OpenShift Assisted Installer is a user-friendly OpenShift installation solution for the various platforms, but focused on bare metal.
It comprises two key components:
The Assisted Service provides hosting of installation artifacts (Ignition files, installation configuration, discovery ISO), exposed UI or REST API, etc.
Assisted Installer provide the following advantages:
- A web interface to perform cluster installation without having to create the installation configuration file.
- Boostrap machine is no longer required, the bootstrapping process takes place on a random node of the cluster.
- A simplified deployment model that does not require in-depth knowledge of OpenShift.
- Flexible API.
- Deploying Single Node OpenShift (SNO).
- Installing OpenShift Virtualization and OpenShift Data Foundation (formerly OpenShift Container Storage) from the web interface.
This article is the first in a series of two articles covering Assisted Installer installation. The second part of article explains implemented high availability (HA) and load balancing (LB).
Prerequisites
Network settings are performed in the following modes:
- Cluster-Managed Networking.
- User-Managed Networking.
Assisted Installer requires underlying infrastructure (DNS/DHCP/LB) in User-Managed Networking mode. By default, Assisted Installer expects existing DHCP in both modes. However, it is also possible to use the Assisted Service API to configure static configuration via NMState
CoreDNS provides an internal name resolution within the cluster. External access to the requires either an external DNS server or static entries in the hosts file.
Cluster details
Login to RedHat Hybrid Cloud Console
Click Create cluster to start the process.

Complete the Cluster name, Base Domain and choose OpenShift version. At this step, it is possible to select the SNO installation and change the pull secret if necessary.

Click Next
Host discovery
Here we can choose to install OpenShift Virtualization and OpenShift Data Foundation (ODF). By default ODF will use all non-installation disks for local storage.
Click Add hosts

Choose Full image file and paste SSH-public key for cluster nodes SSH access. The difference between Full image file and Minimal image file it that Full image file is Red Hat Enterprise Linux CoreOS (RHCOS) live ISO with embedded Ignition config. The Minimal image file is significantly smaller because rootfs downloaded during the RHCOS installation.

Click Generate Discovery ISO
Download the created image using any convenient method.

Mount downloaded ISO to all necessary servers via BMC (IPMI).
Boot from the mounted virtual device.
The installation process starts automatically.
After a while, the servers will appear in the RedHat Hybrid Cloud Console.
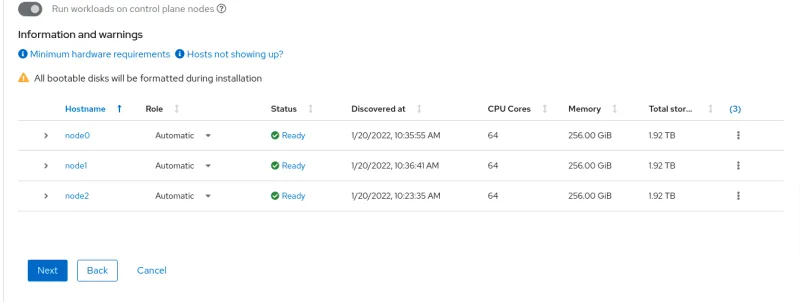
It is possible to change the cluster node hostname, role, and installation disk.

When all nodes will be in Ready state, click Next.
Networking
Choose Cluster-Managed Networking.
Complete Available subnet, API Virtual API and Ingress Virtual API. Please note that VIP addresses cannot be the same.

Also, it is possible to allocate IP addresses via DHCP and Use advanced networking for additional network configuration. For example, change cluster network, cluster network host prefix, service network and choose OpenShift SDN or Open Virtual Networking(OVN).

Click Next
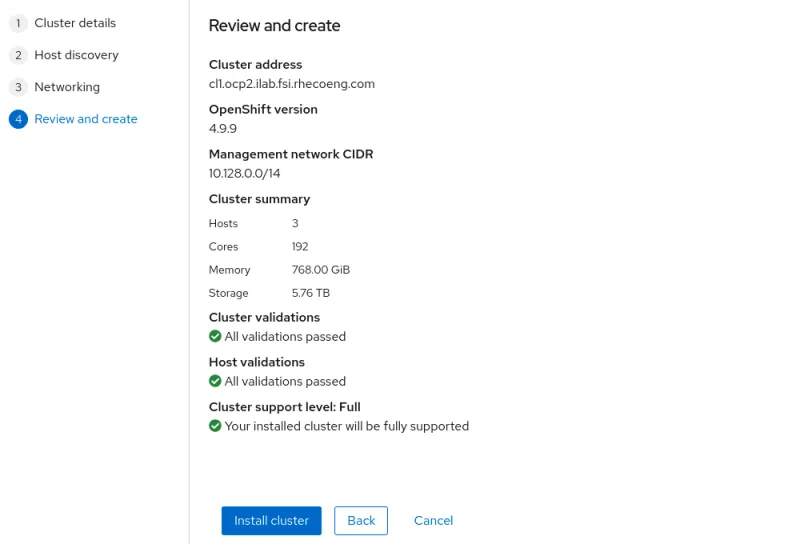
Configuration review
Review the configuration and click Install cluster
Wait for the installation process to finish. During the installation of the cluster, the nodes will reboot several times.
Click View cluster events to show cluster setup events.

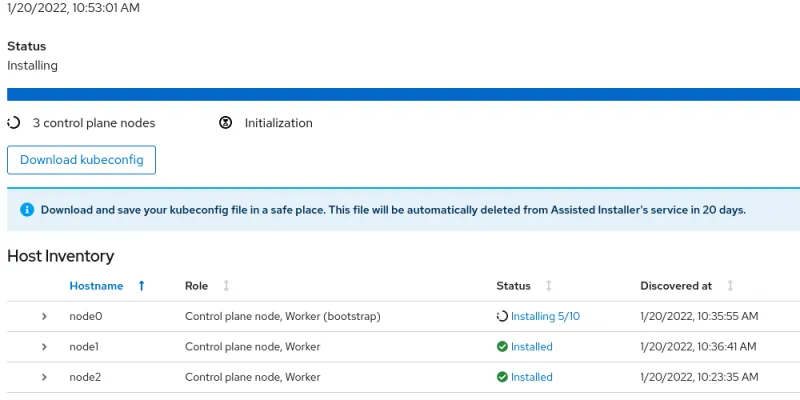

Finished installation
After installing the cluster, download kubeconfig and save the kubeadmin password.
The next part of the article will describe the HA and LB implementation.
About the author
More like this
Looking ahead to 2026: Red Hat’s view across the hybrid cloud
Red Hat to acquire Chatterbox Labs: Frequently Asked Questions
Crack the Cloud_Open | Command Line Heroes
Edge computing covered and diced | Technically Speaking
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
