最新の AI トレーニング、とくに大規模モデルのトレーニングの場合に、計算能力の規模と厳格なデータプライバシーの遵守が同時に要求されます。従来の機械学習 (ML) では、トレーニングデータを一元化する必要があるため、データのプライバシー、セキュリティー、およびデータの効率/ボリュームに関して大きな課題と労力が生じます。
この課題は、マルチクラウド、ハイブリッドクラウド、およびエッジ環境における異種グローバル・インフラストラクチャ全体で増大するため、組織はデータのプライバシーを保護しながら、既存の分散データセットを使用してモデルをトレーニングする必要があります。
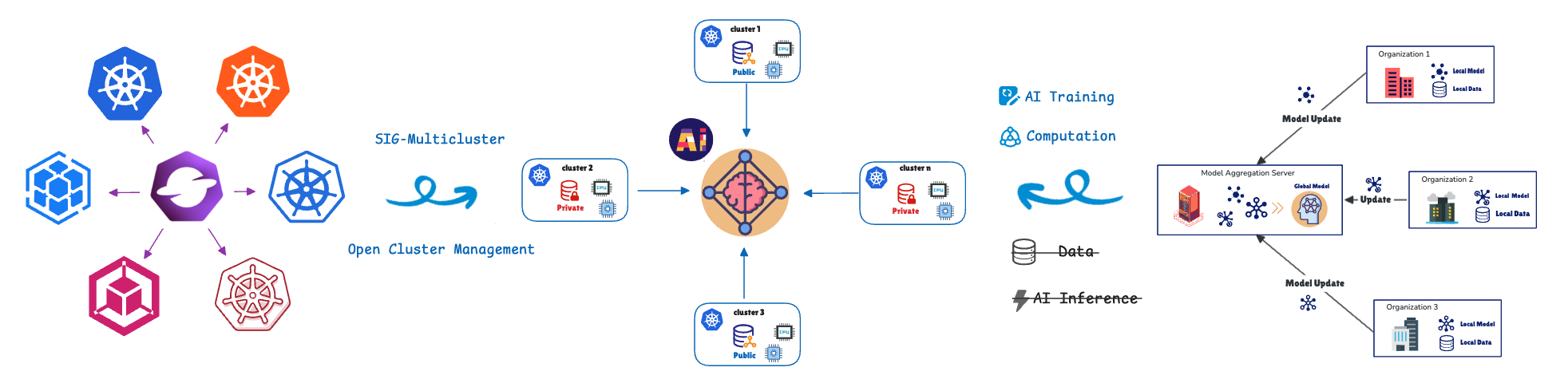
フェデレーテッド・ラーニング (FL) は、モデル・トレーニングをデータに移行することで、この課題に対処します。リモートのクラスタまたはデバイス (コラボレーター/クライアント) は、それらのプライベートデータを使用してローカルでモデルをトレーニングし、中央サーバー (アグリゲーター) にモデルの更新 (未加工データではない) のみを共有します。これにより、エンドツーエンドでデータのプライバシーを保護できます。このアプローチは、医療、小売、産業オートメーション、および高度な運転支援システム (ADAS) と自動運転 (AD) 機能を備えたソフトウェア定義車両 (SDV) (車線逸脱警告、適応型クルーズコントロール、およびドライバー疲労監視など) で見られる、プライバシーに敏感なシナリオや高データ負荷シナリオに不可欠です。
これらの分散コンピューティング・ユニットを管理およびオーケストレーションするために、Open Cluster Management (OCM) のフェデレーテッド・ラーニング・カスタム・リソース定義 (CRD) を利用します。
OCM: 分散運用の基盤
OCM は、Kubernetes マルチクラスタ・オーケストレーション・プラットフォームであり、オープンソースの CNCF Sandbox プロジェクトです。
OCM はハブ・スポーク・アーキテクチャを採用し、プルベース・モデルを使用します。
- ハブクラスタ:オーケストレーションを行う中央コントロールプレーン (OCM Control Plane) として機能します。
- 管理対象 (スポーク) クラスタ:ワークロードがデプロイされるリモートのクラスタです。
管理対象クラスタは、必要な状態をプルし、ステータスをハブに報告します。OCM は、ワークロードのスケジュールを行うために ManifestWork や Placement などの API を提供します。フェデレーテッド・ラーニング API の詳細については後述します。
次に、OCM の分散クラスタ管理の設計が、FL コントリビューターのデプロイメントおよび管理の要件にどのように適合するかを説明します。
ネイティブ統合:FL オーケストレーターとしての OCM
1.アーキテクチャの整合性
OCM と FL の組み合わせは、両者の基本的な構造上の類似性により効果的です。OCM は、両方のシステムが同一の基盤設計 (ハブ・スポーク・アーキテクチャとプルベースのプロトコル) を共有しているため、FL をネイティブにサポートします。

OCM コンポーネント | FL コンポーネント | 機能 |
OCM ハブ・コントロールプレーン | アグリゲーター/サーバー | 状態をオーケストレーションし、モデルの更新を集約します。 |
管理対象クラスタ | コラボレーター/クライアント | 必要な状態/グローバル・モデルをプルし、ローカルでトレーニングし、更新をプッシュします。 |
2.マルチアクター・クライアントの選択のための柔軟な配置
OCM の主要な運用上の利点は、その柔軟なクラスタ間でのスケジューリング機能を利用して、FL セットアップでクライアント選択を自動化できることです。この機能は、OCM Placement API を使用して高度な多基準ポリシーを実装し、効率とプライバシー・コンプライアンスを同時に可能にします。
Placement API により、次の要素に基づいて統合されたクライアント選択が可能になります。
- データの局所性 (プライバシー基準):FL ワークロードは、必要なプライベート・データを持つとする管理対象クラスタにのみスケジュールされます。
- リソースの最適化 (効率性基準):OCM スケジューリング戦略は、複数の要因の組み合わせ評価を可能にする柔軟なポリシーを提供します。データが存在するかどうかだけでなく、CPU/メモリーの可用性などのアドバタイズされた属性に基づいてクラスタを選択します。
3.OCM アドオン登録によるコラボレーターとアグリゲーター間のセキュアな通信
