Note from the editor: This blog post was originally published in November 2023 and has been updated to include the latest feature enhancements for Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform subscribers.
Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant is a generative AI (gen AI) service within Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform that is engineered to help automation teams create, adopt and maintain Ansible content more efficiently.
In this post, we’ll walk through the capabilities of Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant to help you turbocharge Ansible content creation experience and start automating faster. We'll also review the options available to help you get hands-on with the service.
Bringing AI to Ansible content creation through collaboration between Red Hat and IBM
Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant is the culmination of Red Hat and IBM teams combining forces to create a cohesive AI experience for Ansible content creation. Tapping into automation-specific IBM watsonx foundation models, it turns text prompts into Ansible content for the creation of Ansible content. The generated content adheres to accepted Ansible best practices and, when combined with the Ansible code bot, helps teams build more confidence in their automation code base.
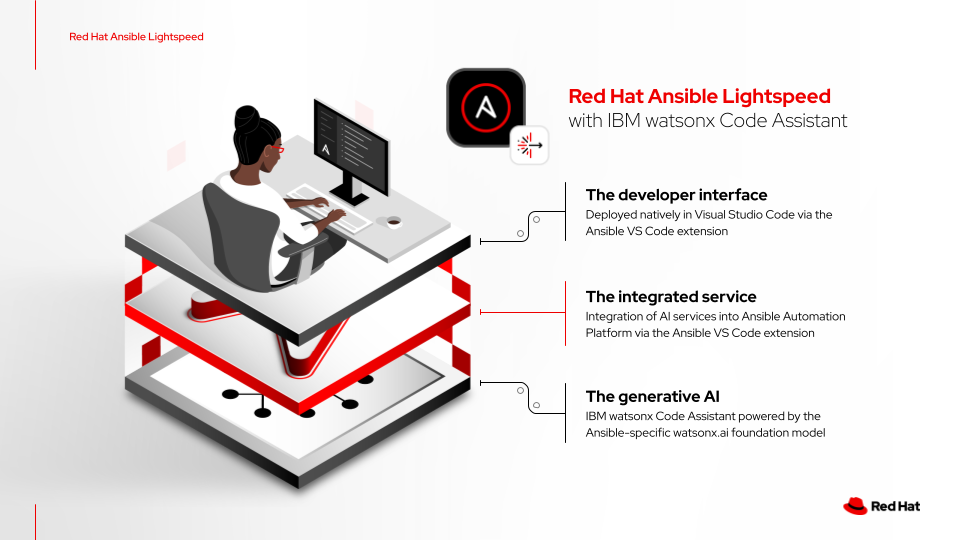
The service consists of three components:
- The developer interface: Built natively into the VS Code extension via the Ansible extension, this allows Ansible content creators to use natural language prompts in the Ansible Playbooks or task files to generate Ansible Lightspeed single and multi-task suggestions.
- The integrated service: This acts as the glue or broker between the developer interface and the watsonx.ai service. It brings the power of AI to Ansible Automation Platform and enhances the responses from the AI with its post-processing capabilities.
- Gen AI: IBM watsonx Code Assistant provides access to Ansible-specific watsonx.ai foundation model that generates Ansible content recommendations. This is the “AI guts'' of the solution.
Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant can be deployed as a software-as-a-service (SaaS) deployment or on-premise in your datacenter.
How to access Ansible Lightspeed
Ansible Lightspeed is included with a subscription to Ansible Automation Platform, however, there is an additional cost to access the IBM watsonx Code Assistant model.
SaaS-based service
Ansible Automation Platform customers: start a 90-day trial
Existing Ansible Automation Platform customers can start experimenting with the service through a free 90-day trial to Ansible Lightspeed. Learn how.
Once your trial expires, explore pay-as-you-go options through an IBM Cloud account. See IBM watsonx Code Assistant pricing plans.
Not currently an Ansible Automation Platform subscriber?
Sign up for a trial subscription, then follow these instructions to activate your Ansible Lightspeed trial.
On-premise service
For on-premise deployments, you will need to install the Ansible Lightspeed software via the Red Hat OpenShift operator, as well as the IBM watsonx Code Assistant via IBM Cloud Pak for Data. Please contact IBM for pricing and additional information.
