Many organizations are considering generative AI (gen AI) as a means of reducing the time employees spend filing IT requests and the time IT teams spend closing these requests. To this end, we’ve created an it-self-service-agent AI quickstart that shows you how to automate IT processes within your organization using agentic AI on Red Hat OpenShift AI.
This AI quickstart provides a reusable framework—including request routing, agent services, knowledge bases, an integration dispatcher, and an evaluation framework—that you can apply across multiple IT processes. While we're demonstrating a laptop refresh process as the working example, the same components can be adapted to privacy impact assessments, RFP generation, access requests, software licensing, and other structured IT workflows.
AI quickstarts are a catalog of ready-to-run, industry-specific use cases for your Red Hat AI environment. Each AI quickstart is designed to be simple to deploy, explore, and extend, giving teams a fast, hands-on way to see how AI can power solutions on enterprise-ready, open source infrastructure. You can read more about AI quickstarts in the article, “AI quickstarts: An easy and practical way to get started with Red Hat AI.”
The business case
Using AI to automate IT processes has a variety of benefits, including:
- Reducing time needed to complete common requests: The agent helps employees create their requests by explaining the options and required information, and helps employees submit those requests once they are ready.
- Improving compliance to process standards: Requests are more complete and aligned with process standards. This reduces the need to contact the requesting employee for additional information and reduces the amount of time and effort needed to review and complete requests.
- Reducing the number of rejected requests due to missing/incorrect information: Rejected requests are frustrating for employees and lead to lower employee satisfaction. Reducing request rejection and eliminating the back and forth on requests helps improve employee satisfaction.
- Reducing ticket resolution times: The agent helps reduce the time needed to close a ticket, improving throughput and reducing ticket idle time.
Meeting employees where they are