FL アドオン・コラボレーターは管理対象クラスタにデプロイされ、OCM のアドオン登録メカニズムを利用して、ハブ上のアグリゲーターとの保護された暗号化通信を確立します。登録すると、各コラボレーター・アドオンは OCM ハブから証明書を自動的に取得します。これらの証明書は、FL 時に交換されるすべてのモデル更新を認証および暗号化し、複数のクラスタにわたる機密性、整合性、およびプライバシーを確保します。
このプロセスは、AI トレーニングタスクを適切なリソースを持つクラスタにのみ効率的に割り当て、データの局所性とリソース容量の両方に基づいて統合されたクライアント選択を提供します。
FL トレーニングのライフサイクル:OCM 駆動のスケジューリング
複数のクラスタにわたる FL のトレーニング・ライフサイクルを管理するために、専用の Federated Learning Controller が開発されました。コントローラーは CRD を利用してワークフローを定義し、Flower や OpenFL などの一般的な FL ランタイムをサポートします。これは拡張可能です。

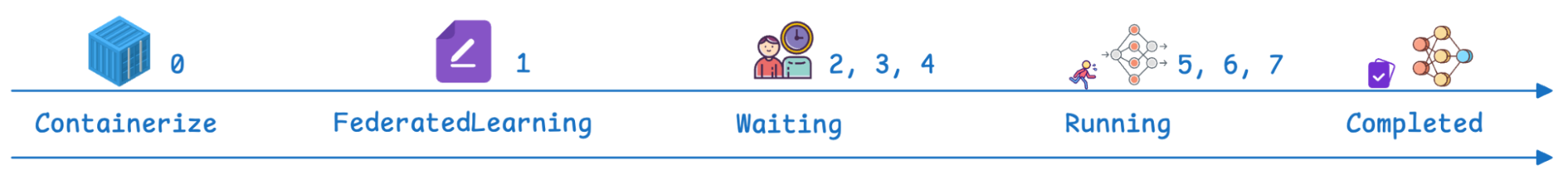
OCM 管理のワークフローは、定義されたステージを通過します。
ステップ | OCM/FL フェーズ | 説明 |
0 | 前提条件 | フェデレーテッド・ラーニング・アドオンがインストールされている。FL アプリケーションは、Kubernetes でデプロイ可能なコンテナとして利用できる。 |
1 | FederatedLearning CR | カスタム・リソースがハブ上に作成され、フレームワーク (例: Flower)、トレーニング・ラウンド数 (各ラウンドはクライアントがローカルでトレーニングし、集計のために更新を返す 1 サイクル)、利用可能なトレーニング・コントリビューターの必要な数、およびモデル・ストレージ構成 (例: PersistentVolumeClaim (PVC) パスの指定) を定義します。 |
2、3、4 | 待機とスケジューリング | リソース・ステータスは「Waiting (待機中)」です。サーバー (アグリゲーター) はハブ上で初期化され、OCM コントローラーは Placement を使用してクライアント (コラボレーター) をスケジュールします。 |
5、6 | 実行中 | ステータスが「Running (実行中)」に変わります。クライアントはグローバル・モデルをプルし、プライベート・データでローカルにモデルをトレーニングし、モデル更新をモデル・アグリゲーターに同期します。トレーニング・ラウンド・パラメーターは、このフェーズが繰り返される頻度を決定します。 |
7 | 完了 | ステータスが「Completed (完了)」になります。 検証は、Jupyter Notebooks をデプロイして、集約されたデータセット全体に対するモデルのパフォーマンスを検証することで実行できます (たとえば、修正された National Institute of Standards and Technology (MNIST) の数字がすべて予測されることを確認します)。 |
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management: FL 環境向けのエンタープライズ管理と運用価値
OCM が提供するコア API とアーキテクチャは、Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management for Kubernetes の基盤として機能します。Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management は、異種インフラストラクチャ・フットプリント全体で同種の FL プラットフォーム (Red Hat OpenShift) のライフサイクル管理を提供します。 Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management で FL コントローラーを実行すると、OCM 単独で提供される以上のメリットが得られます。Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management は、マルチクラスタ資産全体にわたる一元化された可視性、ポリシー駆動型のガバナンス、およびライフサイクル管理を提供し、分散した FL 環境の管理性を大幅に向上させます。
1.可観測性
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management は、分散 FL ワークフロー全体で統合された可観測性を提供し、オペレーターが単一の一貫したインターフェースからトレーニングの進捗状況、クラスタのステータス、およびクラスタ間の連携を監視できるようにします。
