One of the biggest concerns companies running SAP have is minimizing the time SAP applications are unavailable. “Near zero downtime” may be a familiar expression in the IT world—namely in the SAP field—but it is usually sneered as being impossible.
In addition, SAP host maintenance tends to be very inflexible. As a result, it is very common to find customers frequently putting off version upgrades and operating with SAP servers that are quite outdated.
But what if I told you that by running your SAP ecosystem on a Red Hat platform, you can complete a maintenance activity on SAP hosts without chucking users out of the system at any time or cancelling background jobs that are running in the SAP applications? This post will walk you through some of the tools that can be used to keep your SAP estate up-to-date while avoiding service outages.
Fear of downtime can lead to inflexible maintenance windows
Companies need to be compliant with many recommendations from SAP and the operating system (OS) vendor, which makes it important to keep the hosts where these workloads run up-to-date.
IT teams, however, get pushed back frequently from updating the SAP systems since the business cannot afford having them down. As a result, the maintenance windows that are agreed for the interventions tend to be scarce and quite short, making it challenging for the SAP Basis, OS and Infrastructure teams to finish the interventions properly and in time.
Adding to this, maintenance windows often take place outside business hours (at least for production systems), forcing IT teams to spend their free time rushing around trying to get the SAP systems back up and running, with the new updates applied, before the clock strikes the end of the maintenance window.
For these reasons, it is very common to find customers with SAP servers putting off version upgrades (of OS) until their current ones become unsupported.
All this gives us an idea of how inflexible the maintenance of SAP hosts tends to be.
Achieving near zero downtime
How do you plan for a version upgrade while navigating these downtime concerns? The core of this platform is the Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) for SAP Solutions subscription.
Apart from the OS, RHEL for SAP Solutions also provides the Red Hat High Availability Add-On and Red Hat Satellite. It also comes with Red Hat Insights, which detects and makes it possible to remediate potential issues before they occur. These are some of the components that will be used in the solution we will be exploring.
The remaining piece of the puzzle that orchestrates the whole update process is the Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform. Its integration with RHEL for SAP Solutions rounds up to a complete, robust and easy to manage platform for SAP workloads.
This implementation can be deployed anywhere regardless of where the SAP servers reside, on-premise or in the cloud (public, private or hybrid). It can also be in the same datacenter(s) where the SAP servers are, or in different locations as we can see in Figure 1.
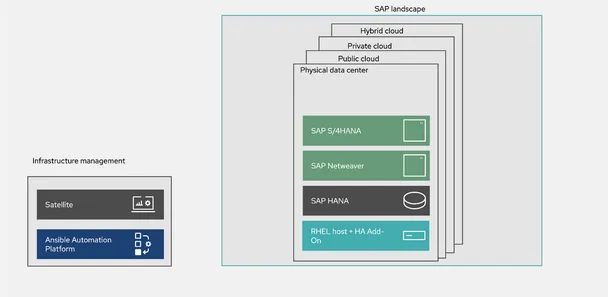
Fig. 1. Logical design
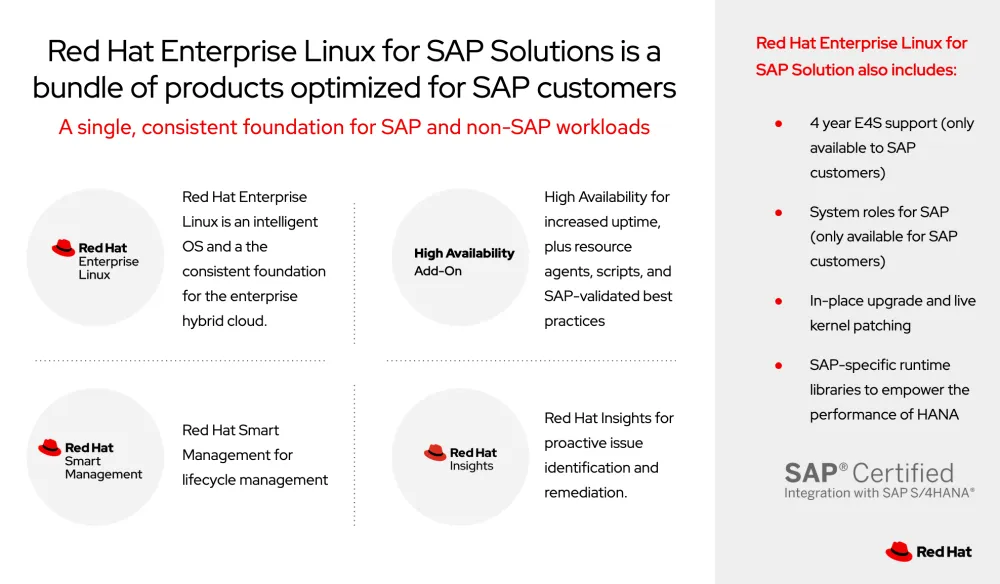
Fig. 2 Components of Red Hat for SAP Solutions
Let’s have a closer look at the different parts of this solution.
