You're tasked with bringing AI into your organization, but the journey from a proof-of-concept to a production-ready application is often a maze of fragmented tools and complex integrations, especially for agentic AI use cases. The real challenge isn't just the technology—it's building an AI strategy that is scalable, reliable, and manageable.
Standardization is a primary factor in meeting this challenge, primarily by reducing complexity and increasing efficiency. By combining Model Context Protocol (MCP) and Llama Stack on a platform like Red Hat OpenShift AI, you can create a unified and portable environment for your AI applications.
OpenShift AI can also support the integration of any other agentic frameworks and components you like, including tools like LangChain, LangGraph, and CrewAI, among others. Red Hat's approach can help simplify development, streamline operations, and give your enterprise the tools it needs to empower your multiple teams, like AI developers and data scientists to turn your AI vision into a reality within a trusted and consistent environment.
Understanding the building blocks of an intelligent agent
To build resilient AI-enabled applications, you need a foundation that enables intelligent agents to access and use your enterprise's specific tools and data. This requires 2 key components: a standardized way to expose your services and a unified framework for interacting with them.
This is the essence of agentic AI, where an autonomous system can determine the best course of action and tools needed to achieve a goal. The combination of MCP and Llama Stack provides the framework for these agents to operate effectively.
MCP is an open protocol that standardizes how your AI systems integrate with external tools and data sources. It has been described as being a "USB-C port for AI applications." Just as USB-C allows you to plug in any compatible device—a monitor, a hard drive, or a keyboard—an MCP server exposes your organization's services in a standardized format.
An AI agent can then plug in to this server to discover and use available tools, whether they are a database, a customer relationship management (CRM) system, or an internal API. This protocol provides a structured way for AI agents to connect with services, making it easy for them to get the information they need to carry out tasks.
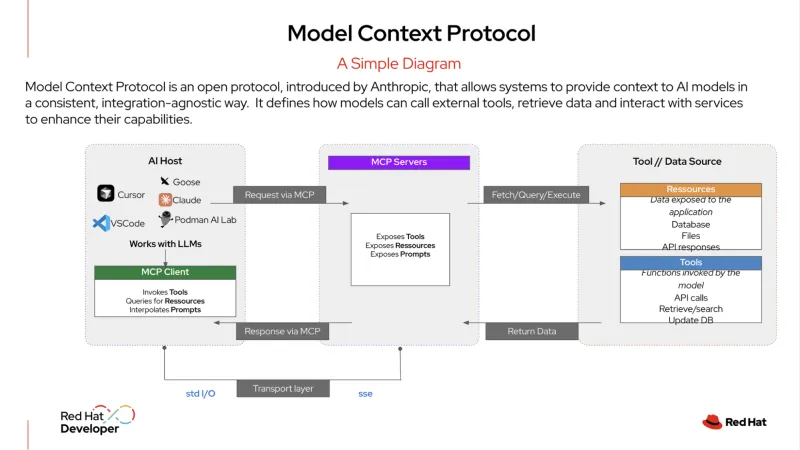
Llama Stack is an open source framework that provides a unified, API-driven approach for building and deploying generative AI (gen AI) applications. It provides a consistent and portable way to abstract away the complexities of AI development and deployment and includes a suite of enterprise tools such as APIs for inference, retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), and AI agents. It also provides built-in components for safety, evaluation, and observability, helping organizations create production-ready AI applications that are both reliable and scalable.
An example of agentic AI in action
In enterprise IT, agentic AI can handle complex, multistep workflows that require dynamic decision-making. As an example, instead of a simple one-to-one request-and-response, a more sophisticated agent can act as an autonomous service desk manager, resolving issues with minimal human intervention.
Here is an example of what that kind of agent might do when a user submits a ticket for a "service outage":
- Llama Stack receives the initial ticket. The system receives the user's report of a service outage and categorizes it as a high-priority incident.
- The agent uses MCP and formulates a plan. The agent uses the MCP to identify and discover the relevant tools it has access to—such as a monitoring service, a log analysis tool, and a runbook automation system. With this context from the MCP, the agent formulates a multistep plan to investigate and resolve the issue.
- The agent executes the plan using MCP to communicate with the discovered tools.
- It first uses a monitoring tool to check the status of relevant services and dependencies.
- It then calls a log analysis tool to review recent logs for a related application or a Red Hat OpenShift container, searching for errors.
- Once a potential issue is identified (e.g., a pod is crashing), it uses a diagnostic tool to pinpoint the underlying problem, such as a misconfigured network policy or a full disk.
- The agent takes corrective action. Based on the diagnosis, it uses MCP to call a pre-approved remediation script to restart the pod and clear the disk space. It then re-checks the service status to confirm the issue is resolved.
