In this installment of our series on setting up Red Hat Satellite for VMware to provision virtual machines (VMs) from Satellite, we are going to work on integrating the VMware resources with Red Hat Satellite.
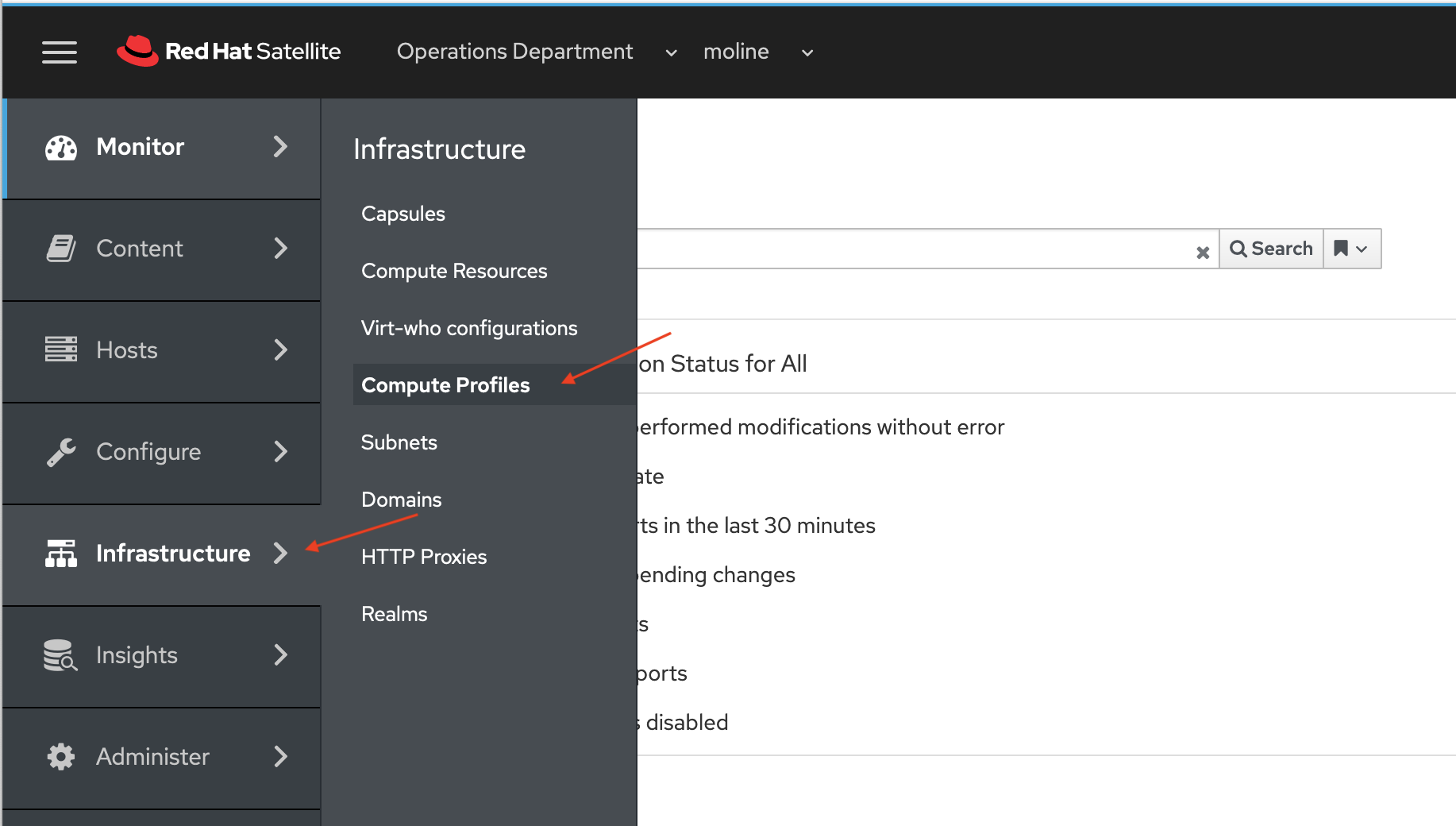
First, we're going to pre-define hardware settings for a virtual machine in Satellite by creating a compute profile. On the Satellite Console chose Infrastructure -> Compute Profiles.