Red Hat Satellite
Red Hat Satellite manages the life cycle of the SAP hosts and makes sure there is consistency across the SAP estate, with the same level of patches, security fixes, etc., in all the servers.
It takes care of the following aspects:
Content Management: It uses a content repository which is curated prior to its distribution to hosts.
Patch Management: Satellite reports on hosts that need patches, fixes or enhancements and applies them automatically when approved.
Provision Management: It provisions to bare metal, private, public and hybrid clouds and uses Ansible roles to automate post-provisioning steps.
Subscription Management: Manages centrally the subscriptions of all the SAP hosts and keeps track of their subscription consumption.
Red Hat High Availability Add-On
Red Hat High Availability Add-On makes the creation of clusters possible on both the database and the application side. It features lock management, cluster management, fencing mechanisms (STONITH and SBD) and specific resources for ASCS and ERS instances and for all the SAP supported databases, namely for SAP HANA which is the one used in this solution.
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform is the component that orchestrates the solution using Ansible playbooks that will automate the whole process of the maintenance (OS kernel upgrade, OS parameter change, package update, security fix application, SAP HANA revision update, SAP HANA parameter change, SAP kernel upgrade, etc.).
It is also the central point from where all the SAP estate can be managed following the Infrastructure as Code approach, with inventories for the different types of servers, departments in the company, etc., and adding a very granular layer of security with Role-Based Access Control (RBAC).
Implementation of the solution
All the SAP hosts need to run on RHEL and be registered with the RHEL for SAP Solutions subscription as mentioned earlier. All of them are connected to Satellite and to the Ansible Automation Platform.
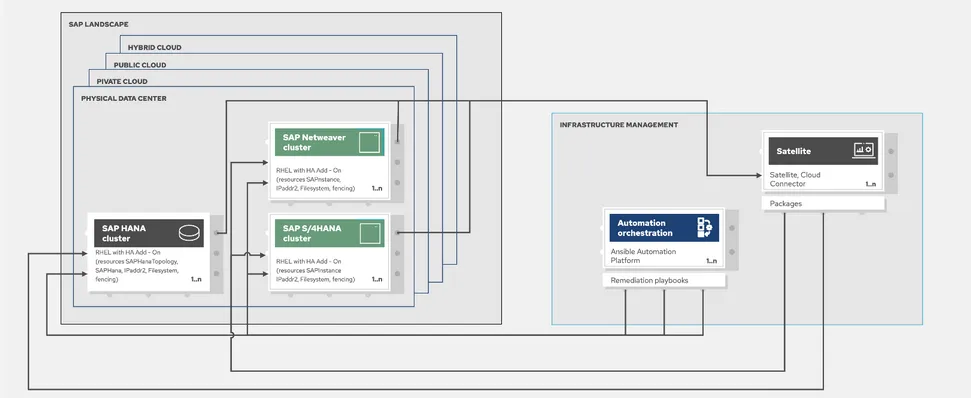
Fig. 3. Solution implementation with data flow
This solution uses the high availability capabilities of SAP HANA System Replication, but since this does not provide for automatic failover of resources, a Pacemaker cluster is implemented to have a replica of the database (DB). This makes it so that at any moment the application servers will be connected to a running instance of the SAP HANA DB and that they can continue to work without interruptions.