2.強化された接続性とセキュリティー
FL CRD は、TLS 対応チャネルを介してアグリゲーターとクライアント間の保護された通信をサポートします。また、LoadBalancer、Route、その他の ingress タイプを含む、NodePort を超える柔軟なネットワーク・オプションも提供し、異種環境全体で保護され、適応性のある接続を提供します。
3.Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management および Red Hat OpenShift AI とのエンドツーエンド ML ライフサイクル統合
Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management と OpenShift AI を活用することで、企業はモデルのプロトタイピングと分散トレーニングから、検証と本番環境へのデプロイメントまで、統合プラットフォーム内で完全な FL ワークフローを構築できます。
まとめ
FL は、モデル・トレーニングをデータに直接移行することで AI を変革し、計算規模、データ転送、および厳格なプライバシー要件の間の摩擦を効果的に解決します。ここでは、Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management が、複雑な分散 Kubernetes 環境を管理するために必要なオーケストレーション、保護、および可観測性をどのように提供するかを説明しました。
フェデレーテッド・ラーニングで組織を強化する方法については、今すぐ Red Hat にお問い合わせください。
リソース
適応力のある企業:AI への対応力が破壊的革新への対応力となる理由
執筆者紹介
Andreas Spanner leads Red Hat’s Cloud Strategy & Digital Transformation efforts across Australia and New Zealand. Spanner has worked on a wide range of initiatives across different industries in Europe, North America and APAC including full-scale ERP migrations, HR, finance and accounting, manufacturing, supply chain logistics transformations and scalable core banking strategies to support regional business growth strategies. He has an engineering degree from the University of Ravensburg, Germany.
Meng Yan is a Senior Software Engineer at Red Hat, specializing in event-driven architectures for multi-cluster management at scale. His research interests focus on agentic AI systems and intelligent automation for software engineering, as well as AI/ML applications in distributed environments such as federated learning and multi-cluster inference.
チャンネル別に見る
自動化
テクノロジー、チームおよび環境に関する IT 自動化の最新情報
AI (人工知能)
お客様が AI ワークロードをどこでも自由に実行することを可能にするプラットフォームについてのアップデート
オープン・ハイブリッドクラウド
ハイブリッドクラウドで柔軟に未来を築く方法をご確認ください。
セキュリティ
環境やテクノロジー全体に及ぶリスクを軽減する方法に関する最新情報
エッジコンピューティング
エッジでの運用を単純化するプラットフォームのアップデート
インフラストラクチャ
世界有数のエンタープライズ向け Linux プラットフォームの最新情報
アプリケーション
アプリケーションの最も困難な課題に対する Red Hat ソリューションの詳細
仮想化
オンプレミスまたは複数クラウドでのワークロードに対応するエンタープライズ仮想化の将来についてご覧ください