One of the key aspects of realizing these benefits is the design philosophy of, "meeting employees where they are." Rather than requiring employees to learn a new system or communication channel, this demo integrates with the tools your organization already uses. If your organization uses Slack and email to communicate with employees, integrating with these existing channels can improve adoption rates and reduce change management overhead compared to introducing yet another new tool. Employees can interact with AI agents using the same familiar interfaces they use for all their other work communication.
To that end, this AI quickstart includes production-ready integrations with Slack, email, and ServiceNow, along with a general-purpose request manager that makes integrating with other existing communication channels straightforward. The top-level architecture is as follows:
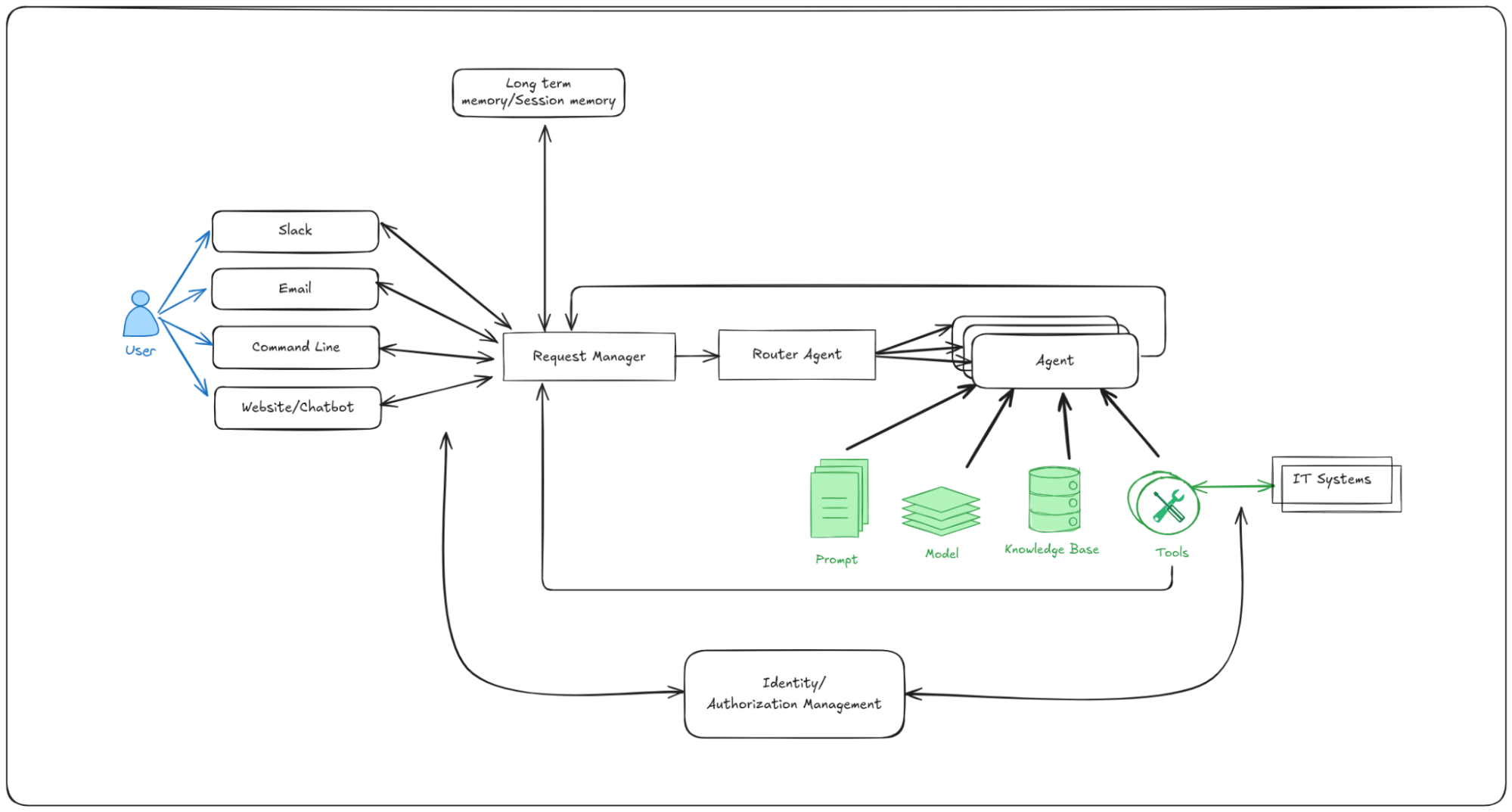
Figure 1: Architecture diagram showing the IT self-service agent components including request manager, agent services, knowledge bases, integration dispatcher, and connections to Slack, email, and ServiceNow
Getting started
Time to complete: 60-90 minutes (depending on whether you explore optional integrations like Slack and ServiceNow).
This AI quickstart is designed for rapid exploration and hands-on learning. In about an hour, you can deploy a fully functional AI agent system and see it handle complete laptop refresh workflows. The optional integrations with Slack, ServiceNow, and email can be added incrementally as you explore further.
Once you have the prerequisites in place, you can install the AI quickstart as shown below. The prerequisites include an existing Red Hat OpenShift environment and a number of local tools as outlined in the requirements.
# Clone the repository
git clone https://github.com/rh-ai-quickstart/it-self-service-agent.git
cd it-self-service-agent
# Set your namespace
export NAMESPACE=your-namespace
# Set LLM configuration
export LLM=llama-3-3-70b-instruct-w8a8
export LLM_ID=llama-3-3-70b-instruct-w8a8
export LLM_API_TOKEN=your-api-token
export LLM_URL=https://your-llm-endpoint
# Log in to OpenShift
oc login --server=https://your-cluster:6443
# Deploy in testing mode (Mock Eventing)
make helm-install-test NAMESPACE=$NAMESPACEThis will deploy the set of pods that make up the quickstart:

Figure 2: Screenshot showing the deployed OpenShift pods that make up the IT self-service agent AI quickstart including agent services, request manager, integration dispatcher, and supporting infrastructure
Once you have the prerequisite OpenShift pods in place, you are now ready to explore the key aspects of the agentic implementation of a laptop refresh process. The AI quickstart takes you through:
- Requesting a laptop refresh through a command-line interface.