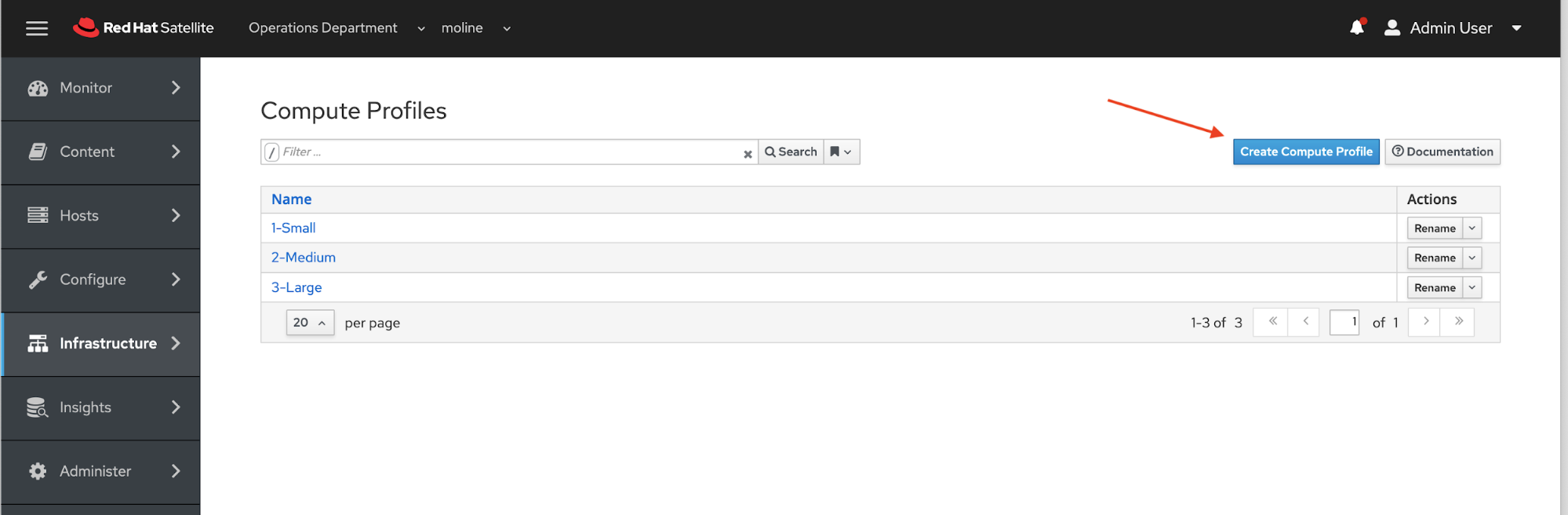
On the Compute Profiles page, click the blue Create Compute Profile button.
On the Compute Profiles > Create Compute Profile, enter cp-vmware-small for the Name and click the blue Submit button.
