Overview
An artificial intelligence (AI) platform is an integrated collection of technologies to develop, train, and run machine learning models. This typically includes automation capabilities, machine learning operations (MLOps), predictive data analytics, and more. Think of it like a workbench–it lays out all of the tools you have to work with and provides a stable foundation on which to build and refine.
There is a growing number of options when it comes to choosing an AI platform and getting started. Here’s what to look for and the top considerations to keep in mind.
Types of AI platforms
The first AI platform decision facing any organization is whether to buy one that’s pre-configured or build a custom platform in-house.
Buy an AI platform
If you’re interested in rapidly deploying AI applications, models, and algorithms, buying a comprehensive pre-configured AI platform is the best option. These platforms come with tools, language repositories, and APIs that are tested ahead of time for security and performance. Some vendors offer pre-trained foundation and generative AI models. Support and onboarding resources help them fit smoothly into your existing environments and workflows.
Popular cloud providers are expanding their portfolios with AI platforms, including Amazon Web Services (AWS) Sagemaker, Google Cloud AI Platform, Microsoft Azure AI Platform, and IBM’s watsonx.ai™ AI studio. In many cases, AI platform providers also offer standalone AI tools that can be partnered and integrated with other AI solutions.
Build an AI platform
To meet specific use cases or advanced privacy needs, some organizations need to fully customize and manage their own AI platform. Uber, for example, developed a custom AI platform that uses technologies like natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision to improve their GPS and crash detection capabilities. Syapse, a data-focused healthcare company, created Syapse Raydar®, an AI-powered data platform that translates oncology data into actionable insights.
Building an AI platform offers full control over the environment and allows you to iterate in line with your business’s specific needs. However, this approach requires more upfront work to get a platform up and running. Maintenance, support, and management cannot be outsourced.
Go open source
Open source communities are driving advancements in artificial intelligence and machine learning. Choosing an open source software solution as the foundation for your AI initiatives means you can rely on a community of peers and practitioners who are constantly improving the frameworks and tools you use the most. Many organizations start with open source tooling and build out from there. Tensorflow and PyTorch are open source platforms that provide libraries and frameworks for developing AI applications.
State of platform engineering in the age of AI
Capabilities to look for in an AI platform
MLOps
Machine learning operations (MLOps) is a set of workflow practices aiming to streamline the process of deploying and maintaining ML models. An AI platform should support MLOps phases like model training, serving, and monitoring.
Large language model operations (LLMOps) is a subset of MLOps that focuses on the practices, techniques and tools used for the operational management of large language models in production environments. LLMs can perform tasks such as generating text, summarizing content, and categorizing information, but they draw significant computational resources from GPUs, meaning that your AI platform needs to be powerful enough to accommodate and support LLM inputs and outputs.
Generative AI
Generative AI relies on neural networks and deep learning models trained on large data sets to create new content. Given sufficient training, the model is able to apply learning from training and apply it to real-world situations, which is called AI inference.
Generative AI encompasses many of the functions that end-users associate with artificial intelligence such as text and image generation, data augmentation, conversational AI such as chatbots, and more. It is important that your AI platform supports generative AI capabilities with speed and accuracy.
Scalability
Models can only be successful if they scale. In order to scale, data science teams need a centralized solution from which to build and deploy AI models, experiment and fine tune, and work with other teams. All of this demands huge amounts of data and computing power, and most importantly, a platform that can handle it all.
Once your models are successful, you’ll want to reproduce them in different environments–on premise, in public cloud platforms, and at the edge. A scalable solution will be able to support deployment across all of these footprints.
Automation
As your organization goes from having a handful of models you want to roll into production to a dozen or more, you'll need to look into automation. Automating your data science pipelines allows you to turn your most successful processes into repeatable operations. This not only speeds up your workflows but results in better, more predictable experiences for users and improved scalability. This also eliminates repetitive tasks and frees up time for data scientists and engineers to innovate, iterate, and refine.
Tools and integrations
Developers and data scientists rely on tools and integrations to build applications and models and deploy them efficiently. Your AI platform needs to support the tools, languages, and repositories your teams already use while integrating with your entire tech stack and partner solutions.
Security and regulation
Mitigate risk and protect your data by establishing strong security practices alongside your AI platform. Throughout the day-to-day operations of training, developing, it’s critical to scan for common vulnerabilities and exposures (CVEs) and establish operational protection for applications and data through access management, network segmentation, and encryption.