Once you're connected, it's time to experience its AI-enhanced content creation experience. The following features are available through both the SaaS and on-premise service.
Hybrid deployment
You can also deploy Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed on-premise and connect to the IBM watsonx Code Assistant model in the cloud. A hybrid deployment gives you more flexibility to run the Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed service in your regional datacenter while connecting to WCA hosted in an IBM-supported location. It also allows you to use Ansible Automation Platform for user authentication, eliminating the need to log into the Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed cloud-based service.
Create
Create an Ansible Playbook
Ansible Lightspeed with watsonx Code Assistant supports full playbook generation and content explanation. You will need to install the latest version of the Ansible VS Code extension (>=24.8.0) to access these features.
To get started, click on the Ansible icon in the left-hand navigation and then the “Get Started” button under the Ansible content creator. Select “Playbook with Ansible Lightspeed” to enter the guided chat interface for full playbook generation.
In the interface, enter your playbook prompt in natural language and click “Analyze”. The service will provide an editable outline of tasks (pseudo code). This chat-like interface allows real-time interaction with the gen AI service where you can refine your prompt. Both the playbook goal and outline are sent to Ansible Lightspeed with watsonx Code Assistant, which suggests a complete playbook. This intuitive and guided experience helps novice to intermediate users generate full Ansible Playbooks using gen AI.
Create an Ansible Role
You can also use Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed to quickly generate role files using the latest version of the VS Code editor (≥ 25.3.0). Once the role is created, you can further enhance the generated files using task generation.
To use the new role generation feature, you need to create the role from within a collection. You can use the ansible-creator CLI tool or Ansible development tools view within the Ansible VSCode extension to scaffold your collection, ensuring that your roles follow best practices from the start.

Content explanation