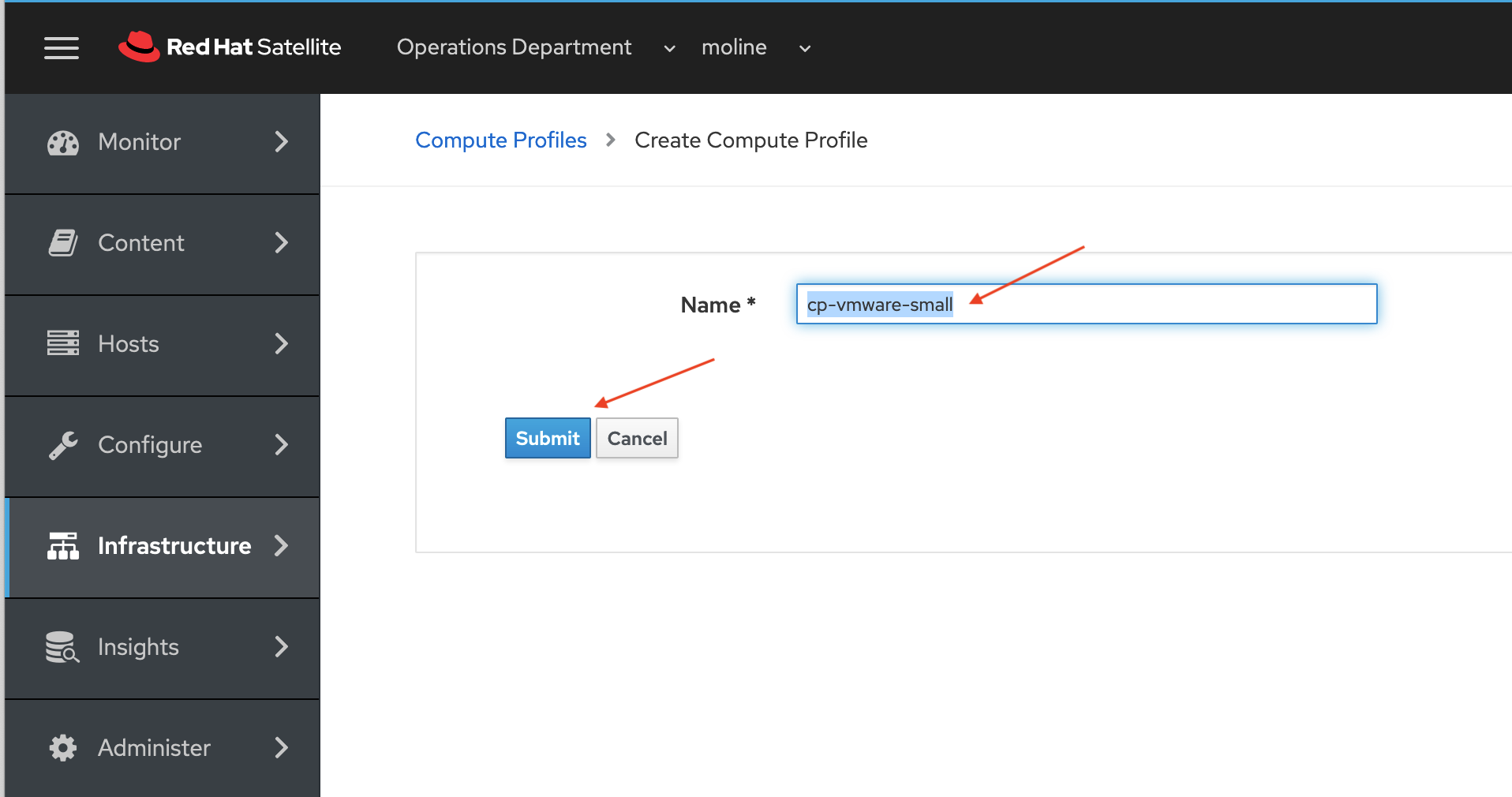
On the Compute Profiles > cp-vmware-small page click the cr-vcenter link to define the new compute profile cp-vmware-small.
