployment process and onboarding.
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
As the number of edge devices expands, so does the complexity of managing and orchestrating the entire infrastructure that is needed. Automation becomes a key factor in scaling and simplifying the processes needed to maintain such a sprawling infrastructure.
This is where the power and flexibility of Ansible Automation Platform comes in, together with the Ansible validated collections, to automate the creation, management and deployment of RHEL-built images, including RHEL and optionally MicroShift for edge installers, to any device. Combined with the added value that an enterprise-grade automation platform can provide to organizations, Red Hat Device Edge configures as the turnkey solution for managing devices at the edge.
Conclusion
Red Hat Device Edge is a new and innovative edge computing solution designed to help organizations develop and deploy innovative edge applications, manage devices at scale, and provide a solid and robust foundation, even in complex edge scenarios.
Red Hat Device Edge is lightweight, resilient, easy to use and manage, and is supported by Red Hat. If you are looking for an edge computing solution, Red Hat Device Edge is one to consider.
Additional resources:
About the author
Alessandro Rossi is an EMEA Senior Specialist Solution Architect for Red Hat Enterprise Linux with a passion for cloud platforms and automation.
Alessandro joined Red Hat in 2021, but he's been working in the Linux and open source ecosystem since 2012. He's done instructing and consulting for Red Hat and delivered training on Red Hat Enterprise Linux, Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform and Red Hat OpenShift, and has supported companies during solutions implementation.
More like this
Deterministic performance with Red Hat Enterprise Linux for industrial edge
Red Hat Enterprise Linux delivers deterministic performance for industrial TSN
Edge IT: A space odyssey | Technically Speaking
A vested interest in 5G | Technically Speaking
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