The Ansible VS Code extension also provides you capability to explain existing and newly generated playbooks and roles so that you can easily understand the details of any playbook. To explain any playbook, open it in VS Code and click on “Explain the current playbook” under the Ansible Lightspeed section. You can also right-click on a playbook and click on “Explain the playbook with Ansible Lightspeed”.
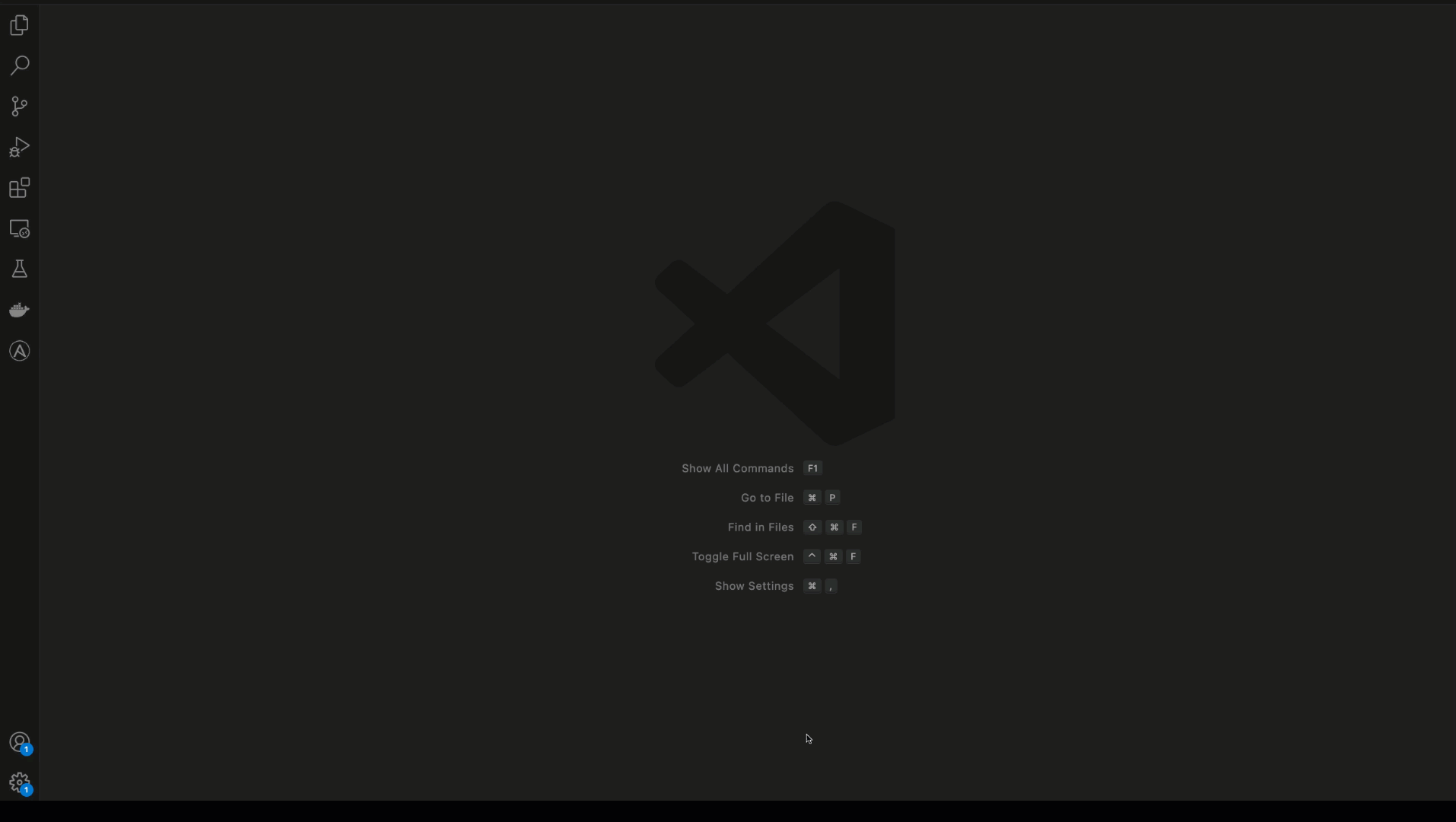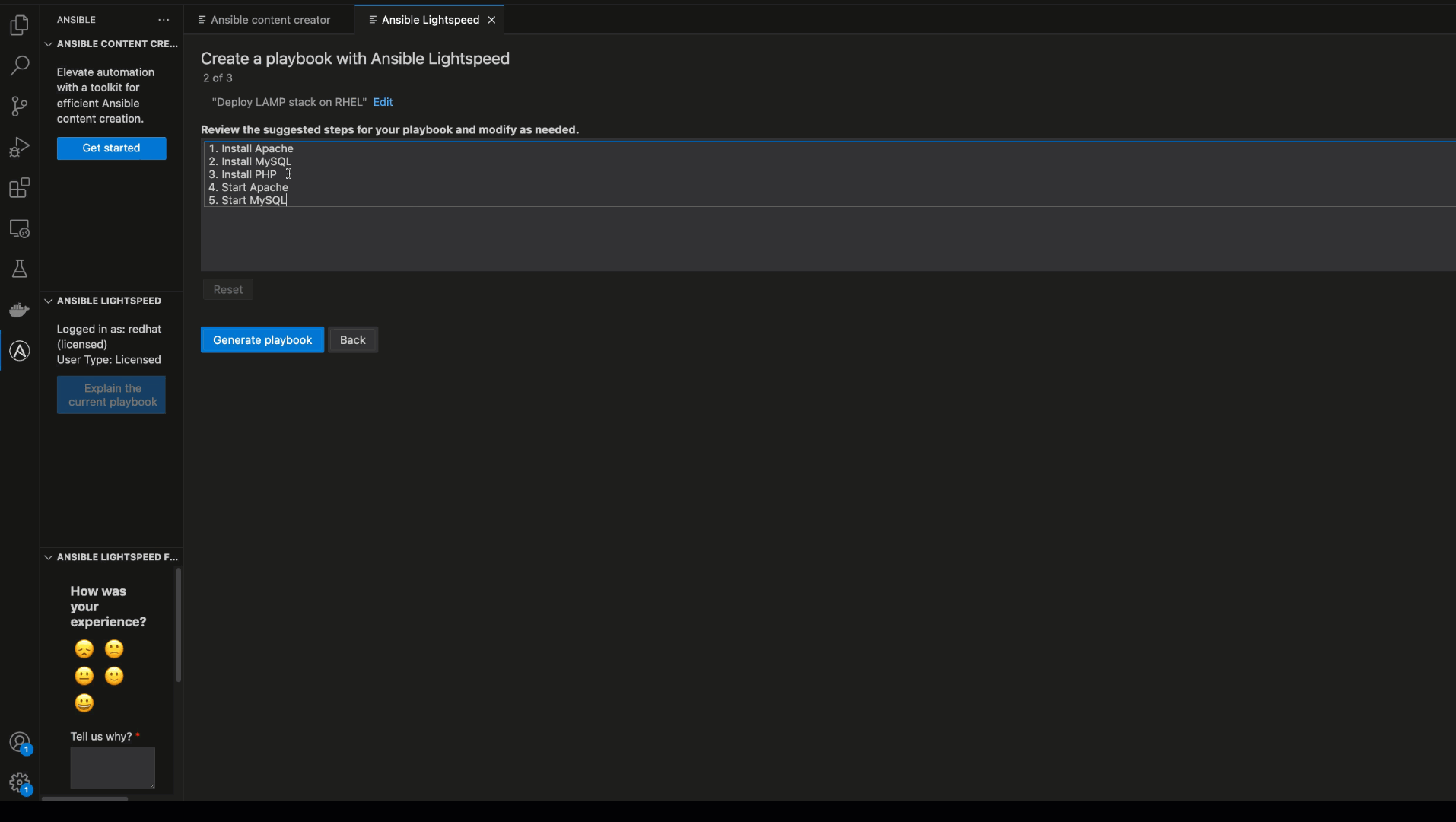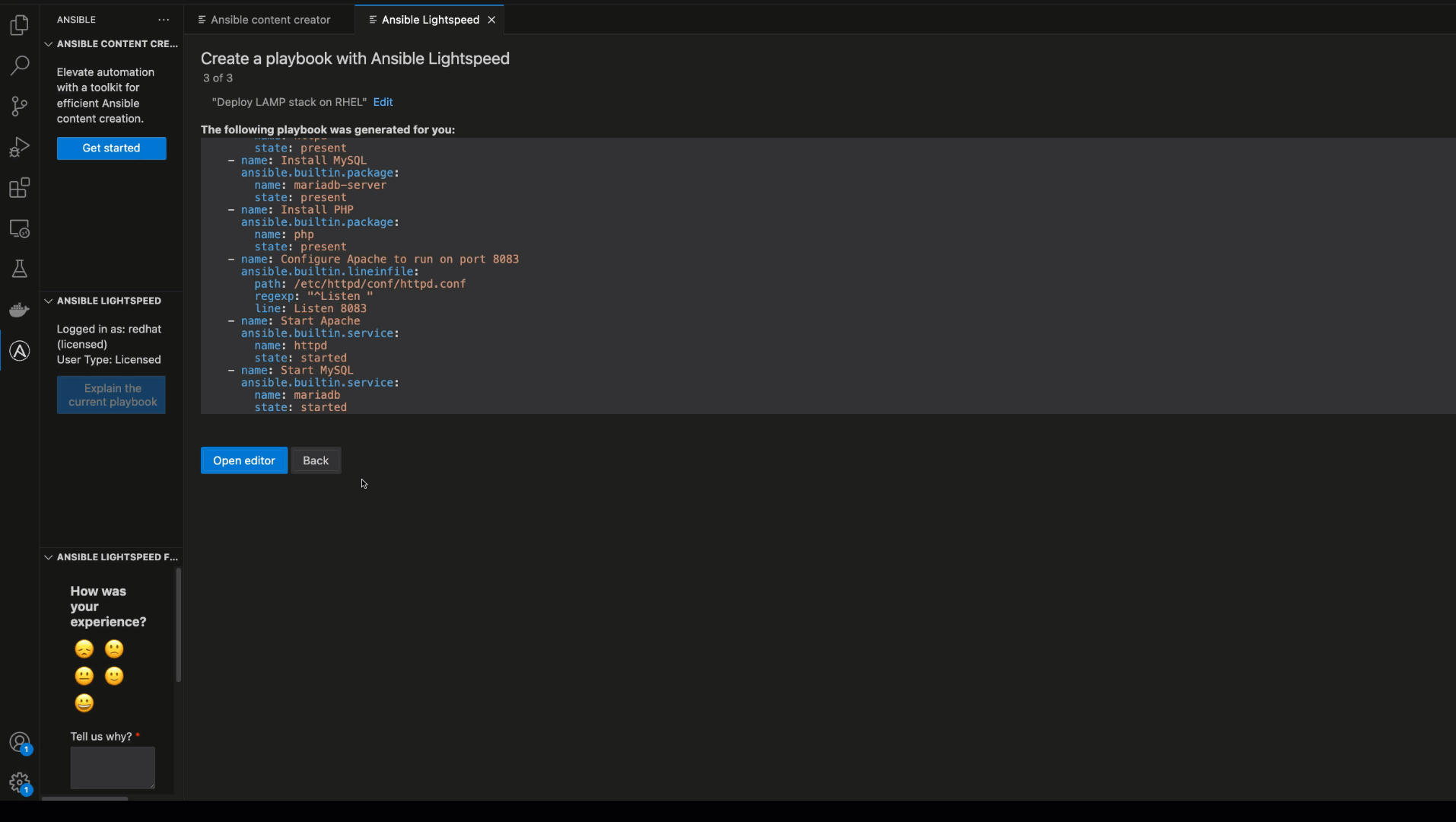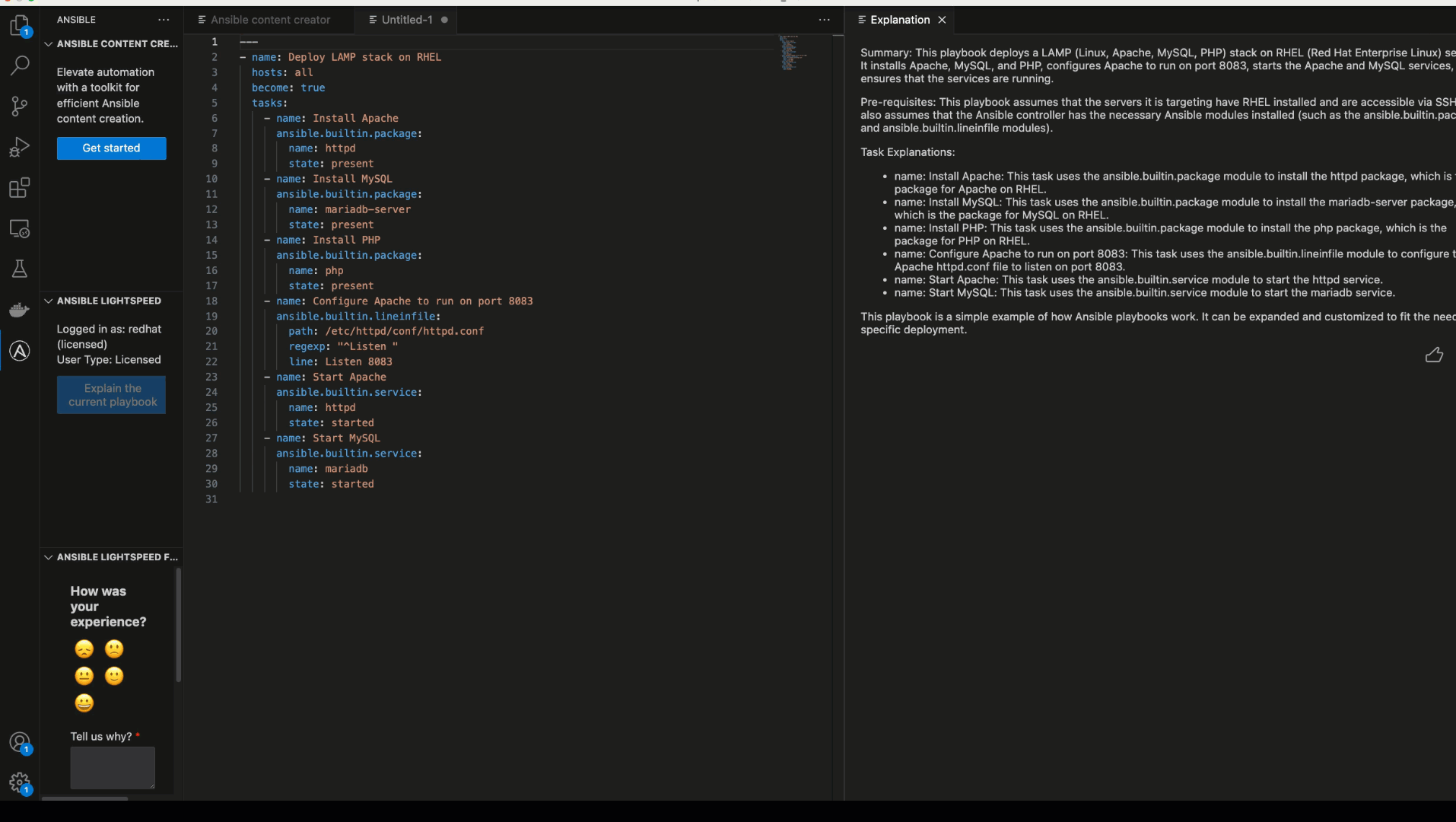
Full playbook generation with explanation
Along with full playbook generation and playbook explanation, Ansible Lightspeed also provides more granular control over the creation process through features like single and multi-task generation.