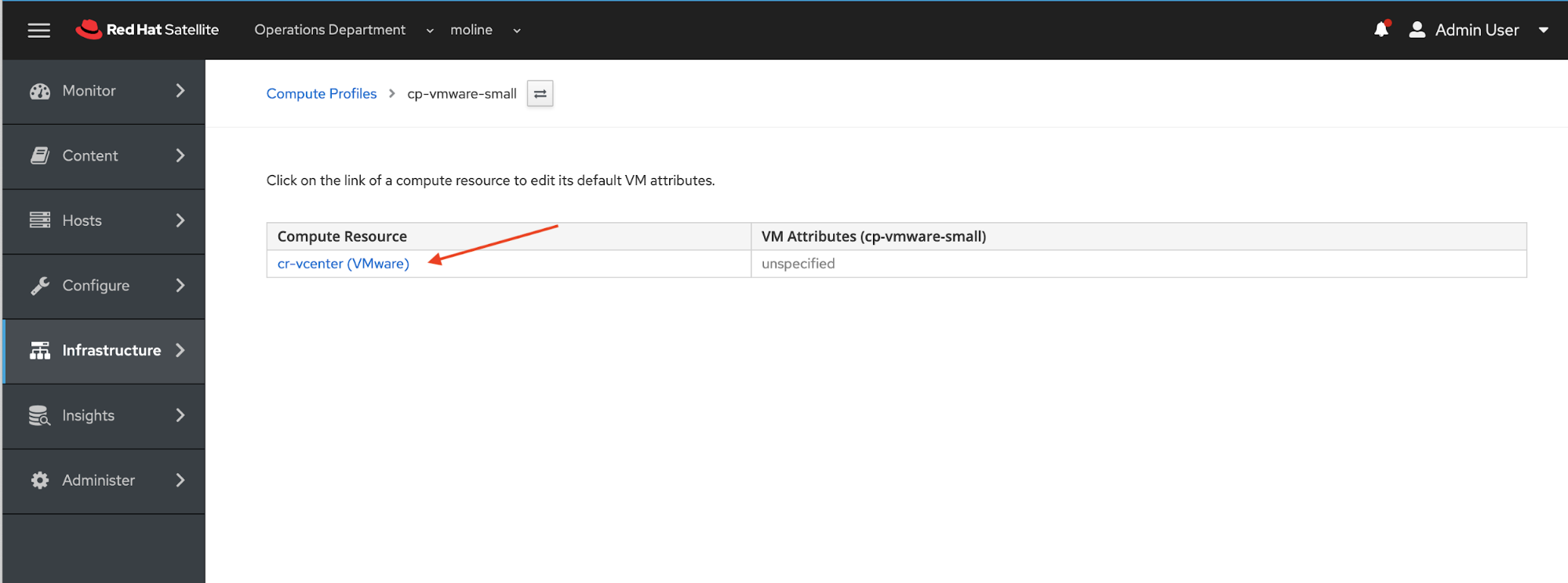
We will now define the configuration of the Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) VM that will be provisioned to VMWare from Satellite. We will mostly accept default values. Configuration changes are listed in the following table.
|
Name |
Value |
|
Cluster |
LabCluster |
|
Guest OS |
Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8 (64 bit) |
|
Virtual H/W version |
14 (EXSi 6.7) |
|
Image |
img-rhel8-prem-server |
|
Create SCSI controller |
VMware Paravirtual |
|
Datastore |
LabDatastore |
|
Size(GB) |
20 GB |
|
Thin Provision |
Uncheck |
|
NIC type |
VNXNET3 |
|
Network |
VM Network |
The next two screenshots show what your configuration should look like. Click the blue Submit button when you have finished with the configuration. You will be returned to the Compute Profiles > cp-vmware-small page.
We will now define a host group within Satellite as a way to bring all these parts together to provision a RHEL 8.3 VM on VMWare.
On the side menu choose Configure -> Host Groups.
On the Host Groups page make sure that you have Operations Department and moline selected for Organization and Location. Click the blue Create Host Group button.
