We released Red Hat Satellite 6.12 last month. The release includes several new features designed to help you manage your Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) environment more effectively, including remote execution pull mode. In this blog entry, I’ll write about the differences between remote execution pull mode and push mode and provide a step-by-step guide on configuring it.
What is remote execution?
Remote execution (or REX) enables you to run shell scripts, Ansible tasks, and Ansible Playbooks on remote hosts managed by Satellite. Brian Smith wrote an extensive introduction to remote execution in Satellite. The official Satellite 6.12 documentation also describes remote execution in great depth.
REX jobs are dispatched to hosts by the Capsule server (or Capsule service running on a Satellite server) using the Secure Shell (SSH) service. Port 22 must be open on hosts to enable REX.
What is remote execution pull mode?
Remote execution pull mode uses Message Queuing Telemetry Transport (MQTT) to publish jobs on Capsule servers (or Capsule service running on a Satellite server). Managed hosts subscribe to the MQTT broker to receive REX job notifications.
Here’s how REX Pull mode works:
- A managed host receives MQTT notification that there is a new REX job.
- The managed host downloads the job “payload” via HTTPS from the Capsule server.
- The job “payload” is run on the host. As the job executes, the progress of the job is reported back to the Capsule server.
Here are the configuration considerations:
- Port 1883 (MQTT) must be opened on the Capsule server to allow incoming traffic, and the host must be allowed to connect to the Capsule server on port 443 (HTTPS) to enable REX pull mode.
- Capsule servers (and Capsule services) must be configured to support either REX push mode or REX pull mode. You cannot configure a Capsule to support both REX modes.
- For existing hosts running the katello agent, you can migrate to REX pull mode by installing the katello-pull-transport-migrate package. Documentation is provided at the bottom of this post. The katello agent has been deprecated as of Satellite 6.7.
For customers with security policies that forbid the opening of port 22, REX pull mode provides some respite. Satellite 6.12 provides the first iteration of the implementation of REX pull mode. Expect to see additional features in Satellite 6.13.
When do I use Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform?
REX and the capability of running Ansible tasks and playbooks within Satellite are intended to automate the configuration of hosts. For example, after provisioning several hosts, one might apply a firewall system role (from the RHEL System Roles Collection) to configure the hosts’ firewall or install Microsoft SQL Server.
Ansible Automation Platform should be considered when configuration and Day 2 operations require automation, such as the following:
- Orchestration of fleets of VMs across the open hybrid cloud
- Managing the configuration of networking devices across data centers
- Enabling application deployment to integrate load balancer changes and CMDB configuration
- Enabling developers to provision their storage objects in an automated fashion when needed
- Embedding the automated configuration of external services into the CI/CD pipeline
- Integrating firewalls with intrusion detection systems into streamlined security remediation workflows
- Managing the life cycle of existing applications and infrastructure, updating applications and hardware in streamlined processes
Go here for more information on Ansible Automation Platform.
Configuring remote execution pull mode
Assumptions
My environment consists of the following:
- Red Hat Satellite 6.12 Satellite server running on RHEL 8.7
- Red Hat Satellite 6.12 Capsule server running on RHEL 8.7
REX pull mode will be configured on the Capsule server.
Satellite Capsule configuration
On the Capsule server, enable pull-based transport.
satellite-installer --foreman-proxy-plugin-remote-execution-script-mode pull-mqtt
Open port 1883 to allow MQTT through the firewall.
firewall-cmd --add-port="1883/tcp" firewall-cmd --runtime-to-permanent
Here’s a list of all the ports you should have open.

Finally, configure your Satellite server so that hosts registered to this Capsule server will continue to receive remote execution jobs from it.
In Satellite, click on “Administer” and “Settings”.

Click on the “Content” tab.

Finally, set the attribute “Prefer registered through Capsule for remote execution” to Yes.

Capsule content
At this point, the new Capsule server may or may not have any content. In this example, the capsule has no content and needs to be synchronized.
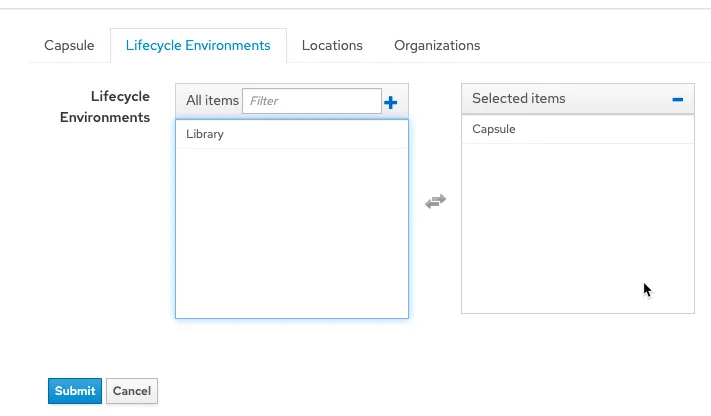
First, check that a lifecycle environment has been assigned to the Capsule. Click on Infrastructure and then the edit button of the Capsule server.

Click on the Lifecycle Environments tab.

Select the desired Lifecycle Environment and click on Submit.
Click on Infrastructure and then the name of the Capsule server. Click on Synchronize and select Optimized Sync.

Host registration
Let’s register a new host. In my Satellite server, I associated the desired Content Views and Activation Keys with a Host group to streamline the registration process.

In the Register Host menu, I will select my host group and the new capsule server configured with remote execution pull mode.

Clicking the Generate button generates the registration command.

SSH into your new host and run the registration command. Here’s the resulting output.
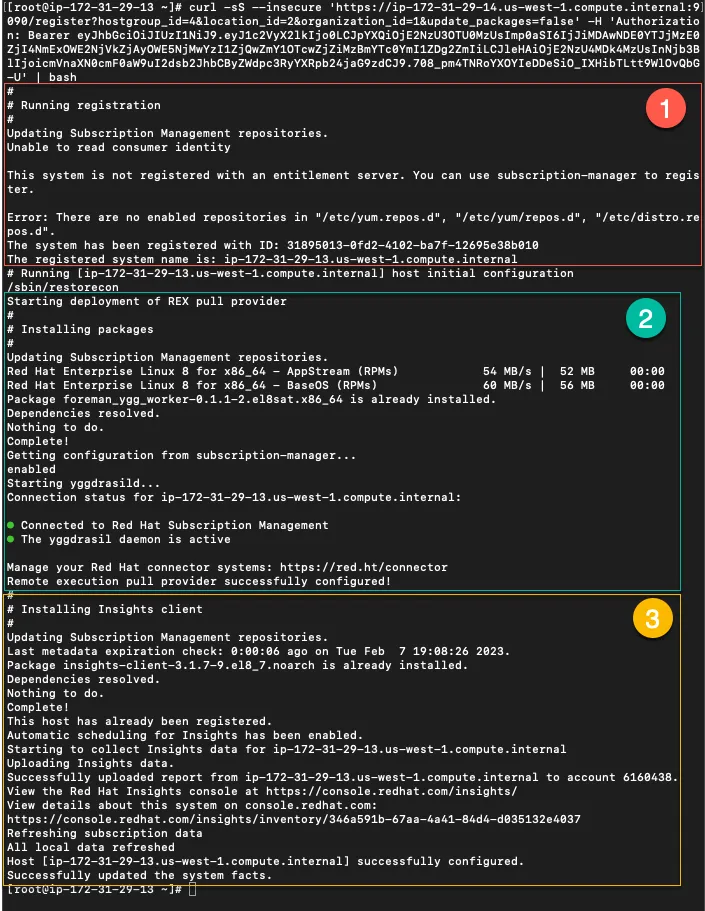
- Shows the registration of the new host.
- Shows the REX Pull agent, yggdrasild being installed.
- The insights client is installed (since I like having Red Hat Insights analyze my hosts for vulnerabilities and being able to remediate them with a button click).
Checking operation
REX pull mode is now configured. You can check that it is working by the following methods:
- Check the yggdrasild service is running with systemctl status yggdrasild.

- Run netstat to check port 1883 is connected.
Let’s test it out by installing a package.

Conclusion
Remote execution pull mode provides a different method of transport for remote execution jobs run by Satellite. Customers unable to open port 22 between hosts and Satellite infrastructure servers can now use alternative ports (MQTT - 1883, HTTPS - 443). For more information, please see the official documentation below.
Official documentation
About the author
As a Senior Principal Technical Marketing Manager in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux business unit, Matthew Yee is here to help everyone understand what our products do. He joined Red Hat in 2021 and is based in Vancouver, Canada.
More like this
2025 Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform: A year in review
New observability features in Red Hat OpenShift 4.20 and Red Hat Advanced Cluster Management 2.15
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
You Can't Automate Buy-In | Code Comments
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
