Red Hat Satellite provides webhooks to notify or perform an action when an event occurs. For example, webhooks can inform you of the completion of errata installation on Red Hat Enterprise Linux (RHEL) hosts (amongst many other events). The webhook mechanism helps integrate Satellite with applications such as Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform, Splunk and ServiceNow, to name a few.
What is a webhook?
In general, a webhook is an API call (or programmatic procedure/function) using the HTTP protocol. In Satellite, specific events can trigger the running of webhooks. Particular events can include creating a host, creating a new Satellite admin user account, or a remote execution job (and many others).

In the diagram above, a Satellite event or job completes, which causes a webhook to fire. This webhook performs an API call on an application across the network. Upon receiving the API call, the application performs another action, perhaps updating a dashboard or triggering an alert.
When a webhook is triggered, it runs against a preconfigured remote endpoint (such as Ansible Automation Platform, etc.). In other words, the webhook contains information about the remote endpoint, such as the URL and the event that triggered the webhook.
The webhook must be configured to speak to the API of the third-party application according to specifications defined by the third party.
Why wouldn’t we just get Satellite to send an email? You could very well do that, but the webhook allows you to do much more, enabling you to integrate Satellite events with third-party applications. As well, you wouldn’t have to read the email, and it’s easier to automate a response to an API call sent by a webhook.
What are errata?
Errata refers to the correction or update of a software package based on a security issue, bug, or the availability of a new feature. Satellite enables you to apply errata to RHEL hosts automatically in bulk.
An errata example
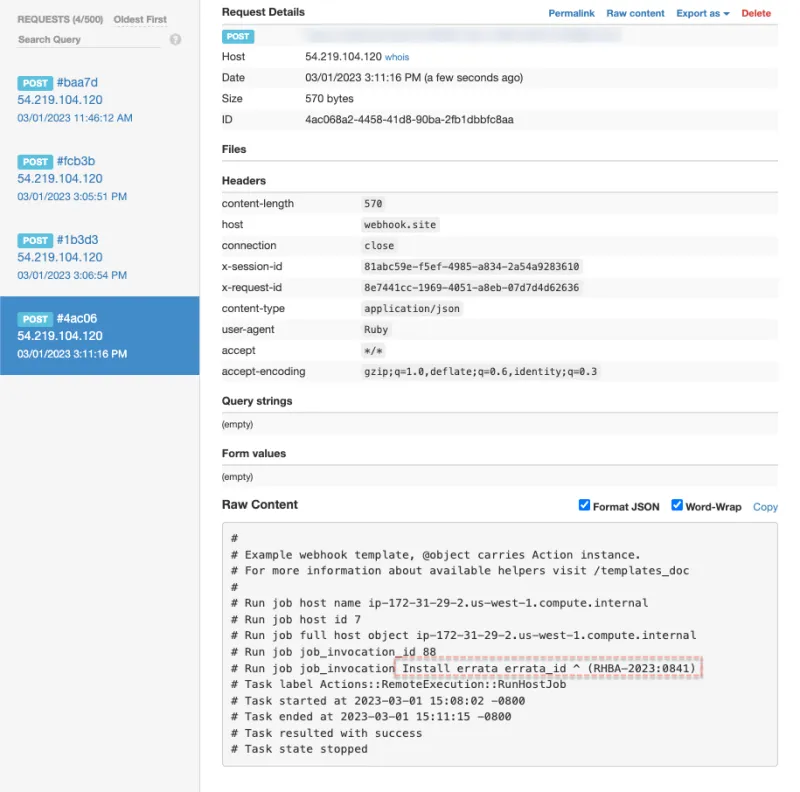
For example, if a new security vulnerability is discovered, like RHSA-2023:0832, you could use Satellite to apply the errata to resolve the vulnerability. After Satellite has completed the installation of the errata, Satellite can run a webhook to notify a secondary system of that event.
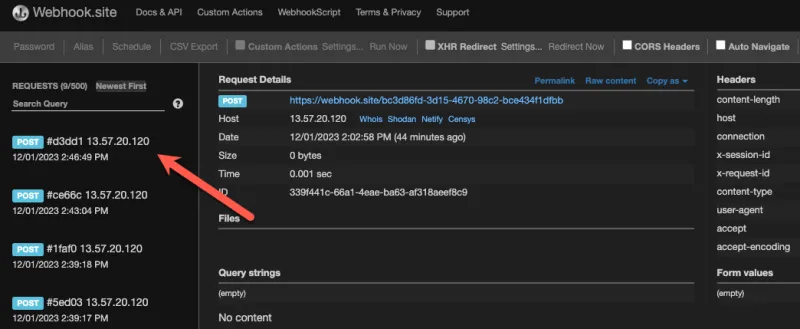
Below is a screenshot of a webhook sent from my test Satellite server, received by https://webhook.site, a webhook testing site. The webhook was fired after I installed the RHSA-2023:0832 errata.
How to configure it
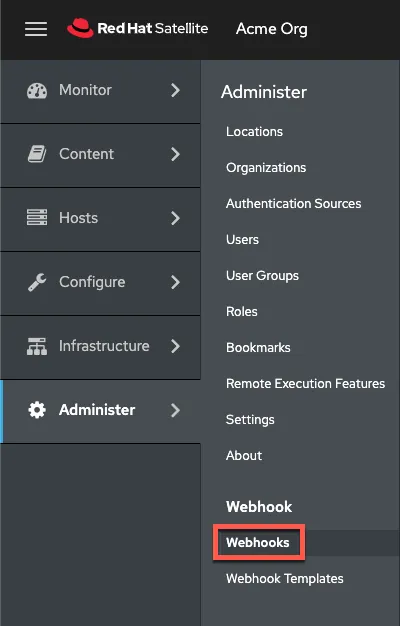
Navigate to the webhook menu
Click on “Administer” and “Webhooks”.
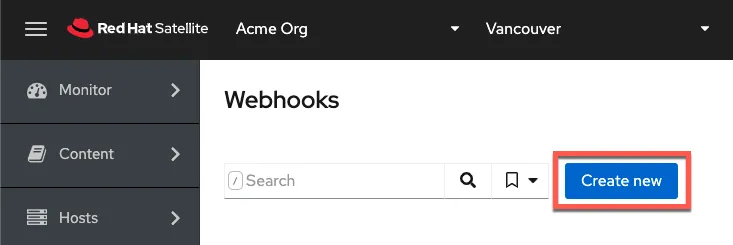
Create a new webhook
Click on “Create new.”
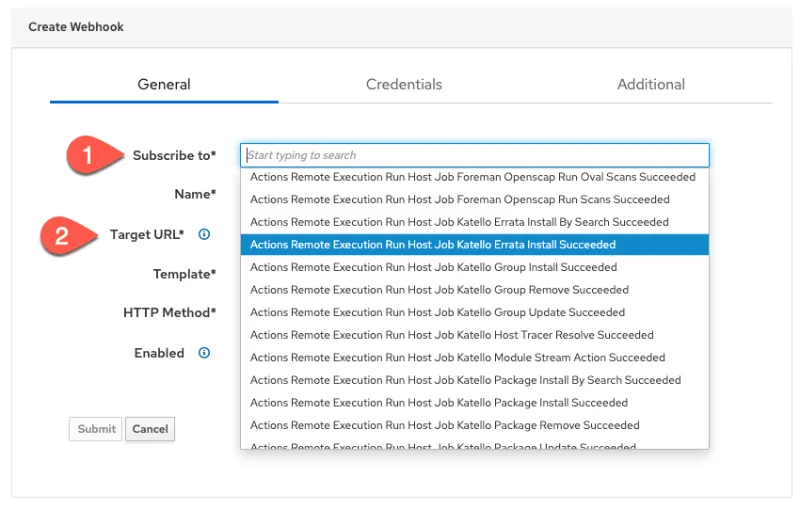
Select the feed
We’ll need to select a feed of Satellite events. The webhook will fire when an event from the chosen feed occurs.
- Click on “Subscribe to”.
- Select a feed. In this particular example, we’ll send webhooks whenever a remote execution run job has been completed.
- Give the webhook a name.
- Give the webhook a target URL. In this example, I use webhook.site as an endpoint for a test.
- Select a template for capturing information contained in the event.
- Choose an HTTP method for executing the API call.
- Enable the webhook.
- Click “Submit” to save the webhook.