- The agent communicates the outcome. It uses an internal tool to update the ticket status to "resolved," including a summary of the actions taken. It then drafts a message to the user, explaining the problem and confirming that the service is back online, all without a single human touchpoint.
By using the MCP to orchestrate these actions, the agent is able to operate as an autonomous and self-contained service desk, reducing the manual burden on IT teams giving them time to focus on more strategic initiatives.
A streamlined approach for development and production
The combination of Llama Stack and MCP significantly improves the developer experience. Instead of building for a specific, monolithic stack, your developers can use a standardized layer of abstraction through a single API. This enables a powerful "inner loop" development methodology, where they can build and test their AI applications on a local machine using a single SDK.
Because the APIs are consistent and the services are discovered through a standardized protocol, your developers can have confidence that their application will work exactly the same way when it is deployed to an enterprise-grade platform.
This portability is vital in the fast-moving AI environment. A developer can build their application to use one model today and, if a new model emerges that is better or more cost-effective, they can switch to it without having to rewrite their code. This reduces development time and effort, accelerates innovation, and provides a clear pathway for moving from development to production.
Gaining operational consistency for AI workloads
For your operations teams, managing a diverse array of AI models and services can be a major source of complexity. However, by running a standardized AI stack tailored for your organization on a platform like OpenShift AI, you gain a centralized and consistent environment.
OpenShift AI provides a comprehensive, trusted platform for deploying and serving LLMs and running the necessary databases for RAG applications. It also allows your teams to take advantage of their existing microservice architectures and connect to internal systems smoothly.
Your operations teams can also use their standard GitOps processes to deploy and manage these AI applications. This means the same workflows used for traditional cloud-native applications can be applied to AI workloads, simplifying management and maintenance at scale. It creates a simplified journey from development to production and provides operational consistency across your hybrid cloud environments.
By combining the power of open source technologies like Llama Stack and MCP—and by enabling the integration of other agentic AI frameworks such as LangChain, Haystack, LlamaIndex, and PydanticAI, among others—Red Hat AI provides a reliable foundation for building, deploying, and managing AI applications across your entire hybrid cloud.
Learn more
Ready to get started? Learn more about Red Hat AI through our product trials, consulting services, training and certification, and more.
Resource
The adaptable enterprise: Why AI readiness is disruption readiness
About the authors
Younes Ben Brahim is a Principal Product Marketing Manager at Red Hat, focusing on the strategic positioning and market adoption of Red Hat's AI platform offerings. Younes has spent over 15 years in the IT industry leading product marketing initiatives, managing product lifecycles for HPC & AI, and delivering consulting services.
Prior to Red Hat, he has worked with companies like NetApp, Dimension Data, and Cisco Systems, providing technical solutions and product strategy for enterprise infrastructure and software projects.
Carlos Condado is a Senior Product Marketing Manager for Red Hat AI. He helps organizations navigate the path from AI experimentation to enterprise-scale deployment by guiding the adoption of MLOps practices and integration of AI models into existing hybrid cloud infrastructures. As part of the Red Hat AI team, he works across engineering, product, and go-to-market functions to help shape strategy, messaging, and customer enablement around Red Hat’s open, flexible, and consistent AI portfolio.
With a diverse background spanning data analytics, integration, cybersecurity, and AI, Carlos brings a cross-functional perspective to emerging technologies. He is passionate about technological innovations and helping enterprises unlock the value of their data and gain a competitive advantage through scalable, production-ready AI solutions.
Will McGrath is a Senior Principal Product Marketing Manager at Red Hat. He is responsible for marketing strategy, developing content, and driving marketing initiatives for Red Hat OpenShift AI. He has more than 30 years of experience in the IT industry. Before Red Hat, Will worked for 12 years as strategic alliances manager for media and entertainment technology partners.
Roberto is a Principal AI Architect working in the AI Business Unit specializing in Container Orchestration Platforms (OpenShift & Kubernetes), AI/ML, DevSecOps, and CI/CD. With over 10 years of experience in system administration, cloud infrastructure, and AI/ML, he holds two MSc degrees in Telco Engineering and AI/ML.
Cedric Clyburn (@cedricclyburn), Senior Developer Advocate at Red Hat, is an enthusiastic software technologist with a background in Kubernetes, DevOps, and container tools. He has experience speaking and organizing conferences including DevNexus, WeAreDevelopers, The Linux Foundation, KCD NYC, and more. Cedric loves all things open-source, and works to make developer's lives easier! Based out of New York.
More like this
Fast and simple AI deployment on Intel Xeon with Red Hat OpenShift
Cracking the inference code: 3 proven strategies for high-performance AI
Technically Speaking | Build a production-ready AI toolbox
Technically Speaking | Platform engineering for AI agents
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds





