I have worked with Red Hat's migration team for the last two years. Early on, I was part of a large group working on the CloudForms management tool. A dedicated team did DevOps, so whenever I got into trouble with Jenkins or made changes to the Jenkins job, I would just email them. Like Genie following Aladdin's wishes, they did everything for me. That felt really good, and it enabled me to focus on test automation, which was my main job.
Recently, I joined a new group that doesn't have a separate infrastructure team. We're establishing processes and tools from scratch. We don't have a dedicated team to manage testing, so I must now automate my testing, create a Jenkins job for it, and publish the reports generated.
[ Want to use Jenkins in your CI/CD processes? Learn about Installing and configuring Jenkins in Linux. ]
After doing a lot of research about what I needed from Jenkins, I learned how to run it successfully, and I'm glad I got this opportunity to learn and implement it. However, I faced some challenges, so I'll share my experience and solutions to help others getting started with Jenkins.
Background
I'm testing a standalone application that needs to be installed, and when it comes up on http://localhost:8080, I need to test various aspects of it. To run it automatically on Jenkins, I create a Dockerfile in an online Git repository that creates a Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) or Fedora image and install my application on it. I use Podman or Docker in a virtual machine (VM) to install the required container image. Once the application is installed and running in a container, I run my automated tests.
Jenkins and agents
Jenkins runs its jobs on agents, choosing them based on availability. You can add a Jenkins agent manually, and Jenkins doesn't know or care whether an agent is a physical or virtual machine.
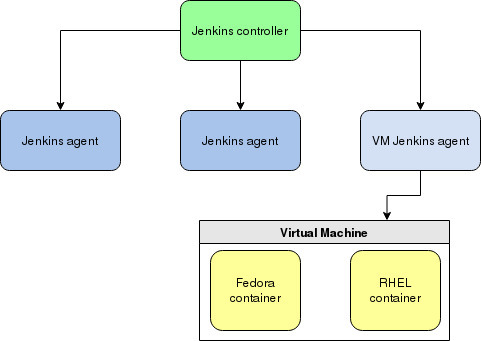
To set this up, you must configure a VM before adding it as a Jenkins agent.
First, add a new user named jenkins to the VM, and then log in as that user:
$ sudo useradd jenkins
$ su - jenkinsCreate a directory named /var/lib/jenkins on the VM:
$ mkdir /var/lib/jenkinsGenerate private and public SSH keys:
$ ssh-keygen -b 2048 -t rsaThis command generates two keys. Copy the contents of id_rsa.pub to the ~/.ssh/authorized_keys file:
$ cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keysThe contents of the private key (~/.ssh/id_rsa) are required when adding credentials in Jenkins.
[ Learn how to Speed Jenkins performance with container storage. ]
Add a VM as a Jenkins agent
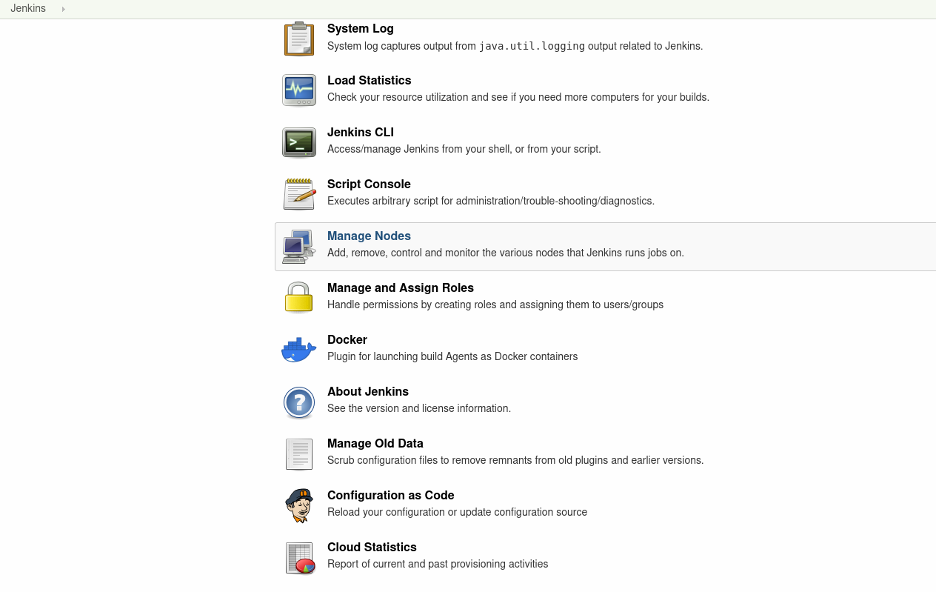
To add your VM as a node in Jenkins, go to the Manage Jenkins panel and select Manage Nodes.
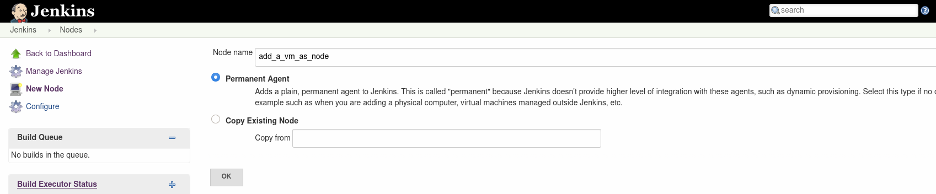
Provide a name for the node, select Permanent Agent, and then click OK.