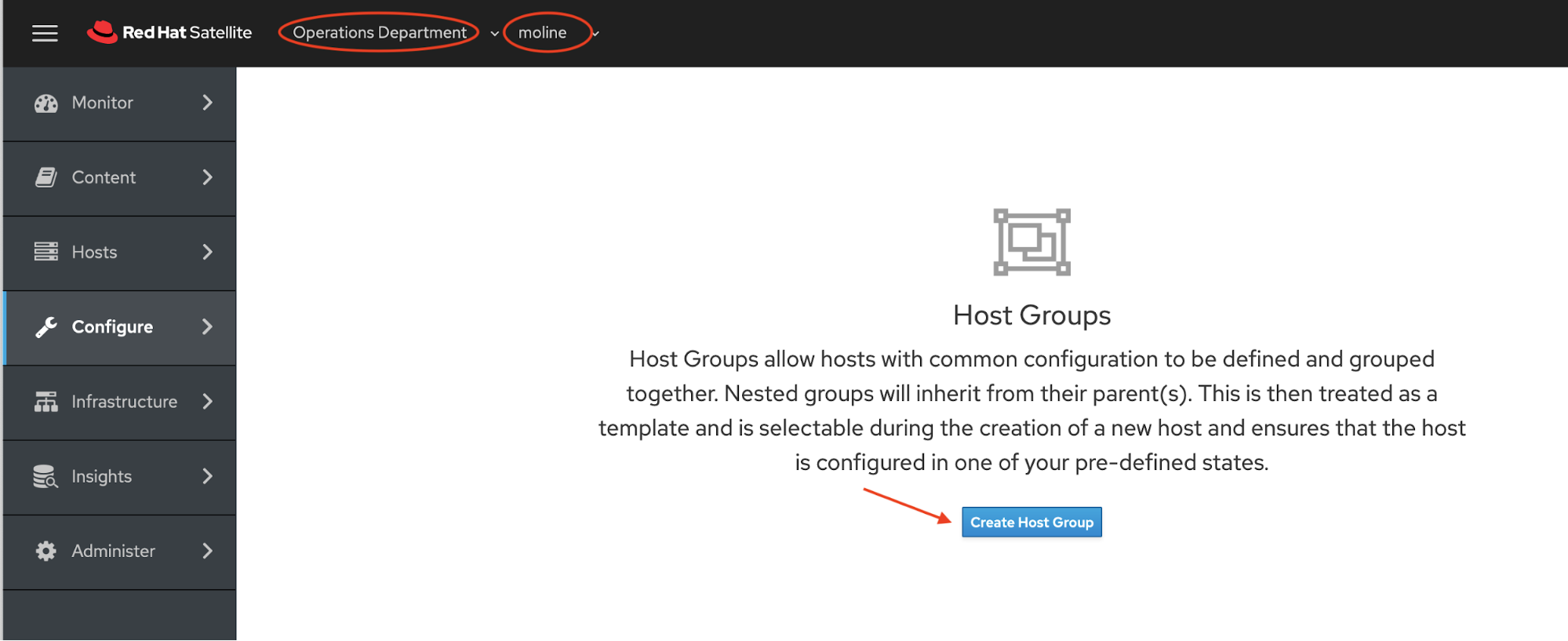
On the Host Groups > Create Host Group page, we will start filling in or selectiong the options on the Host Group Tab
Host Group Tab:
|
Name |
Value |
|
Name |
hg-rhel8-prem-server |
|
Lifecycle Environment |
le-ops-rhel8-prem-server |
|
Content View |
cv-rhel8-prem-server |
|
Content Source |
sat01.example.com |
|
Deploy On |
cr-vcenter |
|
Compute Profile |
cp-vmware-small |
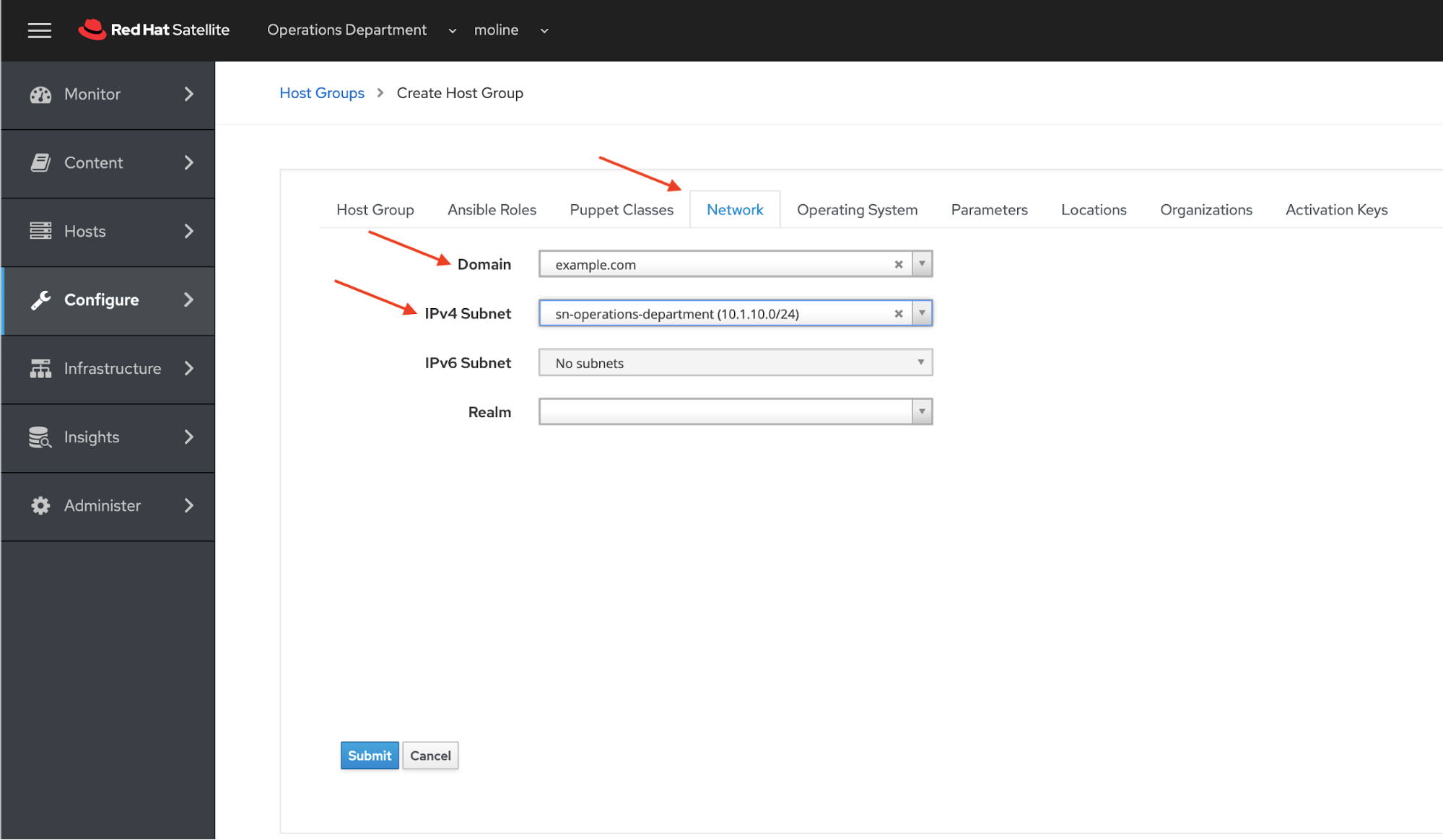
Now click on the Network tab. Fill in or selection the follow optons.
Network Tab:
|
Name |
Value |
|
Domain |
example.com |
|
IPv4 Subnet |
cn-operations-department |
Now click on the Operating System tab. Fill in these options.
Operating System Tab:
|
Name |
Value |
|
Architecture |
x86_64 |
|
Operating System |
RedHat 8.3 |
Check the Locations and Organizations tab to make sure that moline is set for Locations and Operations Department is set for Organizations.
Now click on the Activation Key tab. Fill in ak-ops-rhel8--prem-server in the Activation Keys text field. Click the blue Submit button.