Ansible Automation Platform will orchestrate the entire process, triggering the failover of the cluster resources to the node that is not being upgraded and also launching the update tasks in the target servers.
For purely OS-related interventions like an OS version upgrade, security fixes or errata applications, Satellite will be the main actor doing the patching, conducted by Ansible, which will trigger the execution.
In the case of a SAP HANA upgrade, a change in the DB or OS parameters or a SAP kernel update, the intervention will be done with Ansible playbooks created for these purposes instead of by Satellite.
And this is how the solution works (we have taken the example of a SAP Netweaver or SAP S/4HANA with a SAP HANA scale-up implementation using SAP HANA System Replication and considered a maintenance on the SAP HANA hosts) :
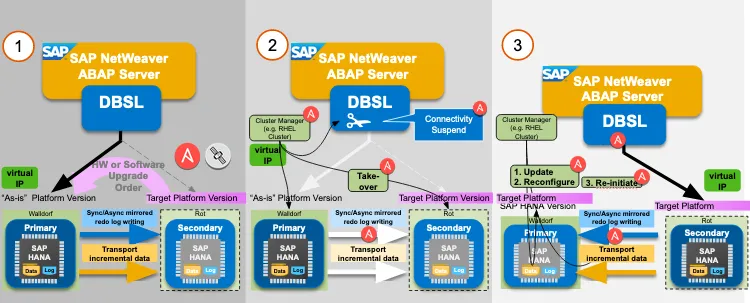
Fig. 4. Steps of the process
The virtual IP resource of the cluster that is used for the application to connect to the DB is pointing initially to the primary SAP HANA node. Ansible Automation Platform triggers the intervention from Satellite (or the playbook to perform the intervention itself if it is not one of the interventions that Satellite does) on the secondary SAP HANA node.
Once the intervention is finished on the secondary SAP HANA node, Ansible Automation Platform triggers the failover of the virtual IP resource of the cluster so that it will now point to the node that has been maintained. It will also promote the SAP HANA DB in this node to primary and will revert the direction of the SAP HANA System Replication. Using the connectivity suspend feature introduced in SAP Netweaver 7.40 SP 5 (see this SAP OSS Note,) the users will not perceive any disconnection while the cluster resources are failed over and promoted/demoted.
Ansible Automation Platform triggers the maintenance on the former primary SAP HANA node. After it is finished we can either revert to the initial situation failing back the resources or maintain the current one.
Summary
The Red Hat platform for SAP workloads, constituted by RHEL for SAP Solutions and Ansible Automation Platform, minimizes the impact that interventions in the SAP hosts have on the availability of the applications.
To recap, the Red Hat platform for SAP automates the failover of the resources as well as the upgrade or patching processes. This minimizes manual intervention, helping eliminate human error and ensuring smooth and successful maintenance.
This solution makes it possible to keep the SAP estate always up to date and compliant with SAP’s and Red Hat’s recommendations, helping the IT teams earn the trust of the business so that agreeing on interventions will not be a difficult struggle anymore.
For more information on the RHEL for SAP Solutions subscription, we invite you to read The Business Value of Red Hat’s Open Source Solutions for SAP Workloads.
If you are interested in more solutions built with these and other products of the Red Hat's portfolio visit the Portfolio Architecture website.
About the author
Ricardo Garcia Cavero joined Red Hat in October 2019 as a Senior Architect focused on SAP. In this role, he developed solutions with Red Hat's portfolio to help customers in their SAP journey. Cavero now works for as a Principal Portfolio Architect for the Portfolio Architecture team.
More like this
How llm-d brings critical resource optimization with SoftBank’s AI-RAN orchestrator
Building the foundation for an AI-driven, sovereign future with Red Hat partners
You Can’t Automate Expectations | Code Comments
You Can’t Automate Collaboration | Code Comments
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