For the Remote root directory, provide /var/lib/jenkins. This is the default directory where Jenkins creates its workspace. Make sure that this directory exists on the VM.
For Launch method, select Launch agent agents via SSH.
For Host, provide the IP address or hostname of the VM.
Under Host Key Verification Strategy, select Manually trusted key Verification Strategy.
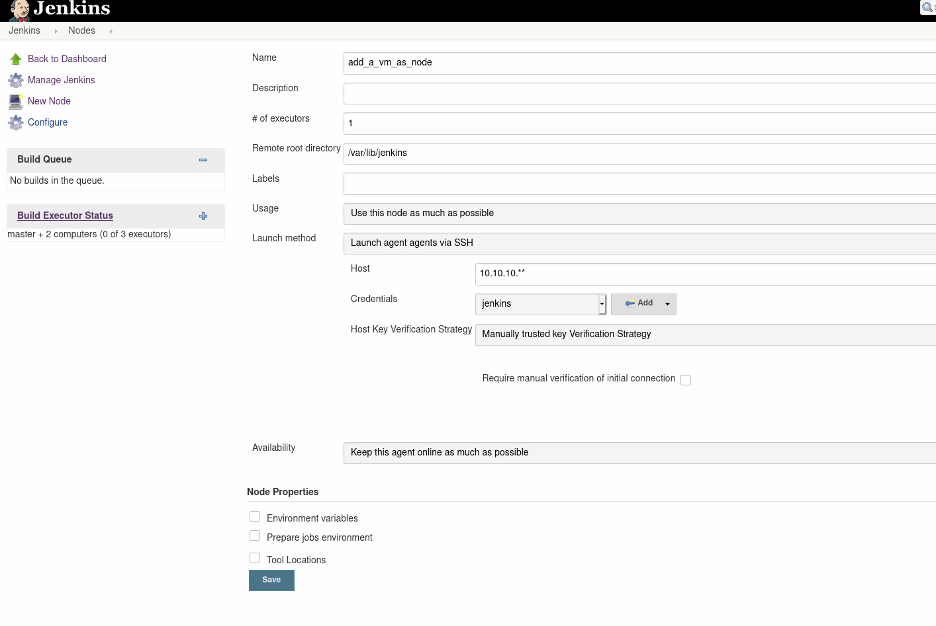
Finally, add the credentials for the VM. Click on Add credentials and select SSH Username with the private key. Give the key a name, and add the contents of ~/.ssh/id_rsa as the Private Key value.
Set the node as an agent
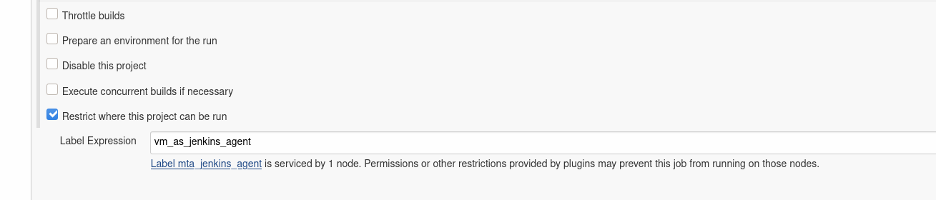
You are almost done! You need to tell Jenkins to use this node as a Jenkins agent. Edit the Jenkins job, and under Source Code Management, select Restrict where this project can be run, and provide the node name in the Label Expression field. Save the job.
Start your build
With the virtual agent configured and ready to go, you can switch back to your VM host (your laptop or workstation running the VM, not the VM itself).
In your local instance of Jenkins, start a build. Jenkins executes all commands on your VM.
Keep learning
This is my first experience in DevOps, and I like what it's done for me so far. Being able to create infrastructure, virtual or otherwise, predictably and reliably has become a powerful tool. I'm always learning, though, so if you have a better way of implementing your tests, think about contributing an article about it, so we can all learn from each other!
About the author
Shveta is a senior software engineer at Red Hat, leading a team. She is a subject-matter expert on the Migration Toolkit for Applications (MTA) and Pathfinder that helps customers migrate their applications to containers (Openshift and Kubernetes) and the latest technologies. She continuously develops her technical and domain expertise in MTA, functional testing, Kubernetes, OpenShift, and DevOps and is involved in reporting and validating dozens of issues ensuring high-quality releases to customers. Shveta has independently built the automation framework from scratch for some Red Hat products and has automated the needed test cases in Python and Cypress. Shveta is also contributing to some DevOps tasks and CI/CD tools like building and maintaining Jenkins pipelines to run automation tests on virtual machines for different operating systems, including Linux, Windows, and macOS.
More like this
Redefining automation governance: From execution to observability at Bradesco
Refactoring isn’t just technical—it’s an economic hedge
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
How Bad Is Betting Wrong On The Future? | Compiler
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