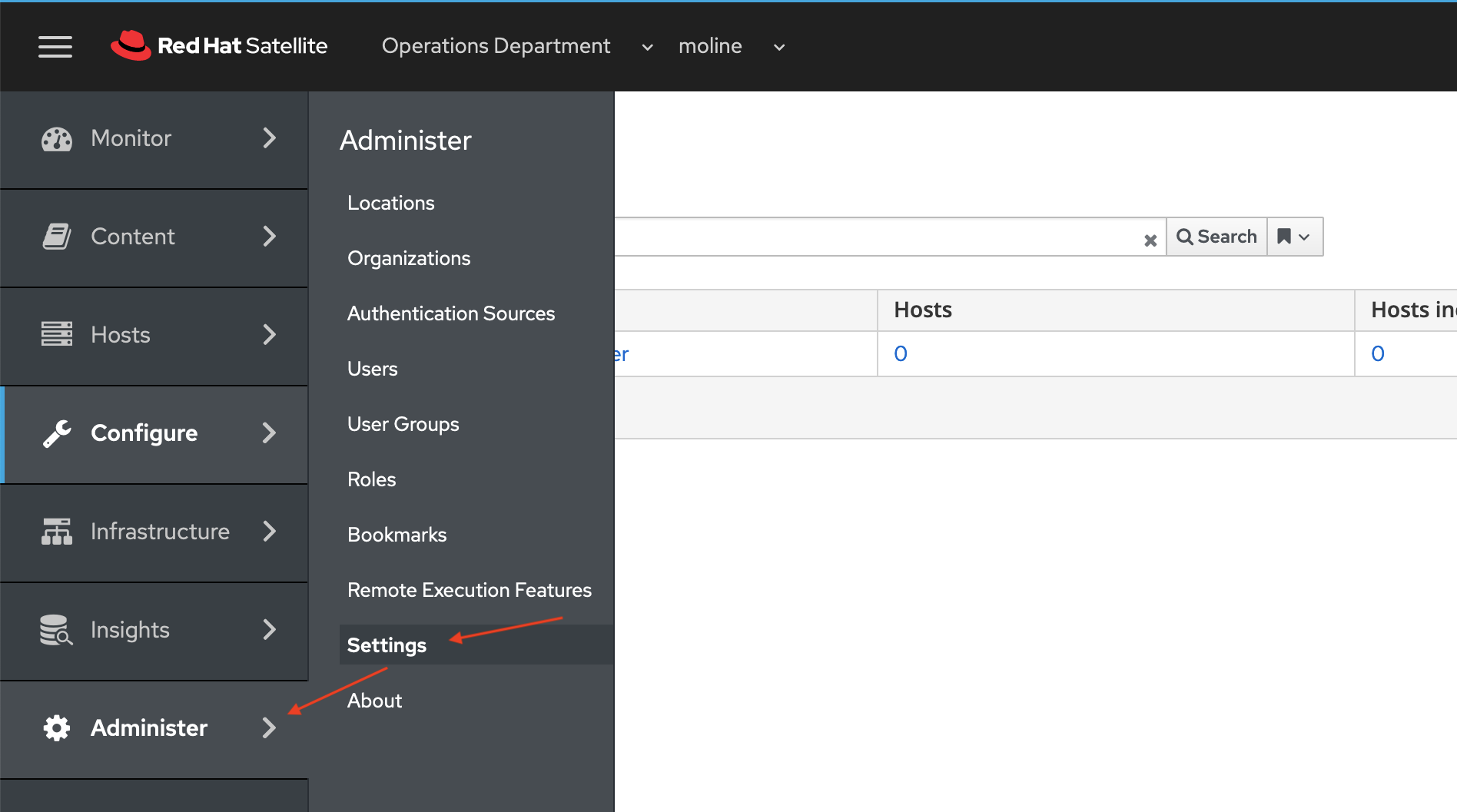
One last option to configure and we are ready to test our deployment. When I de-provision a VM running on vSphere from Satellite, I want the VM deleted. To enable this capability Administer -> Settings from the side menu.
On the Settings page in the Filter/Search text field, enter "Destroy associated VM on host delete" and click the Search button. The result will show the Destroy associated VM on host delete option. Click on the pencil (edit) icon.