Test the webhook
Now we can test the webhook.
Click on “Test webhook”.
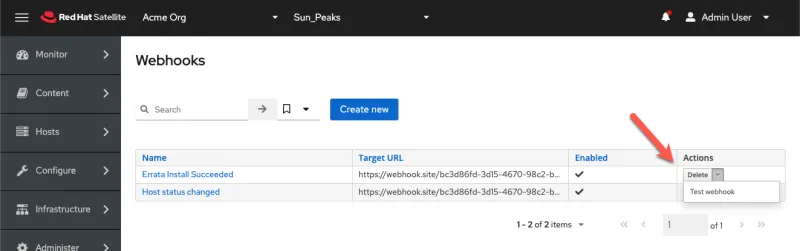
Click “Submit”.

If the webhook is configured correctly, we should see an event at webhook.site.
Streamline Satellite management with webhooks
Webhooks can help you keep track of Satellite events, making it easier to automate processes and operations. As well, Satellite’s events and webhooks are also a source of information to audit patching in real-time to provide assurances that your infrastructure and applications are up to date. Satellite webhooks can be integrated into Event-Driven Ansible to drive automated event responses in your data center and cloud-based infrastructure.
Learn more
About the author
As a Senior Principal Technical Marketing Manager in the Red Hat Enterprise Linux business unit, Matthew Yee is here to help everyone understand what our products do. He joined Red Hat in 2021 and is based in Vancouver, Canada.
More like this
Chasing the holy grail: Why Red Hat’s Hummingbird project aims for "near zero" CVEs
Elevate your vulnerabiFrom challenge to champion: Elevate your vulnerability management strategy lity management strategy with Red Hat
Data Security And AI | Compiler
Data Security 101 | Compiler
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