Responsibility and governance
Your AI platform must also allow you to use and monitor data in a way that upholds ethical standards and avoids compliance breaches. In order to protect both your organization’s data and user data, it’s important to choose a platform that supports visibility, tracking, and risk management strategies throughout the ML lifecycle. The platform must also meet your organization’s existing data compliance and security standards.
Support
One of the most important benefits of a pre-configured, end-to-end AI platform is the support that comes with it. Your models will perform better with the help of continuous bug tracking and remediation that scales across deployments. Some AI platform providers offer onboarding and training resources to help your teams get started quickly. Those opting to build their own platform with open source tooling may want to consider choosing vendors who provide support for machine learning feature sets and infrastructure.
AI platform use cases
Telecommunications
Comprehensive AI services can streamline different parts of the telecommunications industry, such as network performance optimization and quality enhancement for telecommunications products and services. Applications include improved quality of service, audio/visual enhancements, and churn prevention.
Healthcare
A robust AI platform can usher in transformative benefits in healthcare environments like faster diagnosis, advancements in clinical research, and expanded access to patient services. All of this leads to improved patient outcomes by helping doctors and other medical practitioners deliver more accurate diagnoses and treatment plans.
Manufacturing
Intelligent automation powered by machine learning is transforming manufacturing throughout the supply chain. Industrial robotics and predictive analytics are reducing the burden of repetitive tasks and implementing more effective workflows in real-time.
How Red Hat can help
When it comes to AI platforms, we prioritize building flexible, trusted AI solutions at scale.
Red Hat® AI is our portfolio of AI products built on solutions our customers already trust.
Red Hat AI can help organizations:
- Adopt and innovate with AI quickly.
- Break down the complexities of delivering AI solutions.
- Deploy anywhere.
Scale with flexibility
If you’re ready to scale, our Red Hat AI platform gives developers the tools to build, deploy, and manage AI-enabled applications.
With supported, continuous collaboration, you can customize your AI model applications for your enterprise use cases quickly and simply.
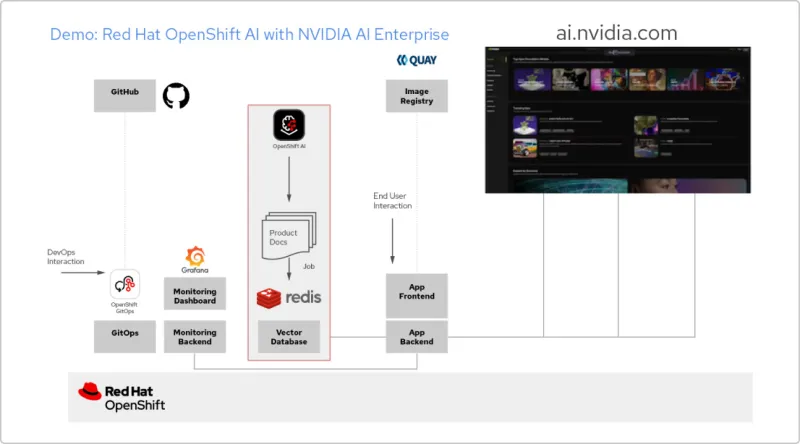
Solution pattern: AI apps with Red Hat & NVIDIA AI Enterprise
Create a RAG application
Red Hat OpenShift AI is a platform for building data science projects and serving AI-enabled applications. You can integrate all the tools you need to support retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), a method for getting AI answers from your own reference documents. When you connect OpenShift AI with NVIDIA AI Enterprise, you can experiment with large language models (LLMs) to find the optimal model for your application.
Build a pipeline for documents
To make use of RAG, you first need to ingest your documents into a vector database. In our example app, we embed a set of product documents in a Redis database. Since these documents change frequently, we can create a pipeline for this process that we’ll run periodically, so we always have the latest versions of the documents.
Browse the LLM catalog
NVIDIA AI Enterprise gives you access to a catalog of different LLMs, so you can try different choices and select the model that delivers the best results. The models are hosted in the NVIDIA API catalog. Once you’ve set up an API token, you can deploy a model using the NVIDIA NIM model serving platform directly from OpenShift AI.
Choose the right model
As you test different LLMs, your users can rate each generated response. You can set up a Grafana monitoring dashboard to compare the ratings, as well as latency and response time for each model. Then you can use that data to choose the best LLM to use in production.
The official Red Hat blog
Get the latest information about our ecosystem of customers, partners, and communities.