- Integration with Slack and requesting a laptop refresh through Slack.
- Integration with a real ServiceNow instance and viewing the request you created in the ServiceNow UI.
- Enabling email support and requesting a laptop refresh through email.
- Running multi-turn evaluations on the conversations with the laptop refresh agents using the open source DeepEval framework. Gen AI agents are non-deterministic, so traditional software testing is insufficient. This evaluation framework validates business-specific requirements—such as policy compliance and information gathering—so agents meet quality standards before deployment, and catch regressions during updates. This is critical for confidently deploying and iterating on AI agents in production.
- Viewing details of the requests to and responses from the laptop refresh agents using OpenShift's built-in OpenTelemetry support, including calls through the Responses API and calls to MCP servers. Agentic AI systems involve complex interactions between multiple components, making production debugging challenging without proper visibility. Distributed tracing enables teams to understand how requests flow through the system, identify performance bottlenecks, diagnose issues in production, and understand user interaction patterns—essential capabilities for maintaining reliable AI agent systems at scale.
- Exploring different prompting approaches and the trade-offs between a single large prompt and multistep prompts using LangGraph.
- Setting up PromptGuard to avoid prompt injection attacks.
- Setting up LlamaGuard to add content moderation.
All of this runs on Red Hat OpenShift AI with production-level scalability built in. By completing this AI quickstart, you will have:
- Deployed a fully functional AI agent system on Red Hat OpenShift AI
- Understood the core platform architecture and components
- Tested the laptop refresh agent through multiple channels
- Run evaluations to validate agent behavior
- Implemented safety checks with PromptGuard and LlamaGuard
- Explored AI observability with OpenTelemetry
- Learned how to customize the system for your own use cases
To learn more
This AI quickstart helps you explore each of the key aspects of automating an IT process with agents and includes a deep dive on each of the components.
We hope you're excited to try out this IT self-service agent AI quickstart. If you find it interesting, be sure to check out the full AI quickstarts catalog—there you'll find other use cases that will help you and your team start using Red Hat AI to solve real-world problems and to inspire you to think about what else you might build with the platform.
リソース
適応力のある企業:AI への対応力が破壊的革新への対応力となる理由
執筆者紹介
Michael Dawson is an active contributor to the Node.js project and chair of the Node.js Technical Steering Committee (TSC). He contributes to a broad range of community efforts including platform support, build infrastructure, N-API, Release, as well as tools to help the community achieve quality with speed (e.g., ci jobs, benchmarking and code coverage reporting). As the Node.js lead for Red Hat and IBM, he works with Red Hat and IBM's internal teams to plan and facilitate their contributions to Node.js and v8 within the Node and Google communities. Dawson's past experience includes building IBM's Java runtime, building and operating client facing e-commerce applications, building PKI and symmetric based crypto solutions as well as a number of varied consulting engagements. In his spare time, he uses Node.js to automate his home and life for fun.
類似検索
Automating Microsoft Endpoint Configuration Manager with Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform
Event-Driven Ansible: Simplified event routing with Event Streams
Technically Speaking | Taming AI agents with observability
You Can’t Automate The Difficult Decisions | Code Comments
チャンネル別に見る
自動化
テクノロジー、チームおよび環境に関する IT 自動化の最新情報
AI (人工知能)
お客様が AI ワークロードをどこでも自由に実行することを可能にするプラットフォームについてのアップデート
オープン・ハイブリッドクラウド
ハイブリッドクラウドで柔軟に未来を築く方法をご確認ください。
セキュリティ
環境やテクノロジー全体に及ぶリスクを軽減する方法に関する最新情報
エッジコンピューティング
エッジでの運用を単純化するプラットフォームのアップデート
インフラストラクチャ
世界有数のエンタープライズ向け Linux プラットフォームの最新情報
アプリケーション
アプリケーションの最も困難な課題に対する Red Hat ソリューションの詳細
仮想化
オンプレミスまたは複数クラウドでのワークロードに対応するエンタープライズ仮想化の将来についてご覧ください