Single and multiple task generation
When you need to add specific inline tasks to your playbooks, Ansible Lightspeed excels with its single and multi-task generation capabilities.
Single task generation
- Start a new task in your playbook and provide a name using the name argument.
- Position your cursor at the end of the task name and hit “Enter” to get a suggestion from Ansible Lightspeed.
Multi-task generation
- Create a comment line at the task block level in your playbook.
- Chain multiple natural language prompts together using ampersands (&).
- At the end of the comment line, hit “Enter” to get a multi-task suggestion from Ansible Lightspeed.
These features streamline the process of creating detailed, multi-step workflows in your Ansible Playbooks, enhancing efficiency and consistency.

Generating an Ansible task

Generating multiple Ansible tasks
Adopt
Content source matching
Another critical feature of Ansible Lightspeed with watsonx Code Assistant is transparency and openness using content source matching. We transparently share the potential source, author and content license of the training data used for the recommendation. Building trust in the community and supporting the relationships between authors and contributors is part of Red Hat’s DNA.
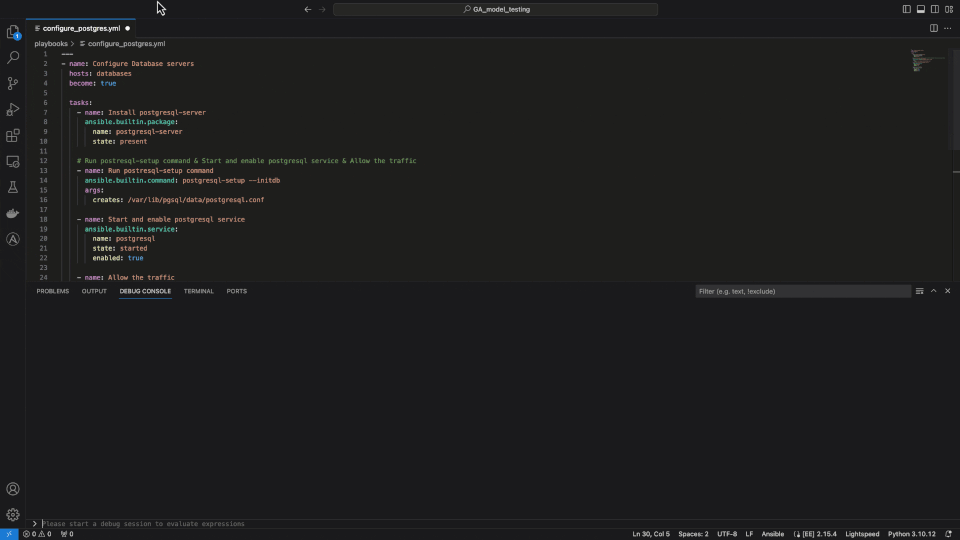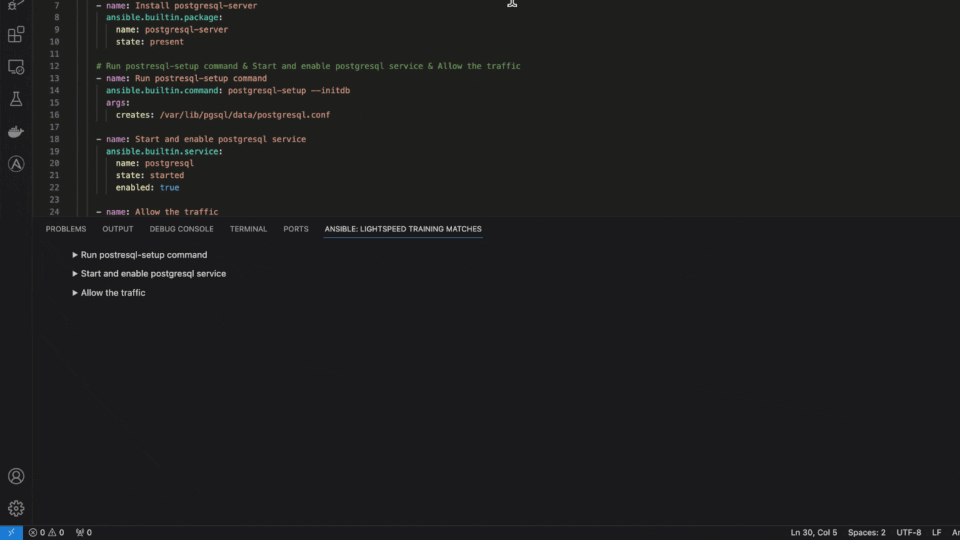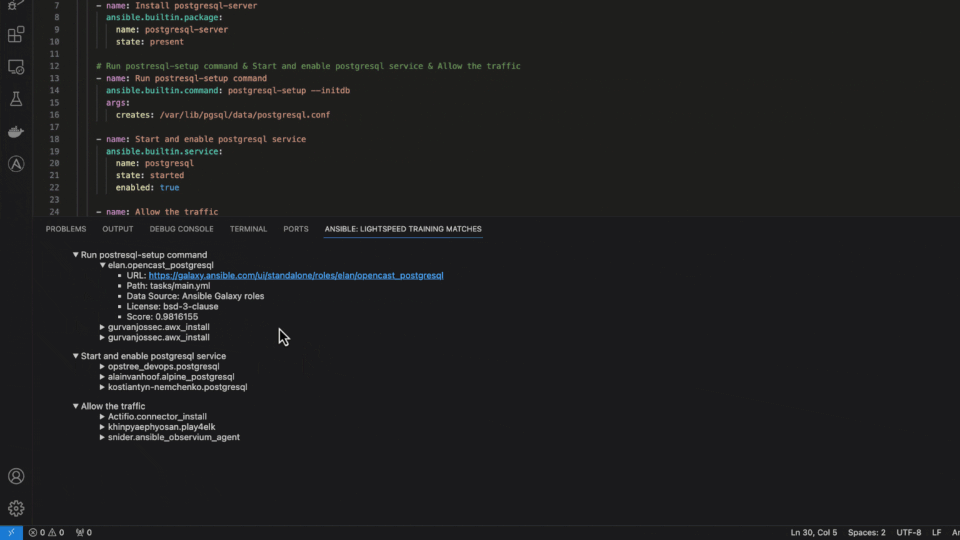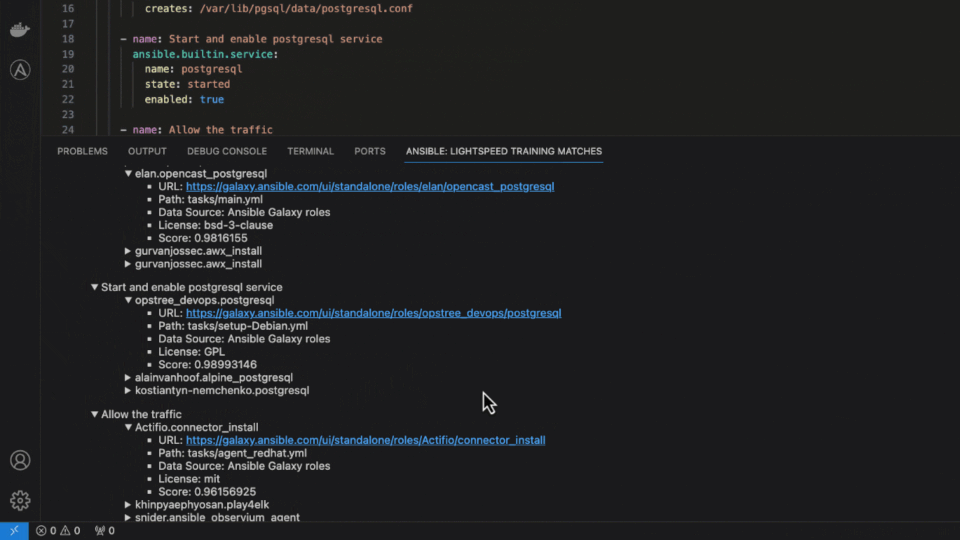
Ansible Lightspeed content source matching
Post-processing
Ansible Lightspeed is purpose-built for automation, providing a streamlined and accurate gen AI experience that is tailored by—and for—IT automation teams. Ansible Lightspeed's post-processing capabilities adhere to accepted Ansible best practices so automation teams can have confidence in the code they are accepting.
Examples of post-processing include using FQCN, doing data anonymization and other variable substitutions. The example provided in the “How to generate a suggestion” section above shows the suggestions generated with FQCNs as one of the post-processing capabilities of the service.
Maintain
Ansible code bot
Customers often ask, “we have the code, but what's next”? How do we move from siloed automation? How do we create a community of practice? Our answer starts with culture, and treating infrastructure workflows as software assets catalyzes the collaborative approach needed for enterprise-level automation. However, this could involve learning new skills like version control, automated testing and code review.
Our goal with Ansible code bot is to extend Ansible content quality improvement beyond creation and into your entire workflow. The Ansible code bot scans existing Ansible Content Collections, roles and playbooks hosted in GitHub repositories, and proactively creates pull requests whenever best practices or quality improvement recommendations are available. The bot automatically submits pull requests to the repository, which proactively alerts the repository owner to a recommended change to their content. You can configure Ansible code bot to scan your existing Git repositories (both public and private).
Prerequisites
- A Red Hat customer portal account that is attached to your organization.
- Your organization should have a valid Ansible Lightspeed subscription enabled.
Procedure
- Log in to your GitHub by using an account associated with your organization.
- Install the GitHub app for the organization that you are a member of.
- Go to the Ansible code bot GitHub app:
- Select the repositories on which you want to install the Ansible code bot.
- Click Install & Authorize.
- When prompted, log in to your Red Hat SSO account.
Ansible code bot in action
After the Ansible code bot is installed for the Git repositories you selected, you can configure a schedule to scan your Git repositories at regular intervals. You can also manually scan your Git repositories by adding a topic called “ansible-code-bot-scan” to your repository, if you have not set up a scanning schedule for your Ansible code bot or if you do not want to wait for the next scheduled scan.
Additional resources
- Website: Red Hat Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant
- Documentation: Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant
- Datasheet: Ansible Lightspeed with IBM watsonx Code Assistant
Thanks for reading and happy automating.
Product trial
Red Hat Ansible Automation Platform | Product Trial
About the author
Anshul is a Principal Marketing Manager at Red Hat, where he brings his software development and QE experience to increase Ansible Automation Platform's adoption experience for customers by producing technical content on all aspects of the product.
More like this
Innovation is a team sport: Top 10 stories from across the Red Hat ecosystem
Production-ready: Red Hat’s blueprint for 2026
Technically Speaking | Build a production-ready AI toolbox
Technically Speaking | Platform engineering for AI agents
Browse by channel
Automation
The latest on IT automation for tech, teams, and environments
Artificial intelligence
Updates on the platforms that free customers to run AI workloads anywhere
Open hybrid cloud
Explore how we build a more flexible future with hybrid cloud
Security
The latest on how we reduce risks across environments and technologies
Edge computing
Updates on the platforms that simplify operations at the edge
Infrastructure
The latest on the world’s leading enterprise Linux platform
Applications
Inside our solutions to the toughest application challenges
Virtualization
The future of enterprise virtualization for your workloads on-premise or across clouds