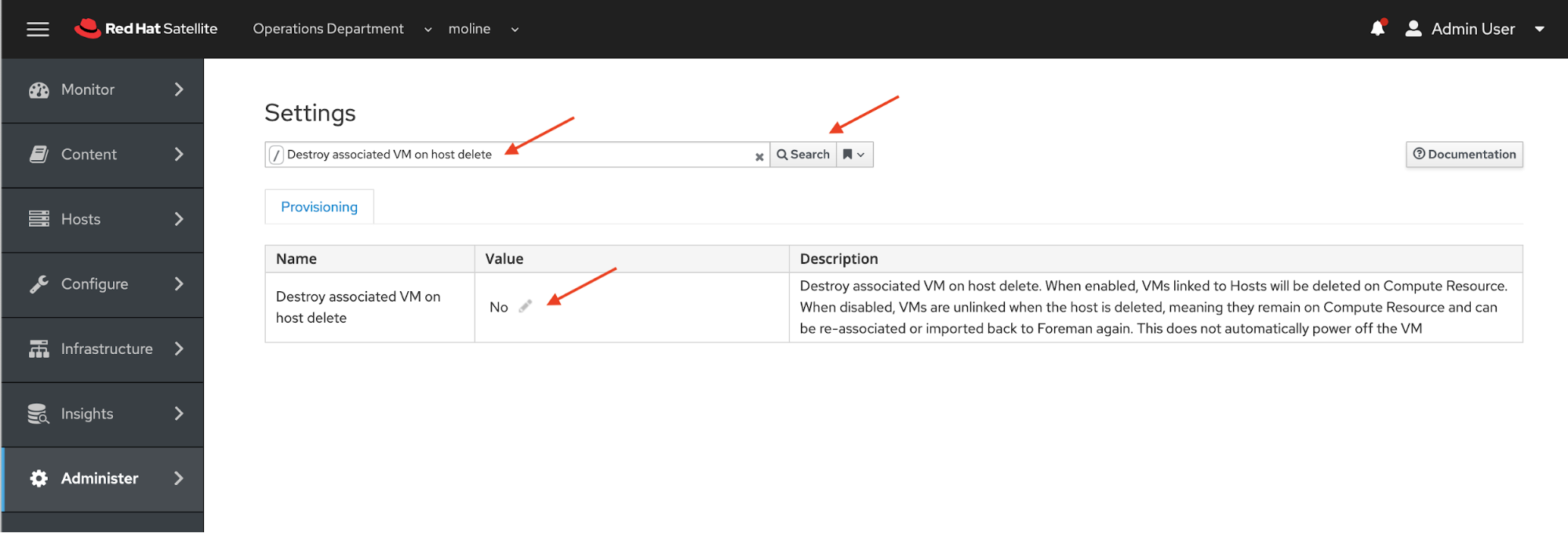
A dialog box will pop up with the title Update value for Destroy associated VM on host delete setting. Click the drop down and choose Yes, and click the blue Submit button to accept the changed value. The setting is now updated.

And that's how we integrate the VMware resources with Red Hat Satellite. In the next and final post in the series, we'll dive into RHEL VM provisioning.
References
- Installing Satellite Server from a Connected Network
- Simple Content Access
- Provisioning VMWare using userdata via Satellite 6.3-6.6
- Understanding Red Hat Content Delivery Network Repositories and their usage with Satellite 6
Provisioning RHEL virtual machines to vSphere from Red Hat Satellite
 In this multi-part tutorial, we cover how to provision Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) virtual machines (VMs) to a vSphere environment from Red Hat Satellite. Missed any steps in the series? Check them out:
In this multi-part tutorial, we cover how to provision Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) virtual machines (VMs) to a vSphere environment from Red Hat Satellite. Missed any steps in the series? Check them out:
About the author
Paul Lucas is a Chicagoland-based Red Hat Solutions Architect working with a variety of enterprise businesses. A 21 year technical sales veteran, Paul was previously a customer working at a benefits consulting firm, where he advised development teams on the use of Java and the then-emerging Java EE.
More like this
Red Hat, NVIDIA, and Palo Alto Networks collaborate to deliver an integrated, security-first foundation for AI-native telecommunications
How llm-d brings critical resource optimization with SoftBank’s AI-RAN orchestrator
Post-quantum Cryptography | Compiler
Understanding AI Security Frameworks | Compiler
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds